Abstract
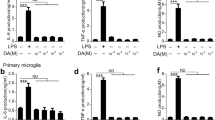
Phenelzine is a potent monoamine oxidase inhibitor that is used in patients with depression. It is also well known that nitric oxide (NO) synthase inhibitors show preclinical antidepressant-like properties, which suggests that NO is involved in the pathogenesis of depression. The purpose of this study was to determine if phenelzine affects the production of NO and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) in activated microglia cells. BV-2 microglia cells and primary microglia cells were cultured in DMEM and DMEM/F12 and then cells were treated with LPS or LPS plus phenelzine for 24 h. The culture medium was collected for determination of NO, TNF-α, and IL-6 and cells were harvested by lysis buffer for Western blot analysis. Phenelzine increased the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), as well as the release of TNF-α and IL-6 in BV-2 microglia cells. It is also confirmed that phenelzine increased the levels of NO, TNF-α and IL-6 in LPS-activated primary microglia cells. Phenelzine increased nuclear translocation of NF-κB by phosphorylation of IκB-α in LPS-activated microglia cells. These findings suggest that high doses of phenelzine could aggravate inflammatory responses in microglia cells that are mediated by NO and TNF-α.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johnson MR, Lydiard RB, Ballenger JC (1995) Panic disorder. Pathophysiology and drug treatment. Drugs 49:328–344
Casacalenda N, Perry JC, Looper K (2002) Remission in major depressive disorder: a comparison of pharmacotherapy, psychotherapy, and control conditions. Am J Psychiatry 159:1354–1360
Michael-Titus AT, Bains S, Jeetle J, Whelpton R (2000) Imipramine and phenelzine decrease glutamate overflow in the prefrontal cortex—a possible mechanism of neuroprotection in major depression? Neuroscience 100:681–684
Parent MB, Master S, Kashlub S, Baker GB (2002) Effects of the antidepressant/antipanic drug phenelzine and its putative metabolite phenylethylidenehydrazine on extracellular gamma-aminobutyric acid levels in the striatum. Biochem Pharmacol 63:57–64
Chiche F, Le Guillou M, Chetrite G, Lasnier F, Dugail I, Carpene C, Moldes M, Feve B (2009) Antidepressant phenelzine alters differentiation of cultured human and mouse preadipocytes. Mol Pharmacol 75:1052–1061
Lee CS, Han ES, Lee WB (2003) Antioxidant effect of phenelzine on mpp+-induced cell viability loss in differentiated pc12 cells. Neurochem Res 28:1833–1841
Tremblay ME, Stevens B, Sierra A, Wake H, Bessis A, Nimmerjahn A (2011) The role of microglia in the healthy brain. J Neurosci 31:16064–16069
Wyss-Coray T, Mucke L (2002) Inflammation in neurodegenerative disease—a double-edged sword. Neuron 35:419–432
Ehde DM, Bombardier CH (2005) Depression in persons with multiple sclerosis. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 16:437–448, ix
Marshall PS (1993) Allergy and depression: a neurochemical threshold model of the relation between the illnesses. Psychol Bull 113:23–43
Katon W, Sullivan MD (1990) Depression and chronic medical illness. J Clin Psychiatry 51Suppl:3–11 (discussion 12–14)
Schrott LM, Crnic LS (1996) Anxiety behavior, exploratory behavior, and activity in nzb x nzw f1 hybrid mice: role of genotype and autoimmune disease progression. Brain Behav Immun 10:260–274
Asnis GM, De La Garza R II (2006) Interferon-induced depression in chronic hepatitis c: a review of its prevalence, risk factors, biology, and treatment approaches. J Clin Gastroenterol 40:322–335
Tyring S, Gottlieb A, Papp K, Gordon K, Leonardi C, Wang A, Lalla D, Woolley M, Jahreis A, Zitnik R et al (2006) Etanercept and clinical outcomes, fatigue, and depression in psoriasis: double-blind placebo-controlled randomised phase iii trial. Lancet 367:29–35
Sluzewska A, Rybakowski J, Bosmans E, Sobieska M, Berghmans R, Maes M, Wiktorowicz K (1996) Indicators of immune activation in major depression. Psychiatry Res 64:161–167
Gantt KR, Goldman TL, McCormick ML, Miller MA, Jeronimo SM, Nascimento ET, Britigan BE, Wilson ME (2001) Oxidative responses of human and murine macrophages during phagocytosis of leishmania chagasi. J Immunol 167:893–901
Akiyama H, Barger S, Barnum S, Bradt B, Bauer J, Cole GM, Cooper NR, Eikelenboom P, Emmerling M, Fiebich BL et al (2000) Inflammation and alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 21:383–421
McGeer PL, McGeer EG (2004) Inflammation and neurodegeneration in parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 10(Suppl 1):S3–S7
Danton GH, Dietrich WD (2003) Inflammatory mechanisms after ischemia and stroke. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62:127–136
Chao CC, Hu S, Peterson PK (1995) Glia, cytokines, and neurotoxicity. Crit Rev Neurobiol 9:189–205
Tracey KJ, Fong Y, Hesse DG, Manogue KR, Lee AT, Kuo GC, Lowry SF, Cerami A (1987) Anti-cachectin/tnf monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature 330:662–664
Baker SJ, Reddy EP (1998) Modulation of life and death by the tnf receptor superfamily. Oncogene 17:3261–3270
Vilcek J, Lee TH (1991) Tumor necrosis factor. New insights into the molecular mechanisms of its multiple actions. J Biol Chem 266:7313–7316
Sweet MJ, Hume DA (1996) Endotoxin signal transduction in macrophages. J Leukoc Biol 60:8–26
Kuprash DV, Udalova IA, Turetskaya RL, Rice NR, Nedospasov SA (1995) Conserved kappa b element located downstream of the tumor necrosis factor alpha gene: distinct nf-kappa b binding pattern and enhancer activity in lps activated murine macrophages. Oncogene 11:97–106
Blasi E, Barluzzi R, Bocchini V, Mazzolla R, Bistoni F (1990) Immortalization of murine microglial cells by a v-raf/v-myc carrying retrovirus. J Neuroimmunol 27:229–237
Chung HS, Lee JH, Kim H, Lee HJ, Kim SH, Kwon HK, Im SH, Bae H (2010) Foxp3 is a novel repressor of microglia activation. Glia 58:1247–1256
Saura J, Tusell JM, Serratosa J (2003) High-yield isolation of murine microglia by mild trypsinization. Glia 44:183–189
Xie QW, Cho HJ, Calaycay J, Mumford RA, Swiderek KM, Lee TD, Ding A, Troso T, Nathan C (1992) Cloning and characterization of inducible nitric oxide synthase from mouse macrophages. Science 256:225–228
Chung HS, Kang M, Cho C, Parvez S, Park CH, Kim D, Oh J, Kim H, Shin M, Hong M et al (2007) Inhibition of nitric oxide and tumor necrosis factor-alpha by moutan cortex in activated mouse peritoneal macrophages. Biol Pharm Bull 30:912–916
Stoll G, Jander S (1999) The role of microglia and macrophages in the pathophysiology of the cns. Prog Neurobiol 58:233–247
Kreutzberg GW (1996) Microglia: a sensor for pathological events in the cns. Trends Neurosci 19:312–318
Vila M, Jackson-Lewis V, Guegan C, Wu DC, Teismann P, Choi DK, Tieu K, Przedborski S (2001) The role of glial cells in parkinson’s disease. Curr Opin Neurol 14:483–489
Sriram K, Matheson JM, Benkovic SA, Miller DB, Luster MI, O’Callaghan JP (2006) Deficiency of tnf receptors suppresses microglial activation and alters the susceptibility of brain regions to mptp-induced neurotoxicity: role of tnf-alpha. FASEB J 20:670–682
Lawrence T, Gilroy DW, Colville-Nash PR, Willoughby DA (2001) Possible new role for nf-kappab in the resolution of inflammation. Nat Med 7:1291–1297
Makarov SS (2001) Nf-kappa b in rheumatoid arthritis: a pivotal regulator of inflammation, hyperplasia, and tissue destruction. Arthritis Res 3:200–206
Boje KM, Arora PK (1992) Microglial-produced nitric oxide and reactive nitrogen oxides mediate neuronal cell death. Brain Res 587:250–256
Majumder S, Zhou LZ, Chaturvedi P, Babcock G, Aras S, Ransohoff RM (1998) P48/stat-1alpha-containing complexes play a predominant role in induction of ifn-gamma-inducible protein, 10 kDa (ip-10) by ifn-gamma alone or in synergy with tnf-alpha. J Immunol 161:4736–4744
Piao HZ, Choi IY, Park JS, Kim HS, Cheong JH, Son KH, Jeon SJ, Ko KH, Kim WK (2008) Wogonin inhibits microglial cell migration via suppression of nuclear factor-kappa b activity. Int Immunopharmacol 12:1658–1662
Henry JA, Antao CA (1992) Suicide and fatal antidepressant poisoning. Eur J Med 1:343–348
Ciocatto E, Fagiano G, Bava GL (1972) Clinical features and treatment of overdosage of monoamine oxidase inhibitors and their interaction with other psychotropic drugs. Resuscitation 1:69–72
Linden CH, Rumack BH, Strehlke C (1984) Monoamine oxidase inhibitor overdose. Ann Emerg Med 13:1137–1144
Waring WS, Wallace WA (2007) Acute myocarditis after massive phenelzine overdose. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 63:1007–1009
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government [MEST] (No. 2011-0006220).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Hwan-Suck Chung and Hyunseong Kim contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chung, HS., Kim, H. & Bae, H. Phenelzine (Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor) Increases Production of Nitric Oxide and Proinflammatory Cytokines via the NF-κB Pathway in Lipopolysaccharide-Activated Microglia Cells. Neurochem Res 37, 2117–2124 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-012-0833-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-012-0833-y