Abstract
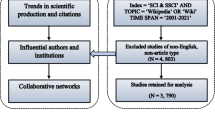
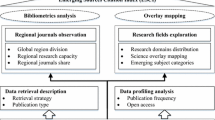
This analysis covers 4494 anoikis-related publications (2003–2022). It explores annual trends, top countries, core journals, leading institutions, keywords, references, authors, and collaborations. Key findings include the United States leading in publications, Chulalongkorn University as the top institution, and Oncogene as the most prolific journal. The Journal of Biological Chemistry holds the highest influence. Burst keywords like “signal transduction,” “apoptosis resistance,” “metabolism,” and “tumor microenvironment” highlight emerging research areas. This study offers a comprehensive overview, aiding researchers in grasping anoikis research trends, contributors, and prospects.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available in the Web of Science™ (WOS).
References
Xiao F et al (2021) Tumor-suppressing STF cDNA 3 overexpression suppresses renal fibrosis by alleviating anoikis resistance and inhibiting the PI3K/Akt pathway. Kidney Blood Press Res 46(5):588–600
Ray U et al (2022) Targeting LRRC15 inhibits metastatic dissemination of ovarian cancer. Can Res 82(6):1038–1054
Jin L et al (2018) The PLAG1-GDH1 axis promotes anoikis resistance and tumor metastasis through CamKK2-AMPK signaling in LKB1-deficient lung cancer. Mol Cell 69(1):87
Tian H et al (2020) AKT-induced lncRNA VAL promotes EMT-independent metastasis through diminishing Trim16-dependent Vimentin degradation. Nat Commun 11(1):5127
Zhao H et al (2020) STIM1 is a metabolic checkpoint regulating the invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Theranostics 10(14):6483–6499
Reginato MJ et al (2003) Integrins and EGFR coordinately regulate the pro-apoptotic protein Bim to prevent anoikis. Nat Cell Biol 5(8):733–740
Douma S et al (2004) Suppression of anoikis and induction of metastasis by the neurotrophic receptor TrkB. Nature 430(7003):1034–1039
Zhang Y et al (2004) Squamous cell carcinoma cell aggregates escape suspension-induced, p53-mediated anoikis: fibronectin and integrin alphav mediate survival signals through focal adhesion kinase. J Biol Chem 279(46):48342–48349
Buchheit CL, Weigel KJ, Schafer ZT (2014) Cancer cell survival during detachment from the ECM: multiple barriers to tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer 14(9):632–641
Acknowledgements
We thank the Web of ScienceTM (WOS) team for using their data.
Funding
This work was funded by Scientific Research Funding Project of Liaoning Provincial Education Department (Grant No. JCZR2020014), Shenyang Science and Technology Plan (Grant No. 22-321-33-23) and 345 Talent Project of Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University (30C Project).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception/design by HZ and EZ. Collection and/or assembly of data by XH, HZ and EZ. Data analysis and interpretation by XH. Manuscript writing by XH. Final approval of manuscript by XH, HZ and EZ.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, X., Zhang, H. & Zhang, E. A bibliometric and knowledge-map analysis of anoikis from 2003 to 2022. Apoptosis 29, 457–459 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-023-01910-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-023-01910-9