Abstract
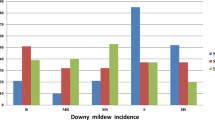
Chokecherry (Prunus virginiana L.) (2n = 4x = 32) is a unique Prunus species for both genetics and disease resistance research due to its tetraploid nature and known variations in X-disease resistance. X-disease is a destructive disease of stone fruit trees, causing yield loss and poor fruit quality. However, genetic and genomic information on chokecherry is limited. In this study, simple sequence repeat (SSR) and amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) markers were used to construct genetic linkage maps and to identify quantitative trait loci (QTLs) associated with X-disease resistance in chokecherry. A segregating population (101 progenies) was developed by crossing an X-disease-resistant chokecherry line (RC) with a susceptible chokecherry line (SC). A total of 498 DNA markers (257 SSR and 241 AFLP markers) were mapped on the two genetic maps of the two parental lines (RC and SC). The map of RC contains 302 markers assigned to 14 linkage groups covering 2,089 cM of the genome. The map of SC has 259 markers assigned to 16 linkage groups covering 1,562.4 cM of the genome. The average distance between two markers was 6.9 cM for the RC map and 6.0 cM for the SC map. One QTL located on linkage group 15 on the map of SC was found to be associated with X-disease resistance. Genetic linkage maps and the identified QTL linked to X-disease resistance will further facilitate genetic research and breeding of X-disease resistance in chokecherry and other Prunus species.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott AG, Rajapakse S, Sosinski B, Lu ZX, Sossey-Alaoui K, Gannavarapu M, Scorza R, Reighard G, Ballard RE, Callahan A, Baird WV (1998) Construction of saturated linkage maps of peach crosses segregating for characters controlling fruit quality, tree architecture and pest resistance. Acta Hortic 465:141–150
Ahn S, Tanksley SD (1993) Comparative linkage maps of rice and maize genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:7980–7984
Al-Janabi SM, Honeycutt RJ, McClelland M, Sobral BWS (1993) A genetic linkage map of Saccharum spontaneum L. ‘SES 208’. Genetics 134:1249–1260
Belthoff LE, Ballard R, Abbott A, Baird WV, Morgens P, Callahan A, Scorza R, Monet R (1993) Development of a saturated linkage map of Prunus persica using molecular based marker systems. Acta Hortic 336:51–56
Bliss FA, Arulsekar S, Foolad MR, Beccerra V, Gillen AM, Warburton AM, Dandekar AM, Kocsisne GM, Mydin KK (2002) An expanded genetic linkage map of Prunus based on an interspecific cross between almond and peach. Genome 45:520–529
Bradshaw JE, Pande B, Bryan GJ, Hackett CA, McLean K, Stewart HE, Waugh R (2004) Interval mapping of quantitative trait loci for resistance to late blight [Phytophthora infestans (Mont.) de Bary], height and maturity in a tetraploid population of potato (Solanum tuberosum subsp. tuberosum). Genetics 168:983–995
Canli FA (2004) Development of a second generation genetic linkage map for sour cherry using SSR markers. Pak J Biol Sci 7:1676–1683
Cantini C, Iezzoni AF, Lamboy WF, Boritzki M, Struss D (2001) DNA fingerprinting of tetraploid cherry germplasm using simple sequence repeats. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 126:205–209
Clarke JB, Sargent DJ, Boskovic RI, Belaj A, Tobutt KR (2009) A cherry map from the inter-specific cross Prunus avium ‘Napoleon’ × P. nipponica based on microsatellite, gene-specific and isoenzyme markers. Tree Genet Genomes 5:41–51
Collard BCY, Jahufer MZZ, Brouwer JB, Pang ECK (2005) An introduction to markers, quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping and marker-assisted selection for crop improvement: the basic concepts. Euphytica 142:169–196
Davis RE, Zhao Y, Dally EL, Lee IM, Jomantiene R, Douglas SM (2013) ‘Candidatus Phytoplasmas pruni’, a novel taxon associated with X-disease of stone fruits, Prunus spp.: multilocus characterization based on 16S rRNA, secY, and ribosomal protein genes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63(Pt 2):766–776. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.041202-0
Dettori MT, Quarta R, Verde I (2001) A peach linkage map integrating RFLPs, SSRs, RAPDs, and morphological markers. Genome 44:783–790
Dirlewanger E, Pascal T, Zuger C, Kervella J (1996) Analysis of molecular markers associated with powdery mildew resistance genes in peach (Prunus persica (L.) Batsch) × Prunus davidiana hybrids. Theor Appl Genet 93:909–919
Dirlewanger E, Moing A, Rothan C, Svanella L, Pronier V, Guye A, Plomion C, Monet R (1999) Mapping QTLs controlling fruit quality in peach (Prunus persica (L.) Batsch). Theor Appl Genet 98:18–31
Dirlewanger E, Graziano E, Joobeur T, Garriga-Caldere F, Cosson P, Howad W, Arús P (2004a) Comparative mapping and marker-assisted selection in Rosaceae fruit crops. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:9891–9896
Dirlewanger E, Cosson P, Howard W, Capdeville G, Bosselut N, Claverie M, Voisin R, Poizat C, Lafargue B, Baron O, Laigret F, Kleinhentz M, Arús P, Esmenjaud D (2004b) Microsatellite genetic linkage maps of myrobalan plum and an almond–peach hybrid—location of root-knot nematode resistance genes. Theor Appl Genet 109:827–838
Dondini L, Lain O, Geuna F, Banfi R, Gaiotti F, Tartarini S, Bassi D, Testolin R (2007) Development of a new SSR-based linkage map in apricot and analysis of synteny with existing Prunus maps. Tree Genet Genomes 3:239–249
Dondini L, Lain O, Vendramin V, Rizzo M, Vivoli D, Adami M, Guidarelli M, Gaiotti F, Palmisano F, Bazzoni A, Boscia D, Geuna F, Tartarini S, Negri P, Castellano M, Savino V, Bassi D, Testolin R (2010) Identification of QTL for resistance to plum pox virus strains M and D in Lito an dHarcot apricot cultivars. Mol Breed 27:289–299
Downey SL, Iezzoni AF (2000) Polymorphic DNA markers in black cherry (Prunus serotina) are identified using sequences from sweet cherry, peach, and sour cherry. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 125:76–80
Foulongne M, Pascal T, Pfeiffer F, Kervella J (2003) QTLs for powdery mildew resistance in peach × Prunus davidiana crosses: consistency across generations and environments. Mol Breed 12:33–50
Gar O, Sargent DJ, Tsai C-J, Pleban T, Shalev G, Byrne DH, Zamir D (2011) An autotetraploid linkage map of rose (Rosa hybrida) validated using the strawberry (Fragaria vesca) genome sequence. PLoS ONE 6:e20463
Gasic K, Han Y, Kerbundit S, Shulaev V, Iezzoni AF, Stover EW et al (2009) Characteristics and transferability of new apple EST-derived SSRs to other Rosaceae species. Mol Breed 23:397–411
Ghislain M, Spooner DM, Rodríguez F, Villamón F, Nuñez J, Vásquez C, Waugh R, Bonierbale M (2004) Selection of highly informative and user-friendly microsatellites (SSRs) for genotyping of cultivated potato. Theor Appl Genet 108:881–890
Guo YH, Cheng ZM, Walla JA (2000) Characterization of X-disease phytoplasmas in chokecherry from North Dakota by PCR–RELP and sequence analysis of the rRNA gene region. Plant Dis 84:1235–1240
Hackett CA, Luo ZW (2003) TetraploidMap: construction of a linkage map in autotetraploid species. J Hered 94:358–359
Hackett CA, Wachira FN, Paul S, Powell W, Waugh R (2000) Construction of a genetic linkage map for Camellia sinensis (tea). J Hered 85:346–355
Hackett CA, Milne I, Bradshaw JE, Luo Z (2007) TetraploidMap for Windows: linkage map construction and QTL mapping in autotetraploid species. J Hered 98:727–729
Han Y, Zheng D, Vimolmangkang S, Khan MA, Beever JE et al (2011) Integration of physical and genetic maps in apple confirms whole-genome and segmental duplications in the apple genome. J Exp Bot 62:5117–5130
Hoarau JY, Offman B, D’Hont A, Risterucci AM, Roques D, Glaszmann JC, Grivet L (2001) Genetic dissection of a modern sugarcane cultivar (Saccharum spp.) I. Genome mapping with AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 103:84–97
Hurtado MA, Romero C, Vilanova S, Abbott AG, Llácer G, Badenes ML (2002) Genetic linkage maps of two apricot cultivars (Prunus armeniaca L.), and mapping of PPV (sharka) resistance. Theor Appl Genet 105:182–191
Joehanes R, Nelson JC (2008) QGene 4.0, an extensible Java QTL-analysis platform. Bioinformatics 24:2788–2789
Joobeur T, Viruel MA, de Vicente MC, Jáuregui B, Ballester J, Dettori MT, Verde I, Truco MJ, Messeguer R, Batlle I, Quarta R, Dirlewanger E, Arús P (1998) Construction of a saturated linkage map for Prunus using an almond × peach F2 progeny. Theor Appl Genet 97:1034–1041
Joobeur T, Periam N, de Vicente MC, King GJ, Arús P (2000) Development of a second generation linkage map for almond using RAPD and SSR markers. Genome 43:649–655
Julier B, Flajoulot S, Barre P, Cardinet G, Santoni S, Huguet T, Huyghe C (2003) Construction of two genetic linkage maps in cultivated tetraploid alfalfa (Medicago sativa) using microsatellite and AFLP markers. BMC Plant Biol 3:9–28
Lalli DA, Decroocq V, Blenda AV, Schurdi-Levraud V, Garay L, Le Gall O, Damsteegt V, Reighard GL, Abbott AG (2005) Identification and mapping of resistance gene analogs in Prunus: a resistance map for Prunus. Theor Appl Genet 111:1504–1513
Lodhi MA, Ye GN, Weeden NF, Reisch BI (1994) A simple and efficient method for DNA extraction from grapevine cultivars, Vitis species and Ampelopsis. Plant Mol Biol Rep 12:6–13
Lu ZX, Sosinski B, Reighard GL, Baird WV, Abbott AG (1998) Constriction of a genetic linkage map and identification of AFLP markers for resistance to root-knot nematodes in peach rootstocks. Genome 41:199–207
Luo ZW, Hackett CA, Bradshaw JE, McNicol JW, Milbourne D (2001) Construction of a genetic linkage map in tetraploid species using molecular markers. Genetics 157:1369–1385
Luo ZW, Zhang RW, Kearsey MJ (2004) Theoretical basis for genetic linkage analysis in autotetraploid species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:7040–7045
Mnejja M, Garcia-Mas J, Audergon JM, Arús P (2010) Prunus microsatellite marker transferability across rosaceous crops. Tree Genet Genomes 6:689–700
Ogawa JM (1991) Diseases of temperate zone tree fruit and nut crops. Divisions of Agriculture and Natural Resources, University of California, California
Olmstead JW, Sebolt AM, Cabrera A, Sooriyapathirana SS, Hammar S, Iriarte G et al (2008) Construction of an intra-specific sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) genetic linkage map and synteny analysis with the Prunus reference map. Tree Genet Genomes 4:897–910
Rabinowicz PD, Braun EL, Wolfe AD, Bowen B, Grotewald E (1999) Maize R2R3 Myb genes. Sequence analysis reveals amplification in the higher plants. Genetics 153:427–444
Rajapakse S, Byrne DH, Zhang L, Anderson N, Arumuganathan K, Ballard RE (2001) Two genetic linkage maps of tetraploid roses. Theor Appl Genet 103:575–583
Rehder A (1940) Manual of cultivated trees and shrubs, 2nd edn. MacMillan, New York, pp 452–481
Rong J, Feltus FA, Waghmare VN, Pierce GJ, Chee PW, Draye X, Saranga Y, Wright RJ, Wilkins TA, May OL, Smith CW, Gannaway JR, Wendel JF, Paterson AH (2007) Meta-analysis of polyploid cotton QTL shows unequal contributions of sub-genomes to a complex network of genes and gene clusters implicated in lint fiber development. Genetics 176:2577–2588
Rosenberger DA, Jones AL (1997) Seasonal variation in infectivity of inoculum from X-diseased peach and chokecherry plants. Plant Dis Rep 61:1022–1024
Sim SC, Yu JK, Jo YK, Sorrells ME, Jung G (2009) Transferability of cereal EST-SSR markers to ryegrass. Genome 52:431–437
Socquet-Juglard D, Duffy B, Pothier JF, Christen D, Gessler C, Patocchi A (2013) Identification of a major QTL for Xanthomonas arboricola pv. pruni resistance in apricot. Tree Genet Genomes 9:409–421. doi:10.1007/s11295-012-0562-z
Struss D, Ahmad R, Southwick SM, Boritzki M (2003) Analysis of sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) cultivars using SSR and AFLP markers. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 128:904–909
Tobutt KR, Boskovic R, Cerovic R, Sonneveld T, Ruzic D (2004) Identification of incompatibility alleles in the tetraploid species sour cherry. Theor Appl Genet 108:775–785
Van Ghelder C, Lafargue B, Dirlewanger E, Ouassa A, Voisin R, Polidori J, Kleinhentz M, Esmenjaud D (2010) Characterization of the RMja gene for resistance to root-knot nematode in almond: spectrum, location, and interest for Prunus breeding. Tree Genet Genomes 6:503–511
Vera Ruiz EM, Soriano JM, Romero C, Zhebentyayeva T, Terol J, Zuriaga E, Llacer G, Abbott AG, Badenes ML (2011) Narrowing down the apricot Plum pox virus resistance locus and comparative analysis with the peach genome syntenic region. Mol Plant Pathol 12:535–547
Verde L, Lauria M, Dettori MT, Vendramin E, Balconi C, Micali S, Wang Y, Marrazzo MT, Cipriani G, Hartings H, Testolin R, Abbott AG, Motto M, Quarta R (2005) Microsatellite and AFLP markers in the Prunus persica [L. (Batsch)] × P. ferganensis BC1 linkage map: saturation and coverage improvement. Theor Appl Genet 111:1013–1021
Viruel MA, Messeguer R, de Vicente MC, Garcia-Mas J, Puigdomenech P, Vargas F, Arús P (1995) A linkage map with RFLP and isozyme markers for almond. Theor Appl Genet 91:964–997
Voorrips RE (2002) MapChart, software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered 93:77–78
Wang D, Karle R, Brettin TS, Iezzoni AF (1998) Genetic linkage map in sour cherry using RFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 97:1217–1224
Wang X, Wadl PA, Rinehart TA, Scheffler BE, Windham MT, Spiers JM, Johnson DH, Trigiano RN (2009) A linkage map for flowering dogwood (Cornus florida L.) based on microsatellite markers. Euphytica 165:165–175
Wang H, Walla JA, Zhong S, Huang D, Dai W (2012) Development and cross-species/genera transferability of microsatellite markers discovered using 454 genome sequencing in chokecherry (Prunus virginiana L.). Plant Cell Rep 31:2047–2055
Weeden NF, Hemmatt M, Lawson DM, Lodhi M, Manganaris AG, Reisch BI, Brown SK, Ye GN (1994) Development and application of molecular marker linkage maps in woody fruit crops. Euphytica 77:71–75
Wu KK, Burnquist W, Sorrells ME, Tew TL, Moore PH, Tanksley SD (1992) The detection and estimation of linkage in polyploids using single-dose restriction fragments. Theor Appl Genet 83:294–300
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. Michael Christoffers and Edward Deckard for valuable suggestions and comments while we were preparing this manuscript. This research was supported in part by USDA-CSREES-2005-35300-15457 and McIntire-Stennis Project ND06212.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Walla, J.A., Magnusson, V.A. et al. Construction of genetic linkage maps and QTL mapping for X-disease resistance in tetraploid chokecherry (Prunus virginiana L.) using SSR and AFLP markers. Mol Breeding 34, 143–157 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-014-0025-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-014-0025-3