Abstract
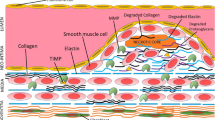
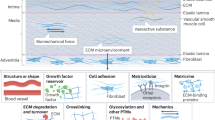
Atherosclerosis (AS) is the leading cause of the human cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). Endothelial dysfunction promotes the monocytes infiltration and inflammation that participate fundamentally in atherogenesis. Endothelial cells (EC) have been recognized as mechanosensitive cells and have different responses to distinct mechanical stimuli. Emerging evidence shows matrix stiffness-mediated EC dysfunction plays a vital role in vascular disease, but the underlying mechanisms are not yet completely understood. This article aims to summarize the effect of matrix stiffness on the pro-atherosclerotic characteristics of EC including morphology, rigidity, biological behavior and function as well as the related mechanical signal. The review also discusses and compares the contribution of matrix stiffness-mediated phagocytosis of macrophages and EC to AS progression. These advances in our understanding of the relationship between matrix stiffness and EC dysfunction open the avenues to improve the prevention and treatment of now-ubiquitous atherosclerotic diseases.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gimbrone MJ, Garcia-Cardena G (2016) Endothelial cell dysfunction and the pathobiology of Atherosclerosis[J]. Circ Res 118(4):620–636
Mehta V, Pang KL, Rozbesky D et al (2020) The guidance receptor plexin D1 is a mechanosensor in endothelial cells[J]. Nature 578(7794):290–295
Dargel R (1989) [The lipid infiltration theory of atherosclerosis] [J]. Z Med Lab Diagn 30(5):251–255
Moore KJ, Tabas I (2011) Macrophages in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis[J]. Cell 145(3):341–355
Feaver RE, Gelfand BD, Blackman BR (2013) Human haemodynamic frequency harmonics regulate the inflammatory phenotype of vascular endothelial cells[J]. Nat Commun 4:1525
Souilhol C, Serbanovic-Canic J, Fragiadaki M et al (2020) Endothelial responses to shear stress in atherosclerosis: a novel role for developmental genes[J]. Nat Rev Cardiol 17(1):52–63
Wang L, Luo JY, Li B et al (2016) Integrin-YAP/TAZ-JNK cascade mediates atheroprotective effect of unidirectional shear flow[J]. Nature 540(7634):579–582
Brown AJ, Teng Z, Evans PC et al (2016) Role of biomechanical forces in the natural history of coronary atherosclerosis[J]. Nat Rev Cardiol 13(4):210–220
Hahn C, Schwartz MA (2008) The role of cellular adaptation to mechanical forces in atherosclerosis[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 28(12):2101–2107
Palombo C, Kozakova M (2016) Arterial stiffness, atherosclerosis and cardiovascular risk: pathophysiologic mechanisms and emerging clinical indications[J]. Vascul Pharmacol 77:1–7
Vania V, Wang L, Tjakra M et al (2020) The interplay of signaling pathway in endothelial cells-matrix stiffness dependency with targeted-therapeutic drugs[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1866(5):165645
Humphrey JD, Eberth JF, Dye WW et al (2009) Fundamental role of axial stress in compensatory adaptations by arteries[J]. J Biomech 42(1):1–8
Lu D, Kassab GS (2011) Role of shear stress and stretch in vascular mechanobiology[J]. J R Soc Interface 8(63):1379–1385
Qu K, Wang C, Huang L et al (2022) TET1s deficiency exacerbates oscillatory shear flow-induced atherosclerosis[J]. Int J Biol Sci 18(5):2163–2180
Raij L, Gonzalez-Ochoa AM (2011) Vascular compliance in blood pressure[J]. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 20(5):457–464
Blacher J, Guerin AP, Pannier B et al (1999) Impact of aortic stiffness on survival in end-stage renal disease[J]. Circulation 99(18):2434–2439
Kohn JC, Lampi MC, Reinhart-King CA (2015) Age-related vascular stiffening: causes and consequences[J]. Front Genet 6:112
Timashev PS, Kotova SL, Belkova GV et al (2016) Atomic Force Microscopy Study of atherosclerosis progression in arterial Walls[J]. Microsc Microanal 22(2):311–325
Gan CT, Lankhaar JW, Westerhof N et al (2007) Noninvasively assessed pulmonary artery stiffness predicts mortality in pulmonary arterial hypertension[J]. Chest 132(6):1906–1912
Huynh J, Nishimura N, Rana K et al (2011) Age-related intimal stiffening enhances endothelial permeability and leukocyte transmigration[J]. Sci Transl Med 3(112):112r–122r
Lusis AJ (2000) Atherosclerosis[J] Nat 407(6801):233–241
Farrar DJ, Bond MG, Riley WA et al (1991) Anatomic correlates of aortic pulse wave velocity and carotid artery elasticity during atherosclerosis progression and regression in monkeys[J]. Circulation 83(5):1754–1763
van Popele NM, Grobbee DE, Bots ML et al (2001) Association between arterial stiffness and atherosclerosis: the Rotterdam Study[J]. Stroke 32(2):454–460
Zureik M, Bureau JM, Temmar M et al (2003) Echogenic carotid plaques are associated with aortic arterial stiffness in subjects with subclinical carotid atherosclerosis[J]. Hypertension 41(3):519–527
Birukov KG (2009) Cyclic stretch, reactive oxygen species, and vascular remodeling[J]. Antioxid Redox Signal 11(7):1651–1667
Oh YS (2018) Arterial stiffness and hypertension[J]. Clin Hypertens 24:17
Samokhin AO, Stephens T, Wertheim BM et al (2018) NEDD9 targets COL3A1 to promote endothelial fibrosis and pulmonary arterial hypertension[J].Sci Transl Med, 10(445)
Payne RA, Wilkinson IB, Webb DJ (2010) Arterial stiffness and hypertension: emerging concepts[J]. Hypertension 55(1):9–14
Lacolley P, Regnault V, Avolio AP (2018) Smooth muscle cell and arterial aging: basic and clinical aspects[J]. Cardiovasc Res 114(4):513–528
Lanzer P, Boehm M, Sorribas V et al (2014) Medial vascular calcification revisited: review and perspectives[J]. Eur Heart J 35(23):1515–1525
Lakatta EG (2003) Arterial and cardiac aging: major shareholders in cardiovascular disease enterprises: part III: cellular and molecular clues to heart and arterial aging[J]. Circulation 107(3):490–497
Zhou T, Zheng Y, Sun L et al (2019) Microvascular endothelial cells engulf myelin debris and promote macrophage recruitment and fibrosis after neural injury[J]. Nat Neurosci 22(3):421–435
Mattace-Raso FU, van der Cammen TJ, Hofman A et al (2006) Arterial stiffness and risk of coronary heart disease and stroke: the Rotterdam Study[J]. Circulation 113(5):657–663
Guthikonda S, Haynes WG (2006) Homocysteine: role and implications in atherosclerosis[J]. Curr Atheroscler Rep 8(2):100–106
Widlansky ME, Gokce N, Keaney JJ et al (2003) The clinical implications of endothelial dysfunction[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol 42(7):1149–1160
Karki P, Birukova AA (2018) Substrate stiffness-dependent exacerbation of endothelial permeability and inflammation: mechanisms and potential implications in ALI and PH (2017 Grover Conference Series) [J]. Pulm Circ, 8(2):767774668
Wang Y, Wang G, Luo X et al (2012) Substrate stiffness regulates the proliferation, migration, and differentiation of epidermal cells[J]. Burns 38(3):414–420
Yeung T, Georges PC, Flanagan LA et al (2005) Effects of substrate stiffness on cell morphology, cytoskeletal structure, and adhesion[J]. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 60(1):24–34
Elosegui-Artola A, Oria R, Chen Y et al (2016) Mechanical regulation of a molecular clutch defines force transmission and transduction in response to matrix rigidity[J]. Nat Cell Biol 18(5):540–548
Le Master E, Ahn SJ, Levitan I (2020) Mechanisms of endothelial stiffening in dyslipidemia and aging: oxidized lipids and shear stress[J]. Curr Top Membr 86:185–215
Yi B, Shen Y, Tang H et al (2020) Stiffness of the aligned fibers affects structural and functional integrity of the oriented endothelial cells[J]. Acta Biomater 108:237–249
Sheng S, Qiu J, Tang C et al (2012) Effect of stiffness of substrate on vascular endothelial cell growth and proliferation [J]. J Chongqing Med Univ 37(08):665–667
Chen G, Zhao L, Feng J et al (2013) Validation of reliable reference genes for real-time PCR in human umbilical vein endothelial cells on substrates with different stiffness[J]. PLoS ONE 8(6):e67360
Vania V, Wang L, Tjakra M et al (2020) The interplay of signaling pathway in endothelial cells-matrix stiffness dependency with targeted-therapeutic drugs[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1866(5):165645
Simmons CS, Ribeiro AJ, Pruitt BL (2013) Formation of composite polyacrylamide and silicone substrates for independent control of stiffness and strain[J]. Lab Chip 13(4):646–649
Hassanisaber H, Jafari L, Campeau MA et al (2019) The effect of substrate bulk stiffness on focal and fibrillar adhesion formation in human abdominal aortic endothelial cells[J]. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 98:572–583
Iozzo RV, Schaefer L (2015) Proteoglycan form and function: a comprehensive nomenclature of proteoglycans[J]. Matrix Biol 42:11–55
Delgadillo LF, Lomakina EB, Kuebel J et al (2021) Changes in endothelial glycocalyx layer protective ability after inflammatory stimulus[J]. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 320(2):C216–C224
Parnigoni A, Viola M, Karousou E et al (2022) Hyaluronan in pathophysiology of vascular diseases: specific roles in smooth muscle cells, endothelial cells, and macrophages[J]. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 323(2):C505–C519
Fischer JW (2019) Role of hyaluronan in atherosclerosis: current knowledge and open questions[J]. Matrix Biol 78–79:324–336
Carava E, Moretto P, Caon I et al HA and HS changes in endothelial inflammatory Activation[J]. Biomolecules, 2021,11(6).
Broekhuizen LN, Lemkes BA, Mooij HL et al (2010) Effect of sulodexide on endothelial glycocalyx and vascular permeability in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Diabetologia 53(12):2646–2655
Nieuwdorp M, Holleman F, de Groot E et al (2007) Perturbation of hyaluronan metabolism predisposes patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus to atherosclerosis[J]. Diabetologia 50(6):1288–1293
Nagy N, Freudenberger T, Melchior-Becker A et al (2010) Inhibition of hyaluronan synthesis accelerates murine atherosclerosis: novel insights into the role of hyaluronan synthesis[J]. Circulation 122(22):2313–2322
Riessen R, Wight TN, Pastore C et al (1996) Distribution of hyaluronan during extracellular matrix remodeling in human restenotic arteries and balloon-injured rat carotid arteries[J]. Circulation 93(6):1141–1147
Kashima Y, Takahashi M, Shiba Y et al (2013) Crucial role of hyaluronan in neointimal formation after vascular injury[J]. PLoS ONE 8(3):e58760
Chai S, Chai Q, Danielsen CC et al (2005) Overexpression of hyaluronan in the tunica media promotes the development of atherosclerosis[J]. Circ Res 96(5):583–591
Kiene LS, Homann S, Suvorava T et al (2016) Deletion of Hyaluronan synthase 3 inhibits neointimal hyperplasia in Mice[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 36(2):e9–e16
Gondelaud F, Ricard-Blum S (2019) Structures and interactions of syndecans[J]. FEBS J 286(15):2994–3007
Thi MM, Tarbell JM, Weinbaum S et al (2004) The role of the glycocalyx in reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton under fluid shear stress: a “bumper-car” model[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101(47):16483–16488
Asplund A, Ostergren-Lunden G, Camejo G et al (2009) Hypoxia increases macrophage motility, possibly by decreasing the heparan sulfate proteoglycan biosynthesis[J]. J Leukoc Biol 86(2):381–388
Zhang GL, Zhang X, Wang XM et al (2014) Towards understanding the roles of heparan sulfate proteoglycans in Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Biomed Res Int 2014:516028
Kaksonen M, Pavlov I, Voikar V et al (2002) Syndecan-3-deficient mice exhibit enhanced LTP and impaired hippocampus-dependent memory[J]. Mol Cell Neurosci 21(1):158–172
Denhez F, Wilcox-Adelman SA, Baciu PC et al (2002) Syndesmos, a syndecan-4 cytoplasmic domain interactor, binds to the focal adhesion adaptor proteins paxillin and Hic-5[J]. J Biol Chem 277(14):12270–12274
Boyanovsky BB, Shridas P, Simons M et al (2009) Syndecan-4 mediates macrophage uptake of group V secretory phospholipase A2-modified LDL[J]. J Lipid Res 50(4):641–650
Nikmanesh M, Cancel LM, Shi ZD et al (2019) Heparan sulfate proteoglycan, integrin, and syndecan-4 are mechanosensors mediating cyclic strain-modulated endothelial gene expression in mouse embryonic stem cell-derived endothelial cells[J]. Biotechnol Bioeng 116(10):2730–2741
Baeyens N, Mulligan-Kehoe MJ, Corti F et al (2014) Syndecan 4 is required for endothelial alignment in flow and atheroprotective signaling[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(48):17308–17313
Lipphardt M, Dihazi H, Maas JH et al Syndecan-4 as a marker of endothelial dysfunction in patients with resistant Hypertension[J].J Clin Med, 2020,9(9).
Haas H, Steitz R, Fasano A et al (2007) Laminar order within Langmuir-Blodgett multilayers from phospholipid and myelin basic protein: a neutron reflectivity study[J]. Langmuir 23(16):8491–8496
Hynes RO, Naba A (2012) Overview of the matrisome–an inventory of extracellular matrix constituents and functions[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 4(1):a4903
Arribas SM, Hinek A, Gonzalez MC (2006) Elastic fibres and vascular structure in hypertension[J]. Pharmacol Ther 111(3):771–791
Humphrey JD, Dufresne ER, Schwartz MA (2014) Mechanotransduction and extracellular matrix homeostasis[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15(12):802–812
Kothapalli D, Liu SL, Bae YH et al (2012) Cardiovascular protection by ApoE and ApoE-HDL linked to suppression of ECM gene expression and arterial stiffening[J]. Cell Rep 2(5):1259–1271
VanderBurgh JA, Reinhart-King CA (2018) The role of age-related Intimal Remodeling and Stiffening in Atherosclerosis[J]. Adv Pharmacol 81:365–391
Rohwedder I, Montanez E, Beckmann K et al (2012) Plasma fibronectin deficiency impedes atherosclerosis progression and fibrous cap formation[J]. EMBO Mol Med 4(7):564–576
Palotie A, Tryggvason K, Peltonen L et al (1983) Components of subendothelial aorta basement membrane. Immunohistochemical localization and role in cell attachment[J]. Lab Invest 49(3):362–370
Byfield FJ, Reen RK, Shentu TP et al (2009) Endothelial actin and cell stiffness is modulated by substrate stiffness in 2D and 3D[J]. J Biomech 42(8):1114–1119
Woodrum DA, Romano AJ, Lerman A et al (2006) Vascular wall elasticity measurement by magnetic resonance imaging[J]. Magn Reson Med 56(3):593–600
Yi B, Shen Y, Tang H et al (2020) Stiffness of the aligned fibers affects structural and functional integrity of the oriented endothelial cells[J]. Acta Biomater 108:237–249
Zhang C, Adamos C, Oh MJ et al (2017) oxLDL induces endothelial cell proliferation via Rho/ROCK/Akt/p27(kip1) signaling: opposite effects of oxLDL and cholesterol loading[J]. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 313(3):C340–C351
Monson KL, Goldsmith W, Barbaro NM et al (2003) Axial mechanical properties of fresh human cerebral blood vessels[J]. J Biomech Eng 125(2):288–294
Henry J, Yu J, Wang A et al (2017) Engineering the mechanical and biological properties of nanofibrous vascular grafts for in situ vascular tissue engineering[J]. Biofabrication 9(3):35007
He L, Zhang CL, Chen Q et al (2022) Endothelial shear stress signal transduction and atherogenesis: from mechanisms to therapeutics[J]. Pharmacol Ther 235:108152
Duprez DA (2010) Arterial stiffness and endothelial function: key players in vascular health[J]. Hypertension 55(3):612–613
Kinlay S, Creager MA, Fukumoto M et al (2001) Endothelium-derived nitric oxide regulates arterial elasticity in human arteries in vivo[J]. Hypertension 38(5):1049–1053
Wilkinson IB, Qasem A, McEniery CM et al (2002) Nitric oxide regulates local arterial distensibility in vivo[J]. Circulation 105(2):213–217
Thacher TN, Silacci P, Stergiopulos N et al (2010) Autonomous effects of shear stress and cyclic circumferential stretch regarding endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress: an ex vivo arterial model[J]. J Vasc Res 47(4):336–345
Gonzalez-Santiago L, Lopez-Ongil S, Rodriguez-Puyol M et al (2002) Decreased nitric oxide synthesis in human endothelial cells cultured on type I collagen[J]. Circ Res 90(5):539–545
Kemeny SF, Figueroa DS, Andrews AM et al (2011) Glycated collagen alters endothelial cell actin alignment and nitric oxide release in response to fluid shear stress[J]. J Biomech 44(10):1927–1935
Thacher T, Gambillara V, Da SR et al (2010) Reduced cyclic stretch, endothelial dysfunction, and oxidative stress: an ex vivo model[J]. Cardiovasc Pathol 19(4):e91–e98
Dejana E (2004) Endothelial cell-cell junctions: happy together[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5(4):261–270
Huynh J, Nishimura N, Rana K et al (2011) Age-related intimal stiffening enhances endothelial permeability and leukocyte transmigration[J]. Sci Transl Med 3(112):112r–122r
Hardin C, Rajendran K, Manomohan G et al (2013) Glassy dynamics, cell mechanics, and endothelial permeability[J]. J Phys Chem B 117(42):12850–12856
Prasain N, Stevens T (2009) The actin cytoskeleton in endothelial cell phenotypes[J]. Microvasc Res 77(1):53–63
Dejana E (2004) Endothelial cell-cell junctions: happy together[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5(4):261–270
Baumgartner W, Schutz GJ, Wiegand J et al (2003) Cadherin function probed by laser tweezer and single molecule fluorescence in vascular endothelial cells[J]. J Cell Sci 116(Pt 6):1001–1011
Ukropec JA, Hollinger MK, Woolkalis MJ (2002) Regulation of VE-cadherin linkage to the cytoskeleton in endothelial cells exposed to fluid shear stress[J]. Exp Cell Res 273(2):240–247
Makita S, Nakamura M, Hiramori K (2005) The association of C-reactive protein levels with carotid intima-media complex thickness and plaque formation in the general population[J]. Stroke 36(10):2138–2142
Chen W, Tian B, Liang J et al (2019) Matrix stiffness regulates the interactions between endothelial cells and monocytes[J]. Biomaterials 221:119362
MacKay JL, Hammer DA (2016) Stiff substrates enhance monocytic cell capture through E-selectin but not P-selectin[J]. Integr Biol (Camb) 8(1):62–72
Wang Y, Shi R, Zhai R et al (2022) Matrix stiffness regulates macrophage polarization in atherosclerosis[J]. Pharmacol Res 179:106236
Wang N, Tytell JD, Ingber DE (2009) Mechanotransduction at a distance: mechanically coupling the extracellular matrix with the nucleus[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10(1):75–82
Doyle AD, Yamada KM (2016) Mechanosensing via cell-matrix adhesions in 3D microenvironments[J]. Exp Cell Res 343(1):60–66
Cho S, Irianto J, Discher DE (2017) Mechanosensing by the nucleus: from pathways to scaling relationships[J]. J Cell Biol 216(2):305–315
Jaalouk DE, Lammerding J (2009) Mechanotransduction gone awry[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10(1):63–73
Wang N, Butler JP, Ingber DE (1993) Mechanotransduction across the cell surface and through the cytoskeleton[J]. Science 260(5111):1124–1127
Hahn C, Schwartz MA (2008) The role of cellular adaptation to mechanical forces in atherosclerosis[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 28(12):2101–2107
Miao H, Hu YL, Shiu YT et al (2005) Effects of flow patterns on the localization and expression of VE-cadherin at vascular endothelial cell junctions: in vivo and in vitro investigations[J]. J Vasc Res 42(1):77–89
Collins C, Osborne LD, Guilluy C et al (2014) Haemodynamic and extracellular matrix cues regulate the mechanical phenotype and stiffness of aortic endothelial cells[J]. Nat Commun 5:3984
Desgrosellier JS, Cheresh DA (2010) Integrins in cancer: biological implications and therapeutic opportunities[J]. Nat Rev Cancer 10(1):9–22
Cox D, Brennan M, Moran N (2010) Integrins as therapeutic targets: lessons and opportunities[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9(10):804–820
Sun Z, Guo SS, Fassler R (2016) Integrin-mediated mechanotransduction[J]. J Cell Biol 215(4):445–456
Hynes RO (2007) Cell-matrix adhesion in vascular development[J]. J Thromb Haemost 5(Suppl 1):32–40
Mobley AK, Tchaicha JH, Shin J et al (2009) Beta8 integrin regulates neurogenesis and neurovascular homeostasis in the adult brain[J]. J Cell Sci 122(Pt 11):1842–1851
Peters JH, Hynes RO (1996) Fibronectin isoform distribution in the mouse. I. The alternatively spliced EIIIB, EIIIA, and V segments show widespread codistribution in the developing mouse embryo[J]. Cell Adhes Commun 4(2):103–125
Astrof S, Crowley D, George EL et al (2004) Direct test of potential roles of EIIIA and EIIIB alternatively spliced segments of fibronectin in physiological and tumor angiogenesis[J]. Mol Cell Biol 24(19):8662–8670
George EL, Baldwin HS, Hynes RO (1997) Fibronectins are essential for heart and blood vessel morphogenesis but are dispensable for initial specification of precursor cells[J]. Blood 90(8):3073–3081
Goh KL, Yang JT, Hynes RO (1997) Mesodermal defects and cranial neural crest apoptosis in alpha5 integrin-null embryos[J]. Development 124(21):4309–4319
Yang JT, Rayburn H, Hynes RO (1993) Embryonic mesodermal defects in alpha 5 integrin-deficient mice[J]. Development 119(4):1093–1105
Davis GE, Senger DR (2005) Endothelial extracellular matrix: biosynthesis, remodeling, and functions during vascular morphogenesis and neovessel stabilization[J]. Circ Res 97(11):1093–1107
Senger DR, Claffey KP, Benes JE et al (1997) Angiogenesis promoted by vascular endothelial growth factor: regulation through alpha1beta1 and alpha2beta1 integrins[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94(25):13612–13617
Liu Y, Senger DR (2004) Matrix-specific activation of src and rho initiates capillary morphogenesis of endothelial cells[J]. FASEB J 18(3):457–468
Dowling J, Yu QC, Fuchs E (1996) Beta4 integrin is required for hemidesmosome formation, cell adhesion and cell survival[J]. J Cell Biol 134(2):559–572
Nikolopoulos SN, Blaikie P, Yoshioka T et al (2004) Integrin beta4 signaling promotes tumor angiogenesis[J]. Cancer Cell 6(5):471–483
Ito K, Sakamoto N, Ohashi T et al (2007) Effects of frequency of pulsatile flow on morphology and integrin expression of vascular endothelial cells[J]. Technol Health Care 15(2):91–101
Himburg HA, Dowd SE, Friedman MH (2007) Frequency-dependent response of the vascular endothelium to pulsatile shear stress[J]. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 293(1):H645–H653
Wojciak-Stothard B, Ridley AJ (2003) Shear stress-induced endothelial cell polarization is mediated by rho and rac but not Cdc42 or PI 3-kinases[J]. J Cell Biol 161(2):429–439
Etienne-Manneville S, Hall A (2002) Rho GTPases in cell biology[J]. Nature 420(6916):629–635
Tzima E, Del PM, Kiosses WB et al (2002) Activation of Rac1 by shear stress in endothelial cells mediates both cytoskeletal reorganization and effects on gene expression[J]. EMBO J 21(24):6791–6800
Tzima E, Kiosses WB, Del PM et al (2003) Localized cdc42 activation, detected using a novel assay, mediates microtubule organizing center positioning in endothelial cells in response to fluid shear stress[J]. J Biol Chem 278(33):31020–31023
Oancea E, Wolfe JT, Clapham DE (2006) Functional TRPM7 channels accumulate at the plasma membrane in response to fluid flow[J]. Circ Res 98(2):245–253
Shyy JY, Chien S (2002) Role of integrins in endothelial mechanosensing of shear stress[J]. Circ Res 91(9):769–775
Summermatter S, Mainieri D, Russell AP et al (2008) Thrifty metabolism that favors fat storage after caloric restriction: a role for skeletal muscle phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase activity and AMP-activated protein kinase[J]. FASEB J 22(3):774–785
Goldfinger LE, Tzima E, Stockton R et al (2008) Localized alpha4 integrin phosphorylation directs shear stress-induced endothelial cell alignment[J]. Circ Res 103(2):177–185
Butler PJ, Norwich G, Weinbaum S et al (2001) Shear stress induces a time- and position-dependent increase in endothelial cell membrane fluidity[J]. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 280(4):C962–C969
Del PM, Alderson NB, Kiosses WB et al (2004) Integrins regulate rac targeting by internalization of membrane domains[J]. Science 303(5659):839–842
Wu Y, Zhang K, Seong J et al (2016) In-situ coupling between kinase activities and protein dynamics within single focal adhesions[J]. Sci Rep 6:29377
Liao X, Lu S, Zhuo Y et al (2011) Bone physiology, Biomaterial and the Effect of Mechanical/Physical Microenvironment on MSC Osteogenesis: a tribute to Shu Chien’s 80th Birthday[J]. Cell Mol Bioeng 4(4):579–590
Kohn JC, Lampi MC, Reinhart-King CA (2015) Age-related vascular stiffening: causes and consequences[J]. Front Genet 6:112
Byfield FJ, Reen RK, Shentu TP et al (2009) Endothelial actin and cell stiffness is modulated by substrate stiffness in 2D and 3D[J]. J Biomech 42(8):1114–1119
Discher DE, Janmey P, Wang YL (2005) Tissue cells feel and respond to the stiffness of their substrate[J]. Science 310(5751):1139–1143
Jalali S, Tafazzoli-Shadpour M, Haghighipour N et al (2015) Regulation of endothelial cell adherence and Elastic Modulus by substrate Stiffness[J]. Cell Commun Adhes 22(2–6):79–89
Yi B, Shen Y, Tang H et al (2020) Stiffness of the aligned fibers affects structural and functional integrity of the oriented endothelial cells[J]. Acta Biomater 108:237–249
Yeh YC, Ling JY, Chen WC et al (2017) Mechanotransduction of matrix stiffness in regulation of focal adhesion size and number: reciprocal regulation of caveolin-1 and beta1 integrin[J]. Sci Rep 7(1):15008
Le Master E, Ahn SJ, Levitan I (2020) Mechanisms of endothelial stiffening in dyslipidemia and aging: oxidized lipids and shear stress[J]. Curr Top Membr 86:185–215
Gavara N, Chadwick RS (2016) Relationship between cell stiffness and stress fiber amount, assessed by simultaneous atomic force microscopy and live-cell fluorescence imaging[J]. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 15(3):511–523
Discher DE, Janmey P, Wang YL (2005) Tissue cells feel and respond to the stiffness of their substrate[J]. Science 310(5751):1139–1143
Avizienyte E, Frame MC (2005) Src and FAK signalling controls adhesion fate and the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition[J]. Curr Opin Cell Biol 17(5):542–547
Sackmann E (2015) How actin/myosin crosstalks guide the adhesion, locomotion and polarization of cells[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta 1853(11 Pt B):3132–3142
Wang Y, Shyy JY, Chien S (2008) Fluorescence proteins, live-cell imaging, and mechanobiology: seeing is believing[J]. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 10:1–38
Wang Y, Botvinick EL, Zhao Y et al (2005) Visualizing the mechanical activation of Src[J]. Nature 434(7036):1040–1045
Sun J, Lei L, Tsai CM et al (2017) Engineered proteins with sensing and activating modules for automated reprogramming of cellular functions[J]. Nat Commun 8(1):477
Liu B, Lu S, Hu YL et al (2014) RhoA and membrane fluidity mediates the spatially polarized Src/FAK activation in response to shear stress[J]. Sci Rep 4:7008
Li J, Wang S, Li Y et al (2020) miRNA-mediated macrophage behaviors responding to matrix stiffness and ox-LDL[J]. J Cell Physiol 235(9):6139–6153
Yan W, Li T, Yin T et al (2020) M2 macrophage-derived exosomes promote the c-KIT phenotype of vascular smooth muscle cells during vascular tissue repair after intravascular stent implantation[J]. Theranostics 10(23):10712–10728
Wang Y, Shi R, Zhai R et al (2022) Matrix stiffness regulates macrophage polarization in atherosclerosis[J]. Pharmacol Res 179:106236
Sridharan R, Cavanagh B, Cameron AR et al (2019) Material stiffness influences the polarization state, function and migration mode of macrophages[J]. Acta Biomater 89:47–59
Sihombing M, Safitri M, Zhou T et al (2021) Unexpected role of Nonimmune cells: amateur Phagocytes[J]. DNA Cell Biol 40(2):157–171
Grutzendler J, Murikinati S, Hiner B et al (2014) Angiophagy prevents early embolus washout but recanalizes microvessels through embolus extravasation[J]. Sci Transl Med 6(226):226r–231r
Lam CK, Yoo T, Hiner B et al (2010) Embolus extravasation is an alternative mechanism for cerebral microvascular recanalization[J]. Nature 465(7297):478–482
Dini L, Lentini A, Diez GD et al (1995) Phagocytosis of apoptotic bodies by liver endothelial cells[J]. J Cell Sci 108(Pt 3):967–973
Steffan AM, Gendrault JL, McCuskey RS et al (1986) Phagocytosis, an unrecognized property of murine endothelial liver cells[J]. Hepatology 6(5):830–836
Nakaya M, Watari K, Tajima M et al (2017) Cardiac myofibroblast engulfment of dead cells facilitates recovery after myocardial infarction[J]. J Clin Invest 127(1):383–401
Wang Y, Botvinick EL, Zhao Y et al (2005) Visualizing the mechanical activation of Src[J]. Nature 434(7036):1040–1045
Seong J, Tajik A, Sun J et al (2013) Distinct biophysical mechanisms of focal adhesion kinase mechanoactivation by different extracellular matrix proteins[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110(48):19372–19377
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Key Foundation of China (Project no. 12032007), Chongqing Talents (cstc2022ycjh-bgzxm0166), the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing in China (cstc2020jcyj-bsh0024, cstc2019jcyj-zdxmX0028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZX, YC, YW, WH and WX collect the related literature materials. ZX wrote the manuscript. GW, XL and TZ provided ideas and designed the overall framework of the article.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interest
Author ZX, Author YC, Author YW, Author WX, Author WH, Author TZ, Author XL and Author GW declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Z., Chen, Y., Wang, Y. et al. Matrix stiffness, endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis. Mol Biol Rep 50, 7027–7041 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08502-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08502-5