Abstract
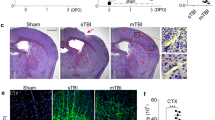
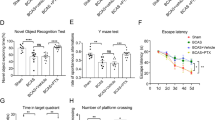
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is accompanied with enhanced matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) activity and elevated levels of plasma fibrinogen (Fg), which is a known inflammatory agent. Activation of MMP-9 and increase in blood content of Fg (i.e. hyperfibrinogenemia, HFg) both contribute to cerebrovascular disorders leading to blood brain barrier disruption. It is well-known that activation of MMP-9 contributes to vascular permeability. It has been shown that at an elevated level (i.e. HFg) Fg disrupts blood brain barrier. However, mechanisms of their actions during TBI are not known. Mild TBI was induced in wild type (WT, C57BL/6 J) and MMP-9 gene knockout (Mmp9−/−) homozygous, mice. Pial venular permeability to fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated bovine serum albumin in pericontusional area was observed 14 days after injury. Mice memory was tested with a novel object recognition test. Increased expression of Fg endothelial receptor intercellular adhesion protein-1 and formation of caveolae were associated with enhanced activity of MMP-9 causing an increase in pial venular permeability. As a result, an enhanced deposition of Fg and cellular prion protein (PrPC) were found in pericontusional area. These changes were attenuated in Mmp9−/− mice and were associated with lesser loss of short-term memory in these mice than in WT mice. Our data suggest that mild TBI-induced increased cerebrovascular permeability enhances deposition of Fg-PrPC and loss of memory, which is ameliorated in the absence of MMP-9 activity. Thus, targeting MMP-9 activity and blood level of Fg can be a possible therapeutic remedy to diminish vasculo-neuronal damage after TBI.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams RA, Bauer J, Flick MJ, Sikorski SL, Nuriel T, Lassmann H, Degen JL, Akassoglou K (2007) The fibrin-derived γ377-395 peptide inhibits microglia activation and suppresses relapsing paralysis in central nervous system autoimmune disease. J Exp Med 204(3):571–582. doi:10.1084/jem.20061931
Ahn HJ, Zamolodchikov D, Cortes-Canteli M, Norris EH, Glickman JF, Strickland S (2010) Alzheimer’s disease peptide β-amyloid interacts with fibrinogen and induces its oligomerization. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107(50):21812–21817. doi:10.1073/pnas.1010373107
Altieri DC, Duperray A, Plescia J, Thornton GB, Languino LR (1995) Structural recognition of a novel fibrinogen gamma chain sequence (117–133) by intercellular adhesion molecule-1 mediates leukocyte-endothelium interaction. J Biol Chem 270(2):696–699
Bevins RA, Besheer J (2006) Object recognition in rats and mice: a one-trial non-matching-to-sample learning task to study ‘recognition memory’. Nat Protocols 1 (3):1,306–1,311. doi:http://www.nature.com/nprot/journal/v1/n3/suppinfo/nprot.2006.205_S1.html
Carson-Walter E, Hampton J, Shue E, Geynisman D, Pillai P, Sathanoori R, Madden S, Hamilton R, Walter K (2005) Plasmalemmal vesicle associated protein-1 is a novel marker implicated in brain tumor angiogenesis. Clin Cancer Res 11(21):7643–7650
Cernich A, Kurtz S, Mordecai K, Ryan P (2010) Cognitive rehabilitation in traumatic brain injury. Curr Treat Options Neurol 12(5):412–423. doi:10.1007/s11940-010-0085-6
Chhabra G, Rangarajan K, Subramanian A, Agrawal D, Sharma S, Mukhopadhayay A (2010) Hypofibrinogenemia in isolated traumatic brain injury in Indian patients. Neurol India 58(5):756–757. doi:10.4103/0028-3886.72175
Choo AM, Miller WJ, Chen Y-C, Nibley P, Patel TP, Goletiani C, Morrison B, Kutzing MK, Firestein BL, Sul J-Y, Haydon PG, Meaney DF (2013) Antagonism of purinergic signalling improves recovery from traumatic brain injury. Brain. doi:10.1093/brain/aws286
Chung E, Ji Y, Sun Y, Kascsak R, Kascsak R, Mehta P, Strittmatter S, Wisniewski T (2010) Anti-PrPC monoclonal antibody infusion as a novel treatment for cognitive deficits in an Alzheimer’s disease model mouse. BMC Neurosci 11:130. doi:10.1186/1471-2202-11-130
Cohen ZVI, Bonvento G, Lacombe P, Hamel E (1996) Serotonin in the regulation of brain microcirculation. Prog Neurobiol 50(4):335–362. doi:10.1016/s0301-0082(96)00033-0
D’Erasmo E, Acca M, Celi FS, Medici F, Palmerini T, Pisani D (1993) Plasma fibrinogen and platelet count in stroke. J Med 24(2–3):185–191
Davalos D, Akassoglou K (2012) Fibrinogen as a key regulator of inflammation in disease. Semin Immunopathol 34(1):43–62
Davalos D, Kyu Ryu J, Merlini M, Baeten KM, Le Moan N, Petersen MA, Deerinck TJ, Smirnoff DS, Bedard C, Hakozaki H, Gonias Murray S, Ling JB, Lassmann H, Degen JL, Ellisman MH, Akassoglou K (2012) Fibrinogen-induced perivascular microglial clustering is required for the development of axonal damage in neuroinflammation. Nat Commun 3:1,227. doi:http://www.nature.com/ncomms/journal/v3/n11/suppinfo/ncomms2230_S1.html
del Zoppo GJ, Levy DE, Wasiewski WW, Pancioli AM, Demchuk AM, Trammel J, Demaerschalk BM, Kaste M, Albers GW, Ringelstein EB (2009) Hyperfibrinogenemia and functional outcome from acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 40(5):1687–1691. doi:10.1161/strokeaha.108.527804
Ernst E, Resch KL (1993) Fibrinogen as a cardiovascular risk factor: a meta-analysis and review of the literature. Ann Intern Med 118:956–963
Fernandez-Patron C, Zouki C, Whittal R, Chan JS, Davidge ST, Filep JG (2001) Matrix metalloproteinases regulate neutrophil-endothelial cell adhesion through generation of endothelin-1 [1–32]. FASEB J 15(12):2230–2240
Fischer MB, Roeckl C, Parizek P, Schwarz HP, Aguzzi A (2000) Binding of disease-associated prion protein to plasminogen. Nature 408(6811):479–483
Flick MJ, Du X, Witte DP, Jirouskova M, Soloviev DA, Busuttil SJ, Plow EF, Degen JL (2004) Leukocyte engagement of fibrin (ogen) via the integrin receptor αMβ2/Mac-1 is critical for host inflammatory response in vivo. J Clin Invest 113(11):1596–1606. doi:10.1172/JCI20741
Gimbel DA, Nygaard HB, Coffey EE, Gunther EC, Laurén J, Gimbel ZA, Strittmatter SM (2010) Memory impairment in transgenic Alzheimer mice requires cellular prion protein. J Neuroradiol 30(18):6367–6374. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.0395-10.2010
Granger D, Senchenkova E (2010) Inflammation and the Microcirculation. Colloquium Series on Integrated Systems Physiology: From Molecule to Function to Disease. Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences, San Rafael
Grossetete M, Phelps J, Arko L, Yonas H, Rosenberg G (2009) Elevation of matrix metalloproteinases 3 and 9 in cerebrospinal fluid and blood in patients with severe traumatic brain injury. Neurosurgery 65(4):702–708
Hadass O, Tomlinson BN, Gooyit M, Chen S, Purdy JJ, Walker JM, Zhang C, Giritharan AB, Purnell W, Robinson CR II, Shin D, Schroeder VA, Suckow MA, Simonyi AY, Sun G, Mobashery S, Cui J, Chang M, Gu Z (2013) Selective inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-9 attenuates secondary damage resulting from severe traumatic brain injury. PLoS One 8(10):e76904. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0076904
Hnasko R, McFarland M, Ben-Jonathan N (2002) Distribution and characterization of plasmalemma vesicle protein-1 in rat endocrine glands. J Endocrinol 175(3):649–661. doi:10.1677/joe.0.1750649
Hu G, Vogel SM, Schwartz DE, Malik AB, Minshall RD (2008) Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1–Dependent Neutrophil Adhesion to Endothelial Cells Induces Caveolae-Mediated Pulmonary Vascular Hyperpermeability. Circ Res 102(12):e120–e131. doi:10.1161/circresaha.107.167486
Johnson VE, Stewart W, Smith DH (2010) Traumatic brain injury and amyloid-[beta] pathology: a link to Alzheimer’s disease? Nat Rev Neurosci 11(5):361–370
Kerlin B, Cooley BC, Isermann BH, Hernandez I, Sood R, Zogg M, Hendrickson SB, Mosesson MW, Lord S, Weiler H (2004) Cause-effect relation between hyperfibrinogenemia and vascular disease. Curr Opin Hematol 103(5):1728–1734
Lauren J, Gimbel DA, Nygaard HB, Gilbert JW, Strittmatter SM (2009) Cellular prion protein mediates impairment of synaptic plasticity by amyloid-[bgr] oligomers. Nature 457 (7233):1,128–1,132. doi:http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v457/n7233/suppinfo/nature07761_S1.html
Letcher RL, Chien S, Pickering TG, Sealey JE, Laragh JH (1981) Direct relationship between blood pressure and blood viscosity in normal and hypertensive subjects. Role of fibrinogen and concentration. Am J Med 70:1195–1202
Lishko VK, Kudryk B, Yakubenko VP, Yee VC, Ugarova TP (2002) Regulated unmasking of the cryptic binding site foriIntegrin αMβ2 in the γC-domain of fibrinogen. Biochemistry 41(43):12942–12951. doi:10.1021/bi026324c
Lominadze D, Joshua IG, Schuschke DA (1998) Increased erythrocyte aggregation in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Hypertens 11:784–789
Lominadze D, Tsakadze N, Sen U, Falcone JC, D’Souza SE (2005) Fibrinogen- and fragment D-induced vascular constriction. Am J Physiol 288(3):H1257–H1264
Lominadze D, Roberts AM, Tyagi N, Tyagi SC (2006) Homocysteine causes cerebrovascular leakage in mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 290(3):H1206–H1213
Lominadze D, Dean WL, Tyagi SC, Roberts AM (2010) Mechanisms of fibrinogen-induced microvascular dysfunction during cardiovascular disease. Acta Physiol 198(1):1–13
Lyon L, Saksida L, Bussey T (2012) Spontaneous object recognition and its relevance to schizophrenia: a review of findings from pharmacological, genetic, lesion and developmental rodent models. Psychopharmacology 220(4):647–672. doi:10.1007/s00213-011-2536-5
Mansoor O, Cayol M, Gachon P, Boirie Y, Schoeffler P, Obled C, Beaufrère B (1997) Albumin and fibrinogen syntheses increase while muscle protein synthesis decreases in head-injured patients. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 273(5):E898–E902
Mehta D, Malik AB (2006) Signaling mechanisms regulating endothelial permeability. Physiol Rev 86(1):279–367
Minshall RD, Tiruppathi C, Vogel SM, Niles WD, Gilchrist A, Hamm HE, Malik AB (2000) Endothelial cell-surface gp60 activates vesicle formation and trafficking via G(i)-coupled Src kinase signaling pathway. J Cell Biol 150(5):1057–1070
Mori T, Wang X, Aoki T, Lo EH (2002) Downregulation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and attenuation of edema via inhibition of ERK mitogen activated protein kinase in traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 19(11):1411–1419. doi:10.1089/089771502320914642
Mozer A, Whittemore S, Benton R (2010) Spinal microvascular expression of PV-1 is associated with inflammation, perivascular astrocyte loss, and diminished EC glucose transport potential in acute SCI. Curr Neurovasc Res 7(3):238–250
Muradashvili N, Lominadz D (2013) Role of fibrinogen in cerebrovascular dysfunction after traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj 27(13–14):1508–1515. doi:10.3109/02699052.2013.823562
Muradashvili N, Tyagi N, Tyagi R, Munjal C, Lominadze D (2011) Fibrinogen alters mouse brain endothelial cell layer integrity affecting vascular endothelial cadherin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 413(4):509–514. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.07.133
Muradashvili N, Qipshidze N, Munjal C, Givvimani S, Benton RL, Roberts AM, Tyagi SC, Lominadze D (2012a) Fibrinogen-induced increased pial venular permeability in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 32(1):150–163. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2011.144
Muradashvili N, Tyagi R, Lominadze D (2012b) A dual-tracer method for differentiating transendothelial transport from paracellular leakage in vivo and in vitro. Front Physiol 3:166–172. doi:10.3389/fphys.2012.00166
Muradashvili N, Benton R, Tyagi S, Lominadz D (2013) Elevated level of fibrinogen increases caveolae formation; Role of matrix metalloproteinase-9. Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics: [Epub ahead of print]
Pahatouridis D, Alexiou G, Zigouris A, Mihos E, Drosos D, Voulgaris S (2010) Coagulopathy in moderate head injury. The role of early administration of low molecular weight heparin. Brain Inj 24(10):1189–1192
Parton RG, Joggerst B, Simons K (1994) Regulated internalization of caveolae. J Cell Biol 127(5):1199–1215. doi:10.1083/jcb.127.5.1199
Patibandla PK, Tyagi N, Dean WL, Tyagi SC, Roberts AM, Lominadze D (2009) Fibrinogen induces alterations of endothelial cell tight junction proteins. J Cell Physiol 221(1):195–203
Phillips PG, Birnby LM (2004) Nitric oxide modulates caveolin-1 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression and distribution at the endothelial cell/tumor cell interface. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 286(5):L1055–L1065. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00262.2003
Pleasant J, Carlson S, Mao H, Scheff S, Yang K, Saatman K (2011) Rate of neurodegeneration in the mouse controlled cortical impact model is influenced by impactor tip shape: implications for mechanistic and therapeutic studies. Journal of Neurotrauma
Plow EF, Haas TA, Zhang L, Loftus J, Smith JW (2000) Ligand binding to integrins. J Biol Chem 275(29):21785–21788
Rosell A, Alvarez-Sabin J, Arenillas JF, Rovira A, Delgado P, Fernandez-Cadenas I, Penalba A, Molina CA, Montaner J (2005) A matrix metalloproteinase protein array reveals a strong relation between MMP-9 and MMP-13 with diffusion-weighted image lesion increase in human stroke. Stroke 36(7):1415–1420
Rosell A, Ortega-Aznar A, Alvarez-Sabin J, Fernandez-Cadenas I, Ribo M, Molina CA, Lo EH, Montaner J (2006) Increased brain expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 after ischemic and hemorrhagic human stroke. Stroke 37(6):1399–1406
Ross R (1999) Mechanisms of disease - Atherosclerosis - An inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med 340(2):115–126
Rybarczyk BJ, Lawrence SO, Simpson-Haidaris PJ (2003) Matrix-fibrinogen enhances wound closure by increasing both cell proliferation and migration. Blood 102(12):4035–4043. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-03-0822
Sahni A, Arévalo MT, Sahni SK, Simpson-Haidaris PJ (2009) The VE-cadherin binding domain of fibrinogen induces endothelial barrier permeability and enhances transendothelial migration of malignant breast epithelial cells. Int J Cancer 125(3):577–584
Sangiorgi S, De Benedictis A, Protasoni M, Manelli A, Reguzzoni M, Cividini A, Dell’Orbo C, Tomei G, Balbi S (2013) Early-stage microvascular alterations of a new model of controlled cortical traumatic brain injury: 3D morphological analysis using scanning electron microscopy and corrosion casting. J Neurosurg 118(4):763–774. doi:10.3171/2012.11.JNS12627
Schwarzmaier S, Kim S, Trabold R, Plesnila N (2010) Temporal profile of thrombogenesis in the cerebral microcirculation after traumatic brain injury in mice. J Neurotrauma 27(1):121–130
Sen U, Tyagi N, Patibandla PK, Dean WL, Tyagi SC, Roberts AM, Lominadze D (2009) Fibrinogen-induced endothelin-1 production from endothelial cells. AJP - Cell Physiol 296(4):C840–C847
Shigemori Y, Katayama Y, Mori T, Maeda T, Kawamata T (2006) Matrix metalloproteinase-9 is associated with blood–brain barrier opening and brain edema formation after cortical contusion in rats. In: Hoff JT, Keep RF, Xi G, Hua Y (eds) Brain Edema XIII, vol 96. Acta Neurochirurgica Supplement vol Supplement 96. Springer, Wien, pp 130–133
Shlosberg D, Benifla M, Kaufer D, Friedman A (2010) Blood–brain barrier breakdown as a therapeutic target in traumatic brain injury. Nat Rev Neurol 6(7):393–403
Shue E, Carson-Walter E, Liu Y, Winans B, Ali Z, Chen J, Walter K (2008) Plasmalemmal vesicle associated protein-1 (PV-1) is a marker of blood–brain barrier disruption in rodent models. BMC Neurosci 9(1):29
Simionescu M, Popov D, Sima A (2009) Endothelial transcytosis in health and disease. Cell Tissue Res 335(1):27–40. doi:10.1007/s00441-008-0688-3
Stan R-V, Marion K, Palade GE (1999) PV-1 is a component of the fenestral and stomatal diaphragms in fenestrated endothelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96(23):13203–13207
Sun Y, Hu G, Zhang X, Minshall RD (2009) Phosphorylation of Caveolin-1 Regulates Oxidant–Induced Pulmonary Vascular Permeability via Paracellular and Transcellular Pathways. Circ Res 105(7):676–685. doi:10.1161/circresaha.109.201673
Sun Y, Wang J, Wu X, Xi C, Gai Y, Liu H, Yuan Q, Wang E, Gao L, Hu J, Zhou L (2011) Validating the incidence of coagulopathy and disseminated intravascular coagulation in patients with traumatic brain injury – analysis of 242 cases. Br J Neurosurg 25(3):363–368. doi:10.3109/02688697.2011.552650
Tran HT, LaFerla FM, Holtzman DM, Brody DL (2011) Controlled cortical impact traumatic brain injury in 3xTg-AD mice causes acute intra-axonal aAmyloid-β accumulation and independently accelerates the development of Tau abnormalities. J Neurosci 31(26):9513–9525. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.0858-11.2011
Tyagi N, Roberts AM, Dean WL, Tyagi SC, Lominadze D (2008) Fibrinogen induces endothelial cell permeability. Mol Cell Biochem 307(1–2):13–22
Wang X, Jung J, Asahi M, Chwang W, Russo L, Moskowitz MA, Dixon CE, Fini ME, Lo EH (2000) Effects of matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene knock-out on morphological and motor outcomes after traumatic brain injury. J Neurosci 20(18):7037–7042
Wei E, Hamm R, Baranova A, Povlishock J (2009) The long-term microvascular and behavioral consequences of experimental traumatic brain injury after hypothermic intervention. J Neurotrauma 26(4):527–537
Yamaguchi M, Jadhav V, Obenaus A, Colohan A, Zhang JH (2007) Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibition Attenuates Brain Edema in An in Vivo Model of Surgically‐Induced Brain Injury. Neurosurgery 61(5):1067–1076, 1010.1227/1001.neu.0000303203.0000307866.0000303218
Yu J, Bergaya S, Murata T, Alp IF, Bauer MP, Lin MI, Drab M, Kurzchalia TV, Stan RV, Sessa WC (2006) Direct evidence for the role of caveolin-1 and caveolae in mechanotransduction and remodeling of blood vessels. J Clin Investig 116(5):1284. doi:10.1172/jci27100
Zhang R, Yang D, Zhou C, Cheng K, Liu Z, Chen L, Fang L, Xie P (2012) β-Actin as a loading control for plasma-based Western blot analysis of major depressive disorder patients. Anal Biochem 427(2):116–120. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2012.05.008
Zlokovic BV, Griffin JH (2011) Cytoprotective protein C pathways and implications for stroke and neurological disorders. Trends Neurosci 34(4):198–209. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2011.01.005
Acknowledgments
Supported in part by NIH grants P30 GM-103507 (Pilot Project to D.L.), NS-084823 (to D.L. and S.C.T.), and NS-051568 (to S.C.T.)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muradashvili, N., Benton, R.L., Saatman, K.E. et al. Ablation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene decreases cerebrovascular permeability and fibrinogen deposition post traumatic brain injury in mice. Metab Brain Dis 30, 411–426 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-014-9550-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-014-9550-3