Abstract
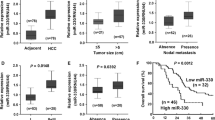
Increasing evidence suggests that dysregulation of microRNAs is correlated with malignant transformation and tumor development. miR-100, a potential tumor suppressor, is downregulated by many human cancers. However, the expression and functions of miR-100 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) are still unclear. The aim of this study was to detect the expression of miR-100 in HCC tissues and investigate its clinicopathological and prognostic significance. Also, the effects of miR-100 on growth and apoptosis of HCC cells and its potential molecular mechanisms were analyzed. Results showed that the expression level of miR-100 in HCC tissues was significantly lower than that in matched non-cancerous liver tissues. Also, low-miR-100 expression was observed to be significantly correlated with higher tumor grade, higher incidence of lymph node metastasis, advanced TNM stage and higher incidence of tumor recurrence in HCC patients. Multivariate survival analyses suggested that low-miR-100 expression was an independent prognostic factor for HCC patients (HR = 1.66, 95 % CI 1.32–2.82, P = 0.019). In addition, we found that upregulation of miR-100 could inhibit growth and increase apoptosis of HCC cells by downregulating polo-like kinase 1 (plk1). In HCC tissues, miR-100 expression was inversely correlated with the expression of plk1 protein (r = −0.418; P = 0.029). Therefore, downregulation of miR-100 was correlated with progressive pathological feature and poor prognosis in HCC patients, and miR-100 could function as a tumor suppressor by targeting plk1. miR-100 may serve as a prognostic marker and molecular therapeutic target in HCC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
McGlynn KA, London WT (2011) The global epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: present and future. Clin Liver Dis 15:223–243
Yuen MF, Hou JL, Chutaputti A et al (2009) Hepatocellular carcinoma in the Asia pacific region. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 24:346–353
Nelson P, Kiriakidou M, Sharma A et al (2003) The microRNA world: small is mighty. Trends Biochem Sci 28:534–540
Subramanian S, Steer CJ (2010) MicroRNAs as gatekeepers of apoptosis. J Cell Physiol 223:289–298
Berardi E, Pues M, Thorrez L et al (2012) miRNAs in ESC differentiation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 303:H931–H939
Roy S, Sen CK (2012) miRNA in wound inflammation and angiogenesis. Microcirculation 19:224–232
Jansson MD, Lund AH (2012) MicroRNA and cancer. Mol Oncol 6:590–610
Braconi C, Henry JC, Kogure T (2011) The role of microRNAs in human liver cancers. Semin Oncol 38:752–763
Negrini M, Gramantieri L, Sabbioni S et al (2011) microRNA involvement in hepatocellular carcinoma. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 11:500–521
Oliveira JC, Brassesco MS, Morales AG et al (2011) MicroRNA-100 acts as a tumor suppressor in human bladder carcinoma 5637 cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 12:3001–3004
Liu J, Lu KH, Liu ZL et al (2012) MicroRNA-100 is a potential molecular marker of non-small cell lung cancer and functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting polo-like kinase 1. BMC Cancer 12:519
Zheng YS, Zhang H, Zhang XJ et al (2012) MiR-100 regulates cell differentiation and survival by targeting RBSP3, a phosphatase-like tumor suppressor in acute myeloid leukemia. Oncogene 31:80–92
Petrelli A, Perra A, Schernhuber K et al (2012) Sequential analysis of multistage hepatocarcinogenesis reveals that miR-100 and PLK1 dysregulation is an earlyevent maintained along tumor progression. Oncogene 31:4517–4526
Tovar V, Alsinet C, Villanueva A et al (2010) IGF activation in a molecular subclass of hepatocellular carcinoma and pre-clinical efficacy of IGF-1R blockage. J Hepatol 52:550–559
Shi W, Alajez NM, Bastianutto C et al (2010) Significance of Plk1 regulation by miR-100 in human nasopharyngeal cancer. Int J Cancer 126:2036–2048
Peng DX, Luo M, Qiu LW et al (2012) Prognostic implications of microRNA-100 and its functional roles in human epithelial ovarian cancer. Oncol Rep 27:1238–1244
Carthew RW (2006) Gene regulation by microRNAs. Curr Opin Genet Dev 16:203–208
Lee S, Vasudevan S (2013) Post-transcriptional stimulation of gene expression by microRNAs. Adv Exp Med Biol 768:97–126
Osman A (2012) MicroRNAs in health and disease–basic science and clinical applications. Clin Lab 58:393–402
Roberts AP, Lewis AP, Jopling CL (2011) The role of microRNAs in viral infection. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 102:101–139
El Tayebi HM, Hosny KA, Esmat G et al (2012) MiR-615-5p is restrictedly expressed in cirrhotic and cancerous liver tissues and its overexpression alleviates the tumorigenic effects in hepatocellular carcinoma. FEBS Lett 586:3309–3316
Zhang L, Yang L, Liu X et al (2013) MicroRNA-657 promotes tumorigenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting transducin-like enhancer protein through nuclear factor kappa B pathways. Hepatology 57:1919–1930
Zhang Y, Wei W, Cheng N et al (2012) Hepatitis C virus-induced up-regulation of microRNA-155 promotes hepatocarcinogenesis by activating Wnt signaling. Hepatology 56:1631–1640
Zhang LY, Liu M, Li X et al (2013) miR-490-3p modulates cell growth and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment protein 3 (ERGIC3). J Biol Chem 288:4035–4047
Furuta M, Kozaki K, Tanimoto K et al (2013) The tumor-suppressive miR-497-195 cluster targets multiple cell-cycle regulators in hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One 8:e60155
Yau WL, Lam CS, Ng L et al (2013) Over-expression of miR-106b promotes cell migration and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma by activating epithelial-mesenchymal transition process. PLoS One 8:e57882
Wang S, Xue S, Dai Y et al (2012) Reduced expression of microRNA-100 confers unfavorable prognosis in patients with bladder cancer. Diagn Pathol 7:159
Wang G, Chen L, Meng J et al (2013) Overexpression of microRNA-100 predicts an unfavorable prognosis in renal cell carcinoma. Int Urol Nephrol 45:373–379
Liu XS, Song B, Liu X (2010) The substrates of Plk1, beyond the functions in mitosis. Protein Cell 1:999–1010
Pellegrino R, Calvisi DF, Ladu S et al (2010) Oncogenic and tumor suppressive roles of polo-like kinases in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 51:857–868
He ZL, Zheng H, Lin H et al (2009) Overexpression of polo-like kinase1 predicts a poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. World J Gastroenterol 15:4177–4182
He Z, Wu J, Dang H et al (2011) Polo-like kinase 1 contributes to the tumorigenicity of BEL-7402 hepatoma cells via regulation of Survivin expression. Cancer Lett 303:92–98
Acknowledgments
Thanks to the sincere help and technical support by the department of biochemistry and molecular biology in Xi’an Jiao Tong University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
P. Chen and X. Zhao should be regarded as joint first authors for their equal contributions.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, P., Zhao, X. & Ma, L. Downregulation of microRNA-100 correlates with tumor progression and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem 383, 49–58 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1753-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1753-0