Abstract
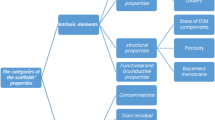
Biologic scaffold materials composed of allogeneic or xenogeneic extracellular matrix (ECM) are commonly used for the repair and remodeling of injured tissue. The clinical outcomes associated with implantation of ECM-based materials range from unacceptable to excellent. The variable clinical results are largely due to differences in the preparation of the material, including characteristics of the source tissue, the method and efficacy of decellularization, and post-decellularization processing steps. The mechanisms by which ECM scaffolds promote constructive tissue remodeling include mechanical support, degradation and release of bioactive molecules, recruitment and differentiation of endogenous stem/progenitor cells, and modulation of the immune response toward an anti-inflammatory phenotype. The methods of ECM preparation and the impact of these methods on the quality of the final product are described herein. Examples of favorable cellular responses of immune and stem cells associated with constructive tissue remodeling of ECM bioscaffolds are described.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- SIS:
-
Small intestinal submucosa
- UBM:
-
Urinary bladder matrix
- GAGs:
-
Glycosaminoglycans
- SDS:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
- DOC:
-
Sodium deoxycholate
- ToF–SIMS:
-
Time of flight secondary ion mass spectroscopy
- HMDI:
-
Hexamethylene diisocyanate
- MBV:
-
Matrix bound nanovesicles
- FDA:
-
United States Food and Drug Administration
- ISO:
-
International Organization for Standardization
- HCT/P:
-
Human cell and tissue product
- EtO:
-
Ethylene oxide
- TOFT:
-
Tissue organization field theory
- DAMPs:
-
Damage associated molecular patterns
- PVSC:
-
Perivascular stem cells
References
Agmon, G., and K. L. Christman. Controlling stem cell behavior with decellularized extracellular matrix scaffolds. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 20:193–201, 2016.
Agrawal, V., S. A. Johnson, J. Reing, L. Zhang, S. Tottey, G. Wang, K. K. Hirschi, S. Braunhut, L. J. Gudas, and S. F. Badylak. Epimorphic regeneration approach to tissue replacement in adult mammals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107:3351–3355, 2010.
Agrawal, V., S. Tottey, S. A. Johnson, J. M. Freund, B. F. Siu, and S. F. Badylak. Recruitment of progenitor cells by an extracellular matrix cryptic peptide in a mouse model of digit amputation. Tissue Eng: Part A 17:2435–2443, 2011.
Aguiari, P., L. Iop, F. Favaretto, C. M. L. Fidalgo, F. Naso, G. Milan, V. Vindigni, M. Spina, F. Bassetto, A. Bagno, R. Vettor, and G. Gerosa. In vitro comparative assessment of decellularized bovine pericardial patches and commercial bioprosthetic heart valves. Biomed. Mater. 12:015021, 2017.
Allman, A. J., T. B. McPherson, S. F. Badylak, L. C. Merrill, B. Kallakury, C. Sheehan, R. H. Raeder, and D. W. Metzger. Xenogeneic extracellular matrix grafts elicit a Th2-restricted immune response. Transplantation 71:1631–1640, 2001.
Allman, A. J., T. B. McPherson, L. C. Merrill, S. F. Badylak, and D. W. Metzger. The Th2-restricted immune response to xenogeneic small intestinal submucosa does not influence systemic protective immunity to viral and bacterial pathogens. Tissue Eng. 8:53–62, 2002.
Armour, A. D., J. S. Fish, K. A. Woodhouse, and J. L. Semple. A comparison of human and porcine acellularized dermis: Interactions with human fibroblasts in vitro. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 117:845–856, 2006.
Badylak, S. F. The extracellular matrix as a biologic scaffold material. Biomaterials 28:3587–3593, 2007.
Badylak, S. F., D. O. Freytes, and T. W. Gilbert. Extracellular matrix as a biological scaffold material: Structure and function. Acta Biomater. 5:1–13, 2009.
Badylak, S. F., and T. W. Gilbert. Immune response to biologic scaffold materials. Semin. Immunol. 20:109–116, 2008.
Badylak, S. F., T. Hoppo, A. Nieponice, T. W. Gilbert, J. M. Davison, and B. A. Jobe. Esophageal preservation in five male patients after endoscopic inner-layer circumferential resection in the setting of superficial cancer: A regenerative medicine approach with a biologic scaffold. Tissue Eng. Part A 17:1643–1650, 2011.
Badylak, S. F., P. V. Kochupura, I. S. Cohen, S. V. Doronin, A. E. Saltman, T. W. Gilbert, D. J. Kelly, R. A. Ignotz, and G. R. Gaudette. The use of extracellular matrix as an inductive scaffold for the partial replacement of functional myocardium. Cell Transplant. 15(Supp 1):S29–S40, 2006.
Badylak, S. F., B. Kropp, T. McPherson, H. Liang, and P. W. Snyder. Small intestional submucosa: A rapidly resorbed bioscaffold for augmentation cystoplasty in a dog model. Tissue Eng. 4:379–387, 1998.
Badylak, S. F., K. Park, N. Peppas, G. McCabe, and M. Yoder. Marrow-derived cells populate scaffolds composed of xenogeneic extracellular matrix. Exp. Hematol. 29:1310–1318, 2001.
Badylak, S. F., R. Tullius, K. Kokini, K. D. Shelbourne, T. Klootwyk, S. L. Voytik, M. R. Kraine, and C. Simmons. The use of xenogeneic small intestinal submucosa as a biomaterial for Achille’s tendon repair in a dog model. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 29:977–985, 1995.
Badylak, S. F., J. E. Valentin, A. K. Ravindra, G. P. McCabe, and A. M. Stewart-Akers. Macrophage phenotype as a determinant of biologic scaffold remodeling. Tissue Eng. Part A 14:1835–1842, 2008.
Baiguera, S., C. Del Gaudio, E. Lucatelli, E. Kuevda, M. Boieri, B. Mazzanti, A. Bianco, and P. Macchiarini. Electrospun gelatin scaffolds incorporating rat decellularized brain extracellular matrix for neural tissue engineering. Biomaterials 35:1205–1214, 2014.
Bailey, A. J., and W. J. Tromans. Effects of ionizing radiation on the ultrastructure of collagen fibrils. Radiat. Res. 23:145–155, 1964.
Balestrini, J. L., A. Liu, A. L. Gard, J. Huie, K. M. S. Blatt, J. Schwan, L. Zhao, T. J. Broekelmann, R. P. Mecham, E. C. Wilcox, and L. E. Niklason. Sterilization of lung matrices by supercritical carbon dioxide. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 22:260–269, 2016.
Bao, J., Q. Wu, Y. Wang, Y. Li, L. Li, F. Chen, X. Wu, M. Xie, and H. Bu. Enhanced hepatic differentiation of rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in spheroidal aggregate culture on a decellularized liver scaffold. Int. J. Mol. Med. 38:457–465, 2016.
Barakat, O., S. Abbasi, G. Rodriguez, J. Rios, R. P. Wood, C. Ozaki, L. S. Holley, and P. K. Gauthier. Use of decellularized porcine liver for engineering humanized liver organ. J. Surg. Res. 173:e11–e25, 2012.
Beattie, A. J., T. W. Gilbert, J. P. Guyot, A. J. Yates, and S. F. Badylak. Chemoattraction of progenitor cells by remodeling extracellular matrix scaffolds. Tissue Eng. Part A 15:1119–1125, 2009.
Berger, A. Th1 and Th2 responses: What are they ? BMJ 321:424, 2000.
Bernhardt, A., M. Wehrl, B. Paul, T. Hochmuth, M. Schumacher, K. Schütz, and M. Gelinsky. Improved sterilization of sensitive biomaterials with supercritical carbon dioxide at low temperature. PLoS ONE 10:1–19, 2015.
Bhrany, A. D., C. J. Lien, B. L. Beckstead, N. D. Futran, N. H. Muni, C. M. Giachelli, and B. D. Ratner. Crosslinking of an oesophagus acellular matrix tissue scaffold. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2:365–372, 2008.
Bissell, M. J., and T. G. Ram. Regulation of functional cytodifferentiation and histogenesis in mammary epithelial cells: Role of the extracellular matrix. Environ. Health Perspect. 80:61–70, 1989.
Bonandrini, B., M. Figliuzzi, E. Papadimou, M. Morigi, N. Perico, F. Casiraghi, C. Dipl, F. Sangalli, S. Conti, A. Benigni, A. Remuzzi, and G. Remuzzi. Recellularization of well-preserved acellular kidney scaffold using embryonic stem cells. Tissue Eng. Part A 20:1486–1498, 2014.
Boruch, A. V., A. Nieponice, I. R. Qureshi, T. W. Gilbert, and S. F. Badylak. Constructive remodeling of biologic scaffolds is dependent on early exposure to physiologic bladder filling in a canine partial cystectomy model. J. Surg. Res. 161:217–225, 2010.
Brennan, E. P., X. Tang, A. M. Stewart-Akers, L. J. Gudas, and S. F. Badylak. Chemoattractant activity of degradation products of fetal and adult skin extracellular matrix for keratinocyte progenitor cells. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2:491–498, 2008.
Brightman, A. O., B. P. Rajwa, J. E. Sturgis, M. E. Mccallister, J. P. Robinson, and S. L. Voytik-Harbin. Time-lapse confocal reflection microscopy of collagen fibrillogenesis and extracellular matrix assembly in vitro. Biopolymers 54:222–234, 2000.
Browe, D. C., O. R. Mahon, P. J. Díaz-Payno, N. Cassidy, I. Dudurych, A. Dunne, C. T. Buckley, and D. J. Kelly. Glyoxal cross-linking of solubilised extracellular matrix to produce highly porous, elastic and chondro-permissive scaffolds for orthopaedic tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2019. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.36731.
Brown, B. N., C. A. Barnes, R. T. Kasick, R. Michel, T. W. Gilbert, D. Beer-Stolz, D. G. Castner, B. D. Ratner, and S. F. Badylak. Surface characterization of extracellular matrix scaffolds. Biomaterials 31:428–437, 2010.
Brown, B. N., J. M. Freund, L. Han, J. P. Rubin, J. E. Reing, E. M. Jeffries, M. T. Wolf, S. Tottey, C. A. Barnes, B. D. Ratner, and S. F. Badylak. Comparison of three methods for the derivation of a biologic scaffold composed of adipose tissue extracellular matrix. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 17:411–421, 2010.
Brown, B. N., R. Londono, S. Tottey, L. Zhang, K. A. Kukla, M. T. Wolf, K. A. Daly, J. E. Reing, and S. F. Badylak. Macrophage phenotype as a predictor of constructive remodeling following the implantation of biologically derived surgical mesh materials. Acta Biomater. 8:978–987, 2012.
Brown, B. N., J. E. Valentin, A. M. Stewart-Akers, G. P. McCabe, and S. F. Badylak. Macrophage phenotype and remodeling outcomes in response to biologic scaffolds with and without a cellular component. Biomaterials 30:1482–1491, 2009.
Burgkart, R., A. Tron, P. Prodinger, M. Culmes, J. Tuebel, M. Van Griensven, B. Saldamli, and A. Schmitt. Decellularized kidney matrix for perfused bone engineering. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 20:553–561, 2014.
Butler, C. E., N. K. Burns, K. T. Campbell, A. B. Mathur, M. V. Jaffari, and C. N. Rios. Comparison of cross-linked and non-cross-linked porcine acellular dermal matrices for ventral hernia repair. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 211:368–376, 2010.
Campbell, K. T., N. K. Burns, C. N. Rios, A. B. Mathur, and C. E. Butler. Human versus non-cross-linked porcine acellular dermal matrix used for ventral hernia repair: Comparison of in vivo fibrovascular remodeling and mechanical repair strength. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 127:2321–2332, 2011.
Carver, D. A., A. W. Kirkpatrick, T. L. Eberle, and C. G. Ball. Performance of biological mesh materials in abdominal wall reconstruction: Study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open 9:e024091, 2019.
Casali, D. M., R. M. Handleton, T. Shazly, and M. A. Matthews. A novel supercritical CO2-based decellularization method for maintaining scaffold hydration and mechanical properties. J. Supercrit. Fluids 131:72–81, 2018.
Cavallo, J. A., S. C. Greco, J. Liu, M. M. Frisella, C. R. Deeken, and B. D. Matthews. Remodeling characteristics and biomechanical properties of a crosslinked versus a non-crosslinked porcine dermis scaffolds in a porcine model of ventral hernia repair. Hernia 19:207–218, 2015.
Cebotari, S., I. Tudorache, T. Jaekel, A. Hilfiker, S. Dorfman, W. Ternes, A. Haverich, and A. Lichtenberg. Detergent decellularization of heart valves for tissue engineering: Toxicological effects of residual detergents on human endothelial cells. Artif. Organs 34:206–210, 2010.
Chen, L., Z. He, B. Chen, M. Yang, Y. Zhao, W. Sun, Z. Xiao, J. Zhang, and J. Dai. Loading of VEGF to the heparin cross-linked demineralized bone matrix improves vascularization of the scaffold. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 21:309–317, 2010.
Cheng, A. M. Y. W., M. A. Abbas, and T. Tejirian. Outcome of abdominal wall hernia repair with biologic mesh: Permacol versus Strattice. Am. Surg. 80:999–1002, 2014.
Cheng, N. C., B. T. Estes, H. A. Awad, and F. Guilak. Chondrogenic differentiation of adipose-derived adult stem cells by a porous scaffold derived from native articular cartilage extracellular matrix. Tissue Eng. Part A 15:231–241, 2009.
Cheng, N.-C., B. T. Estes, T.-H. Young, and F. Guilak. Genipin-crosslinked cartilage-derived matrix as a scaffold for human adipose-derived stem cell chondrogenesis. Tissue Eng. Part A 19:484–496, 2012.
Choi, J. S., H. J. Yang, B. S. Kim, J. D. Kim, J. Y. Kim, B. Yoo, K. Park, H. Y. Lee, and Y. W. Cho. Human extracellular matrix (ECM) powders for injectable cell delivery and adipose tissue engineering. J. Control. Release 139:2–7, 2009.
Christo, S. N., K. R. Diener, A. Bachhuka, K. Vasilev, and J. D. Hayball. Innate Immunity and Biomaterials at the Nexus : Friends or Foes. Biomed Res. Int. 2015:342304, 2015.
Consigliere, P., I. Polyzois, T. Sarkhel, R. Gupta, O. Levy, and A. A. Narvani. Preliminary results of a consecutive series of large & massive rotator cuff tears treated with arthroscopic rotator cuff repairs augmented with extracellular matrix. Arch. Bone Jt. Surg. 5:14–21, 2017.
Constantinou, C. D., and S. A. Jimenez. Structure of cDNAs encoding the triple-helical domain of murine alpha 2 (VI) collagen chain and comparison to human and chick homologues. Use of polymerase chain reaction and partially degenerate oligonucleotide for generation of novel cDNA clones. Matrix 11:1–9, 1991.
Cook, J. L., D. B. Fox, K. Kuroki, M. Jayo, and P. G. De Deyne. In vitro and in vivo comparison of five biomaterials used for orthopedic soft tissue augmentation. Am. J. Vet. Res. 69:148–156, 2008.
Cortiella, J., J. Niles, A. Cantu, A. Brettler, A. Pham, G. Vargas, S. Winston, J. Wang, S. Walls, and J. E. Nichols. Influence of acellular natural lung matrix on murine embryonic stem cell differentiation and tissue formation. Tissue Eng. Part A 16:2565–2580, 2010.
Costa, A., J. D. Naranjo, R. Londono, and S. F. Badylak. Biologic scaffolds. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 7:a025676, 2017.
Courtman, D. W., B. F. Errett, and G. J. Wilson. The role of crosslinking in modification of the immune response elicited against xenogenic vascular acellular matrices. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 55:576–586, 2001.
Crapo, P. M., T. W. Gilbert, and D. V. M. Badylak. An overview of tissue and whole organ decellularization processes. Biomaterials 32:3233–3243, 2011.
Crapo, P. M., C. J. Medberry, J. E. Reing, S. Tottey, Y. van der Merwe, K. E. Jones, and S. F. Badylak. Biologic scaffolds composed of central nervous system extracellular matrix. Biomaterials 33:3539–3547, 2012.
Daly, A. B., J. M. Wallis, Z. D. Borg, R. W. Bonvillain, B. Deng, B. A. Ballif, D. M. Jaworski, G. B. Allen, and D. J. Weiss. Initial binding and recellularization of decellularized mouse lung scaffolds with bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Tissue Eng. Part A 18:1–16, 2012.
Davis, G. E., K. J. Bayless, M. J. Davis, and G. A. Meininger. Regulation of tissue injury responses by the exposure of matricryptic sites within extracellular matrix molecules. Am. J. Pathol. 156:1489–1498, 2000.
De Waele, J., K. Reekmans, J. Daans, H. Goossens, Z. Berneman, and P. Ponsaerts. 3D culture of murine neural stem cells on decellularized mouse brain sections. Biomaterials 41:122–131, 2015.
Dearth, C. L., T. J. Keane, C. A. Carruthers, J. E. Reing, L. Huleihel, C. A. Ranallo, E. W. Kollar, and S. F. Badylak. The effect of terminal sterilization on the material properties and in vivo remodeling of a porcine dermal biologic scaffold. Acta Biomater. 33:78–87, 2016.
Deeken, C. R., L. Melman, E. D. Jenkins, S. C. Greco, M. M. Frisella, and B. D. Matthews. Histologic and biomechanical evaluation of crosslinked and non-crosslinked biologic meshes in a porcine model of ventral incisional hernia repair. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 212:880–888, 2011.
Dejardin, L. M., S. P. Arnoczky, B. J. Ewers, R. C. Haut, and R. B. Clarke. Tissue-engineered rotator cuff tendon using porcine small intestine submucosa: Histologic and mechanical evaluation in dogs. Am. J. Sports Med. 29:175–184, 2001.
del Barrio, J. L. A., M. Chiesa, N. Garagorri, N. Garcia-Urquia, J. Fernandez-Delgado, L. Bataille, A. Rodriguez, F. Arnalich-Montiel, T. Zarnowski, J. P. Á. de Toledo, J. L. Alio, and M. P. De Miguel. Acellular human corneal matrix sheets seeded with human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells integrate functionally in an experimental animal model. Exp. Eye Res. 132:91–100, 2015.
Dellarco, V. L., W. M. Generoso, G. A. Sega, J. R. Fowle, D. Jacobson-Kram, and H. E. Brockman. Review of the mutagenicity of ethylene oxide. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 16:85–103, 1990.
Dellavalle, A., G. Maroli, Azzoni E. CovarelloD, A. Innocenzi, L. Perani, S. Antonini, R. Sambasivan, S. Brunelli, S. Tajbakhsh, and G. Cossu. Pericytes resident in postnatal skeletal muscle differentiate into muscle fibres and generate satellite cells. Nat. Commun. 2:411–499, 2011.
Dequach, J. A., V. Mezzano, A. Miglani, S. Lange, G. M. Keller, and K. L. Christman. Simple and high yielding method for preparing tissue specific extracellular matrix coatings for cell culture. PLoS ONE 5:1–11, 2010.
Dequach, J. A., S. H. Yuan, L. S. B. Goldstein, and K. L. Christman. Decellularized porcine brain matrix for cell culture and tissue engineering scaffolds. Tissue Eng. Part A 17:2583–2592, 2011.
Duan, Y., Z. Liu, J. O’Neill, L. Q. Wan, D. O. Freytes, and G. Vunjak-Novakovic. Hybrid gel composed of native heart matrix and collagen induces cardiac differentiation of human embryonic stem cells without supplemental growth factors. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 4:605–615, 2011.
Dziki, J., S. Badylak, M. Yabroudi, B. Sicari, F. Ambrosio, K. Stearns, N. Turner, A. Wyse, M. L. Boninger, E. H. P. Brown, and J. P. Rubin. An acellular biologic scaffold treatment for volumetric muscle loss: Results of a 13-patient cohort study. NPJ Regen. Med. 1:16008, 2016.
Dziki, J. L., L. Huleihel, M. E. Scarritt, and S. F. Badylak. Extracellular matrix bioscaffolds as immunomodulatory biomaterials. Tissue Eng. Part A 23:1152–1159, 2017.
Dziki, J. L., B. M. Sicari, M. T. Wolf, M. C. Cramer, and S. F. Badylak. Immunomodulation and mobilization of progenitor cells by extracellular matrix bioscaffolds for volumetric muscle loss treatment. Tissue Eng. Part A 22:1129–1139, 2016.
Dziki, J. L., D. S. Wang, C. Pineda, B. M. Sicari, T. Rausch, and S. F. Badylak. Solubilized extracellular matrix bioscaffolds derived from diverse source tissues differentially influence macrophage phenotype. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 105:138–147, 2017.
Efraim, Y., B. Schoen, S. Zahran, T. Davidov, G. Vasilyev, L. Baruch, E. Zussman, and M. Machluf. 3D structure and processing methods direct the biological attributes of ECM-based cardiac scaffolds. Sci. Rep. 9:1–13, 2019.
Exposito, J. Y., M. D’Alessio, M. Solursh, and F. Ramirez. Sea urchin collagen evolutionarily homologous to vertebrate pro-α2(I) collagen. J. Biol. Chem. 267:15559–15562, 1992.
Faulk, D. M., C. A. Carruthers, H. J. Warner, C. R. Kramer, J. E. Reing, L. Zhang, A. D’Amore, and S. F. Badylak. The effect of detergents on the basement membrane complex of a biologic scaffold material. Acta Biomater. 10:183–193, 2014.
Faulk, D. M., J. D. Wildemann, and S. F. Badylak. Decellularization and cell seeding of whole liver biologic scaffolds composed of extracellular matrix. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 5:69–80, 2015.
Faust, A., A. Kandakatla, Y. Van Der Merwe, T. Ren, L. Huleihel, G. Hussey, J. D. Naranjo, S. Johnson, S. Badylak, and M. Steketee. Urinary bladder extracellular matrix hydrogels and matrix-bound vesicles differentially regulate central nervous system neuron viability and axon growth and branching. J. Biomater. Appl. 31:1277–1295, 2017.
Fishman, J. M., M. W. Lowdell, L. Urbani, T. Ansari, A. J. Burns, M. Turmaine, J. North, P. Sibbons, A. M. Seifalian, K. J. Wood, M. A. Birchall, and P. De Coppi. Immunomodulatory effect of a decellularized skeletal muscle scaffold in a discordant xenotransplantation model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 110:14360–14365, 2013.
Franz, S., S. Rammelt, D. Scharnweber, and J. C. Simon. Immune responses to implants—A review of the implications for the design of immunomodulatory biomaterials. Biomaterials 32:6692–6709, 2011.
French, K., A. Boopathy, J. DeQuach, L. Chingozha, H. Lu, K. L. Christman, and M. E. Davis. A naturally derived cardiac extracellular matrix enhances cardiac progenitor cell behavior in vitro. Acta Biomater. 8:4357–4364, 2012.
Freytes, D. O., S. F. Badylak, T. J. Webster, L. A. Geddes, and A. E. Rundell. Biaxial strength of multilaminated extracellular matrix scaffolds. Biomaterials 25:2353–2361, 2004.
Freytes, D. O., J. Martin, S. S. Velankar, A. S. Lee, and S. F. Badylak. Preparation and rheological characterization of a gel form of the porcine urinary bladder matrix. Biomaterials 29:1630–1637, 2008.
Freytes, D. O., J. D. O’Neill, Y. Duan-Arnold, E. Wrona, and G. Vunjak-Novakovic. Native cardiac extracellular matrix hydrogels for cultivation of human stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Methods Mol Biol 1181:69–81, 2014.
Freytes, D. O., A. E. Rundell, J. Vande Geest, D. A. Vorp, T. J. Webster, and S. F. Badylak. Analytically derived material properties of multilaminated extracellular matrix devices using the ball-burst test. Biomaterials 26:5518–5531, 2005.
Freytes, D. O., R. M. Stoner, and S. F. Badylak. Uniaxial and biaxial properties of terminally sterilized porcine urinary bladder matrix scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B. Appl. Biomater. 84B:408–414, 2008.
Freytes, D. O., R. S. Tullius, J. E. Valentin, A. M. Stewart-Akers, and S. F. Badylak. Hydrated versus lyophilized forms of porcine extracellular matrix derived from the urinary bladder. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 87:862–872, 2008.
Gaetani, R., C. Yin, N. Srikumar, R. Braden, P. A. Doevendans, J. P. G. Sluijter, and K. L. Christman. Cardiac-derived extracellular matrix enhances cardiogenic properties of human cardiac progenitor cells. Cell Transplant. 25:1653–1663, 2016.
Geiger, S. E., O. A. Deigni, J. T. Watson, and B. A. Kraemer. Management of open distal lower extremity wounds with exposed tendons using porcine urinary bladder matrix. Wounds: A Compend. Clin. Res. Pract. 28:306–316, 2016.
Gilbert, T. W., J. Freund, and S. F. Badylak. Quantification of DNA in biologic scaffold materials. J. Surg. Res. 152:135–139, 2009.
Gilbert, T. W., A. Nieponice, A. R. Spievack, J. Holcomb, S. Gilbert, and S. F. Badylak. Repair of the thoracic wall with an extracellular matrix scaffold in a canine model. J. Surg. Res. 147:61–67, 2008.
Gilbert, T. W., A. M. Stewart-Akers, A. Simmons-Byrd, and S. F. Badylak. Degradation and remodeling of small intestinal submucosa in canine Achilles tendon repair. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 89:621–630, 2007.
Gilbert, T. W., D. B. Stolz, F. Biancaniello, A. Simmons-Byrd, and S. F. Badylak. Production and characterization of ECM powder: Implications for tissue engineering applications. Biomaterials 26:1431–1435, 2005.
Gilot, G. J., A. M. Alvarez-Pinzon, L. Barcksdale, D. Westerdahl, M. Krill, and E. Peck. Outcome of large to massive rotator cuff tears repaired with and without extracellular matrix augmentation: A prospective comparative study. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 31:1459–1465, 2015.
Gilpin, S. E., X. Ren, T. Okamoto, J. P. Guyette, H. Mou, J. Rajagopal, D. J. Mathisen, J. P. Vacanti, and H. C. Ott. Enhanced lung epithelial specification of human induced pluripotent stem cells on decellularized lung matrix. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 98:1721–1729, 2014.
Gilpin, A., and Y. Yang. Decellularization strategies for regenerative medicine: From processing techniques to applications. Biomed Res. Int. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9831534.
Glasberg, S. B., and D. Light. AlloDerm and Strattice in breast reconstruction: A comparison and techniques for optimizing outcomes. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 129:1223–1233, 2012.
Godin, L. M., B. J. Sandri, D. E. Wagner, C. M. Meyer, A. P. Price, I. Akinnola, D. J. Weiss, and A. P. M. Panoskaltsis-Mortari. Decreased laminin expression by human lung epithelial cells and fibroblasts cultured in acellular lung scaffolds from aged mice. PLoS ONE 11:1–17, 2016.
Gordon, S., and P. R. Taylor. Monocyte and macrophage heterogeneity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 5:953–964, 2005.
Gouk, S.-S., T.-M. Lim, S.-H. Teoh, and W. Q. Sun. Alterations of human acellular tissue matrix by gamma irradiation: Histology, biomechanical property, stability, in vitro cell repopulation, and remodeling. J Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 84B:205–217, 2008.
Guler, S., B. Aslan, P. Hosseinian, and H. M. Aydin. Supercritical carbon dioxide-assisted decellularization of aorta and cornea. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 23:540–547, 2017.
Harth, K. C., A. M. Broome, M. R. Jacobs, J. A. Blatnik, F. Zeinali, S. Bajaksouzian, and M. J. Rosen. Bacterial clearance of biologic grafts used in hernia repair: An experimental study. Surg. Endosc. 25:2224–2229, 2011.
Hashimoto, Y., S. Funamoto, T. Kimura, K. Nam, T. Fujisato, and A. Kishida. The effect of decellularized bone/bone marrow produced by high-hydrostatic pressurization on the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials 32:7060–7067, 2011.
Haykal, S., Y. Zhou, P. Marcus, M. Salna, T. Machuca, S. O. P. Hofer, and T. K. Waddell. The effect of decellularization of tracheal allografts on leukocyte infiltration and of recellularization on regulatory T cell recruitment. Biomaterials 34:5821–5832, 2013.
Hennessy, R. S., S. Jana, B. J. Tefft, M. R. Helder, M. D. Young, R. R. Hennessy, N. J. Stoyles, and A. Lerman. Supercritical carbon dioxide–based sterilization of decellularized heart valves. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2:71–84, 2017.
Hirsh, S. L., D. R. McKenzie, N. J. Nosworthy, J. A. Denman, O. U. Sezerman, and M. M. M. Bilek. The Vroman effect: Competitive protein exchange with dynamic multilayer protein aggregates. Coll. Surf. B Biointerfaces 103:395–404, 2013.
HO, K. L., V. M. N. Witte, and E. T. Bird. 8-ply small intestinal submucosa tension-free sling: Spectrum of postoperative inflammation. J. Urol. 171:268–271, 2004.
Hodde, J., A. Janis, D. Ernst, D. Zopf, D. Sherman, and C. Johnson. Effects of sterilization on an extracellular matrix scaffold: Part I. Composition and matrix architecture. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 18:537–543, 2007.
Hodde, J., A. Janis, and M. Hiles. Effects of sterilization on an extracellular matrix scaffold: Part II. Bioactivity and matrix interaction. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 18:545–550, 2007.
Hoganson, D. M., A. M. Meppelink, C. J. Hinkel, S. M. Goldman, X.-H. Liu, R. M. Nunley, J. P. Gaut, and J. P. Vacanti. Differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on decellularized extracellular matrix materials. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 102:2875–2883, 2014.
Hong, X., Y. Yuan, X. Sun, M. Zhou, G. Guo, Q. Zhang, J. Hescheler, and J. Xi. Skeletal extracellular matrix supports cardiac differentiation of embryonic stem cells: A potential scaffold for engineered cardiac tissue. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 45:319–331, 2018.
Hoppo, T., S. F. Badylak, and B. A. Jobe. A novel esophageal-preserving approach to treat high-grade dysplasia and superficial adenocarcinoma in the presence of chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease. World J. Surg. 36:2390–2393, 2012.
Huang, Y. H., F. W. Tseng, W. H. Chang, I. C. Peng, D. J. Hsieh, S. W. Wu, and M. L. Yeh. Preparation of acellular scaffold for corneal tissue engineering by supercritical carbon dioxide extraction technology. Acta Biomater. 58:238–243, 2017.
Huleihel, L., J. G. Bartolacci, J. L. Dziki, T. Vorobyov, B. Arnold, M. E. Scarritt, C. Pineda Molina, S. T. LoPresti, B. N. Brown, J. D. Naranjo, and S. F. Badylak. Matrix-bound nanovesicles recapitulate extracellular matrix effects on macrophage phenotype. Tissue Eng. Part A 23:1283–1294, 2017.
Huleihel, L., J. L. Dziki, J. G. Bartolacci, T. Rausch, M. E. Scarritt, M. C. Cramer, T. Vorobyov, S. T. LoPresti, I. T. Swineheart, L. J. White, B. N. Brown, and S. F. Badylak. Macrophage phenotype in response to ECM bioscaffolds. Semin. Immunol. 29:2–13, 2017.
Huleihel, L., G. S. Hussey, J. D. Naranjo, L. Zhang, J. L. Dziki, N. J. Turner, D. B. Stolz, and S. F. Badylak. Matrix-bound nanovesicles within ECM bioscaffolds. Sci. Adv. 2:e1600502, 2016.
Hutter, H., B. E. Vogel, J. D. Plenefisch, C. R. Norris, R. B. Proenca, J. Spieth, C. Guo, S. Mastwal, X. Zhu, J. Scheel, and E. M. Hedgecock. Conservation and novelty in the evolution of cell adhesion and extracellular matrix genes. Science (80-) 287:989–1010, 2000.
Hynes, R. O. The evolution of metazoan extracellular matrix. J. Cell Biol. 196:671–679, 2012.
Iozzo, R. V. Perlecan: A gem of a proteoglycan. Matrix Biol. 14:203–208, 1994.
ISO 13408-1. Aseptic processing of health care products — Part 1: General requirements., 2008.
ISO 22442-1. Medical devices utilizing animal tissues and their derivatives — Part 1: Application of risk management., 2015.
Jackson, D. W., E. S. Grood, P. Wilcox, D. L. Butler, T. M. Simon, and J. P. Holden. The effects of processing techniques on the mechanical properties of bone-anterior cruciate ligament-bone allografts. An experimental study in goats. Am. J. Sports Med. 16:101–105, 1988.
Jackson, D. W., G. E. Windler, and T. M. Simon. Intraarticular reaction associated with the use of freeze-dried, ethylene oxide-sterilized bone-patella tendon-bone allografts in the reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament. Am. J. Sports Med. 18:1–11, 1990.
Jang, J., T. G. Kim, B. S. Kim, S. W. Kim, S. M. Kwon, and D. W. Cho. Tailoring mechanical properties of decellularized extracellular matrix bioink by vitamin B2-induced photo-crosslinking. Acta Biomater. 33:88–95, 2016.
Ji, R., N. Zhang, N. You, Q. Li, W. Liu, N. Jiang, J. Liu, H. Zhang, D. Wang, K. Tao, and K. Dou. The differentiation of MSCs into functional hepatocyte-like cells in a liver biomatrix scaffold and their transplantation into liver-fibrotic mice. Biomaterials 33:8995–9008, 2012.
John, T. T., N. Aggarwal, A. K. Singla, and R. A. Santucci. Intense inflammatory reaction with porcine small intestine submucosa pubovaginal sling or tape for stress urinary incontinence. Urology 72:1036–1039, 2008.
Johnson, T. D., R. L. Braden, and K. L. Christman. Injectable ECM scaffolds for cardiac repair. Methods Mol. Biol. 1181:109–120, 2014.
Johnson, T. D., J. A. Dequach, R. Gaetani, J. Ungerleider, D. Elhag, V. Nigam, A. Behfar, and K. L. Christman. Human versus porcine tissue sourcing for an injectable myocardial matrix hydrogel. Biomater. Sci. 29:13–17, 2014.
Johnson, T. D., S. Y. Lin, and K. L. Christman. Tailoring material properties of a nanofibrous extracellular matrix derived hydrogel. Nanotechnology 22:494015, 2011.
Kaufmann, R., A. P. Jairam, I. M. Mulder, Z. Wu, J. Verhelst, S. Vennix, L. J. X. Giesen, M. C. Clahsen-van Groningen, and J. Jeekel. Lange JF (2019) Non-cross-linked collagen mesh performs best in a physiologic, noncontaminated rat model. Surg. Innov. 26:302–311, 2019.
Kaufmann, R., A. P. Jairam, I. M. Mulder, Z. Wu, J. Verhelst, S. Vennix, L. J. X. Giesen, M. C. Clahsen-van Groningen, J. Jeekel, and J. F. Lange. Characteristics of different mesh types for abdominal wall repair in an experimental model of peritonitis. Br. J. Surg. 104:1884–1893, 2017.
Keane, T. J., and S. F. Badylak. The host response to allogeneic and xenogeneic biological scaffold materials. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 9:504–511, 2015.
Keane, T. J., A. DeWard, R. Londono, L. T. Saldin, A. A. Castleton, L. Carey, A. Nieponice, E. Lagasse, and S. F. Badylak. Tissue-specific effects of esophageal extracellular matrix. Tissue Eng. Part A 21:2293–2300, 2015.
Keane, T. J., J. Dziki, E. Sobieski, A. Smoulder, A. Castleton, N. Turne, L. J. White, and S. F. Badylak. Restoring mucosal barrier function and modifying macrophage phenotype with an extracellular matrix hydrogel: Potential therapy for ulcerative colitis. J. Crohn’s Colitis 11:360–368, 2017.
Keane, T. J., R. Londono, N. J. Turner, and S. F. Badylak. Consequences of ineffective decellularization of biologic scaffolds on the host response. Biomaterials 33:1771–1781, 2012.
Keane, T. J., I. T. Swinehart, and S. F. Badylak. Methods of tissue decellularization used for preparation of biologic scaffolds and in vivo relevance. Methods 84:25–34, 2015.
Kelly, D. J., A. B. Rosen, A. J. T. Schuldt, P. V. Kochupura, S. V. Doronin, I. A. Potapova, E. U. Azeloglu, S. F. Badylak, P. R. Brink, I. S. Cohen, and G. R. Gaudette. Increased myocyte content and mechanical function within a tissue-engineered myocardial patch following implantation. Tissue Eng. Part A 15:2189–2201, 2009.
Kimmel, H., M. Rahn, and T. W. Gilbert. The clinical effectiveness in wound healing with extracellular matrix derived from porcine urinary bladder matrix: A case series on severe chronic wounds. J. Am. Col. Certif. Wound Spec. 2:55–59, 2010.
Knoll, L. D. Use of small intestinal submucosa graft for the surgical management of Peyronie’s disease. J. Urol. 178:2474–2478, 2007.
Kochupura, P. V., E. U. Azeloglu, D. J. Kelly, S. V. Doronin, S. F. Badylak, I. B. Krukenkamp, I. S. Cohen, and G. R. Gaudette. Tissue-engineered myocardial patch derived from extracellular matrix provides regional mechanical function. Circulation 112:144–149, 2005.
Koci, Z., K. Vyborny, J. Dubisova, I. Vackova, A. Jager, O. Lunov, K. Jirakova, and S. Kubinova. Extracellular matrix hydrogel derived from human umbilical cord as a scaffold for neural tissue repair and its comparison with extracellular matrix from porcine tissues. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 23:333–345, 2017.
Kramer, J. Extracellular matrix. In: C. elegans II, edited by D. Riddle, T. Blumenthal, and B. Meyer. Boston: Springer, 1997.
Kropp, B. P., B. L. Eppley, C. D. Prevel, M. K. Rippy, R. C. Harruff, S. F. Badylak, M. C. Adams, R. C. Rink, and M. A. Keating. Experimental assessment of small intestinal submucosa as a bladder wall substitute. Urology 46:396–400, 1995.
Kulig, K. M., X. Luo, E. B. Finkelstein, X. H. Liu, S. M. Goldman, C. A. Sundback, J. P. Vacanti, and C. M. Neville. Biologic properties of surgical scaffold materials derived from dermal ECM. Biomaterials 34:5776–5784, 2013.
Lee, J. S., J. Shin, H. M. Park, Y. G. Kim, B. G. Kim, J. W. Oh, and S. W. Cho. Liver extracellular matrix providing dual functions of two-dimensional substrate coating and three-dimensional injectable hydrogel platform for liver tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules 15:206–218, 2014.
Liang, R., G. Yang, K. E. Kim, A. D’Amore, A. N. Pickering, C. Zhang, and S. L.-Y. Woo. Positive effects of an extracellular matrix hydrogel on rat anterior cruciate ligament fibroblast proliferation and collagen mRNA expression. J. Orthop. Transl. 3:114–122, 2015.
Liao, J., E. M. Joyce, and M. S. Sacks. Effects of decellularization on the mechanical and structural properties of the porcine aortic valve leaflet. Biomaterials 29:1065–1074, 2008.
Liu, C. J., S. D. Dib-Hajj, and S. G. Waxman. Fibroblast growth factor homologous factor 1B binds to the C terminus of the tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channel rNav1.9a (NaN). J. Biol. Chem. 276:18925–18933, 2001.
Liu, X., N. Li, D. Gong, C. Xia, and Z. Xu. Comparison of detergent-based decellularization protocols for the removal of antigenic cellular components in porcine aortic valve. Xenotransplantation 25:1–13, 2018.
Liu, Z., R. Tang, Z. Zhou, Z. Song, H. Wang, and Y. Gu. Comparison of two porcine-derived materials for repairing abdominal wall defects in rats. PLoS ONE 6:e20520, 2011.
Londono, R., J. L. Dziki, E. Haljasmaa, N. J. Turner, C. A. Leifer, and S. F. Badylak. The effect of cell debris within biologic scaffolds upon the macrophage response. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 105:2109–2118, 2017.
Loneker, A. E., D. M. Faulk, G. S. Hussey, A. D’Amore, and S. F. Badylak. Solubilized liver extracellular matrix maintains primary rat hepatocyte phenotype in-vitro. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 104:957–965, 2016.
Longaker, M. T., E. S. Chu, N. S. Adzick, M. Stern, M. R. Harrison, and R. Stern. Studies in fetal wound healing. V. A prolonged presence of hyaluronic acid characterizes fetal wound fluid. Ann. Surg. 213:292–296, 1991.
Longaker, M. T., D. J. Whitby, M. W. J. Ferguson, M. R. Harrison, T. M. Crombleholme, J. C. Langer, K. C. Cochrum, E. D. Verrier, and R. Stern. Studies in fetal wound healing: III. Early deposition of fibronectin distinguishes fetal from adult wound healing. J. Pediatr. Surg. 24:799–805, 1989.
LoPresti, S. T., and B. N. Brown. Effect of source animal age upon macrophage response to extracellular matrix biomaterials. J. Immunol. Regen. Med. 1:57–66, 2018.
Lovvorn, III, H. N., D. T. Cheung, M. E. Nimni, N. Perelman, J. M. Estes, and N. S. Adzick. Relative distribution and crosslinking of collagen distinguish fetal from adult sheep wound repair. J. Pediatr. Surg. 34:218–223, 1999.
Lu, Q., M. Li, Y. Zou, and T. Cao. Delivery of basic fibroblast growth factors from heparinized decellularized adipose tissue stimulates potent de novo adipogenesis. J. Control. Release 174:43–50, 2014.
Lumpkins, S. B., N. Pierre, and P. S. McFetridge. A mechanical evaluation of three decellularization methods in the design of a xenogeneic scaffold for tissue engineering the temporomandibular joint disc. Acta Biomater. 4:808–816, 2008.
Ma, B., X. Wang, C. Wu, and J. Chang. Crosslinking strategies for preparation of extracellular matrix-derived cardiovascular scaffolds. Regen. Biomater. 1:81–89, 2014.
Manji, R. A., L. F. Zhu, N. K. Nijjar, D. C. Rayner, G. S. Korbutt, T. A. Churchill, R. V. Rajotte, A. Koshal, and D. B. Ross. Glutaraldehyde-fixed bioprosthetic heart valve conduits calcify and fail from xenograft rejection. Circulation 114:318–327, 2006.
Mantovani, A., S. K. Biswas, M. R. Galdiero, A. Sica, and M. Locati. Macrophage plasticity and polarization in tissue repair and remodelling. J. Pathol. 229:176–185, 2013.
Mantovani, A., A. Sica, S. Sozzani, P. Allavena, A. Vecchi, and M. Locati. The chemokine system in diverse forms of macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol. 25:677–686, 2004.
Mase, V., J. Hsu, S. Wolf, J. Wenke, D. Baer, J. Owens, S. Badylak, and T. Walters. Clinical application of an acellular biologic scaffold for surgical repair of a large, traumatic quadriceps femoris muscle defect. Orthopedics 33:511, 2010.
Matuska, A. M., and P. S. McFetridge. The effect of terminal sterilization on structural and biophysical properties of a decellularized collagen-based scaffold; Implications for stem cell adhesion. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 103:397–406, 2015.
Medberry, C. J., P. M. Crapo, B. F. Siu, C. A. Carruthers, M. T. Wolf, S. P. Nagarkar, V. Agrawal, K. E. Jones, J. Kelly, S. A. Johnson, S. S. Velankar, S. C. Watkins, M. Modo, and S. F. Badylak. Hydrogels derived from central nervous system extracellular matrix. Biomaterials 34:1033–1040, 2013.
Melman, L., E. D. Jenkins, N. A. Hamilton, L. C. Bender, M. D. Brodt, C. R. Deeken, S. C. Greco, M. M. Frisella, and B. D. Matthews. Early biocompatibility of crosslinked and non-crosslinked biologic meshes in a porcine model of ventral hernia repair. Hernia 15:157–164, 2011.
Meng, F. W., P. F. Slivka, C. L. Dearth, and S. F. Badylak. Solubilized extracellular matrix from brain and urinary bladder elicits distinct functional and phenotypic responses in macrophages. Biomaterials 46:131–140, 2015.
Mercuri, J. J., S. Patnaik, G. Dion, S. S. Gill, J. Liao, and D. T. Simionescu. Regenerative potential of decellularized porcine nucleus pulposus hydrogel scaffolds: Stem cell differentiation, matrix remodeling, and biocompatibility studies. Tissue Eng. Part A 19:952–966, 2013.
Merguerian, P. A., P. P. Reddy, D. J. Barrieras, G. J. Wilson, K. Woodhouse, D. J. Bagli, G. A. McLorie, and A. E. Khoury. Acellular bladder matrix allografts in the regeneration of functional bladders: Evaluation of large-segment (> 24 cm) substitution in a porcine model. BJU Int. 85:894–898, 2000.
Mestak, O., Z. Spurkova, K. Benkova, P. Vesely, V. Hromadkova, J. Miletin, R. Juzek, J. Mestak, M. Molitor, and A. Sukop. Comparison of cross-linked and non-cross-linked acellular porcine dermal scaffolds for long-term full-thickness hernia repair in a small animal model. Eplasty 14:172–183, 2014.
Meyer, S. R., B. Chiu, T. A. Churchill, L. Zhu, J. R. T. Lakey, and D. B. Ross. Comparison of aortic valve allograft decellularization techniques in the rat. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 79A:254–262, 2006.
Mills, C. D., K. Kincaid, J. M. Alt, M. J. Heilman, and A. M. Hill. M-1/M-2 macrophages and the Th1/Th2 paradigm. J. Immunol. 164:6166–6173, 2000.
Miyazaki, K., and T. Maruyama. Partial regeneration and reconstruction of the rat uterus through recellularization of a decellularized uterine matrix. Biomaterials 35:8791–8800, 2014.
Mora-Solano, C., and J. H. Collier. Engaging adaptive immunity with biomaterials. J. Mater. Chem. B 2:2409–2421, 2014.
Moreau, M. F., Y. Gallois, M. F. Baslé, and D. Chappard. Gamma irradiation of human bone allografts alters medullary lipids and releases toxic compounds for osteoblast-like cells. Biomaterials 21:369–376, 2000.
Morris, A. H., J. Chang, and T. R. Kyriakides. Inadequate processing of decellularized dermal matrix reduces cell viability in vitro and increases apoptosis and acute inflammation in vivo. Biores. Open Access 5(1):177–187, 2016.
Mosmann, T. R., and S. Sad. The expanding universe of T-cell subsets: Th1, Th2 and more. Immunol. Today 17:138–146, 1996.
Mulder, I. M., E. B. Deerenberg, W. A. Bemelman, J. Jeekel, and J. F. Lange. Infection susceptibility of crosslinked and non-crosslinked biological meshes in an experimental contaminated environment. Am. J. Surg. 210:159–166, 2015.
Nakatsu, H., T. Ueno, A. Oga, M. Nakao, T. Nishimura, S. Kobayashi, and M. Oka. Influence of mesenchymal stem cells on stomach tissue engineering using small intestinal submucosa. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 9:296–304, 2015.
Nakayama, K. H., C. C. I. Lee, C. A. Batchelder, and A. F. Tarantal. Tissue specificity of decellularized rhesus monkey kidney and lung scaffolds. PLoS ONE 8:e64134, 2013.
Naso, F., A. Gandaglia, T. Bottio, V. Tarzia, M. B. Nottle, A. J. F. d’Apice, P. J. Cowan, E. Cozzi, C. Galli, I. Lagutina, G. Lazzari, L. Iop, M. Spina, and G. Gerosa. First quantification of alpha-Gal epitope in current glutaraldehyde-fixed heart valve bioprostheses. Xenotransplantation 20:252–261, 2013.
Navarro-Tableros, V., M. B. Herrera Sanchez, F. Figliolini, R. Romagnoli, C. Tetta, and G. Camussi. Recellularization of rat liver scaffolds by human liver stem cells. Tissue Eng. Part A 21:1929–1939, 2015.
Ngo, M. D., H. M. Aberman, M. L. Hawes, B. Choi, and A. A. Gertzman. Evaluation of human acellular dermis versus porcine acellular dermis in an in vivo model for incisional hernia repair. Cell Tissue Bank. 12:135–145, 2011.
Nieponice, A., F. F. Ciotola, F. Nachman, B. A. Jobe, T. Hoppo, R. Londono, S. Badylak, and A. E. Badaloni. Patch esophagoplasty: Esophageal reconstruction using biologic scaffolds. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 97:283–288, 2014.
Nieponice, A., K. McGrath, I. Qureshi, E. J. Beckman, J. D. Luketich, T. W. Gilbert, and S. F. Badylak. An extracellular matrix scaffold for esophageal stricture prevention after circumferential EMR. Gastrointest. Endosc. 69:289–296, 2009.
Novitsky, Y. W., S. B. Orenstein, and D. L. Kreutzer. Comparative analysis of histopathologic responses to implanted porcine biologic meshes. Hernia 18:713–721, 2014.
O’Neill, J. D., D. O. Freytes, A. Anandappa, J. A. Oliver, and G. Vunjak-Novakovic. The regulation of growth and metabolism of kidney stem cell with regional specificity using extracellular matrix derived from kidney. Biomaterials 34:1–7, 2013.
Okumura, M., R. J. Matthews, B. Robb, G. W. Litman, P. Bork, and M. L. Thomas. Comparison of CD45 extracellular domain sequences from divergent vertebrate species suggests the conservation of three fibronectin type III domains. J. Immunol. 157:1569–1575, 1996.
Omae, H., C. Zhao, L. S. Yu, K. N. An, and P. C. Amadio. Multilayer tendon slices seeded with bone marrow stromal cells: A novel composite for tendon engineering. J. Orthop. Res. 27:937–942, 2009.
Oswal, D., S. Korossis, S. Mirsadraee, H. Wilcox, and K. Watterson. Biomechanical characterization of decellularized and cross-linked bovine pericardium. J. Heart Valve Dis. 16:165–174, 2007.
Pashos, N. C., M. E. Scarritt, Z. R. Eagle, J. M. Gimble, A. E. Chaffin, and B. A. Bunnell. Characterization of an acellular scaffold for a tissue engineering approach to the nipple-areolar complex reconstruction. Cells Tissues Organs 203:183–193, 2017.
Pati, F., J. Jang, D.-H. Ha, S. Won Kim, J.-W. Rhie, J.-H. Shim, D.-H. Kim, and D.-W. Cho. Printing three-dimensional tissue analogues with decellularized extracellular matrix bioink. Nat. Commun. 5:3935, 2014.
Patil, P. B., P. B. Chogue, V. K. Kumar, S. Almstrom, H. Backdahl, D. Banerjee, G. Hernlenius, M. Olausson, and S. Sumitran-Holgersson. Recellularization of acellular human small intestine using bone marrow stem cells. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2:307–315, 2013.
Perniconi, B., D. Coletti, P. Aulino, A. Costa, P. Aprile, L. Santacroce, E. Chiaravalloti, L. Coquelin, N. Chevallier, L. Teodori, S. Adamo, M. Marrelli, and M. Tatullo. Muscle acellular scaffold as a biomaterial: Effects on C2C12 cell differentiation and interaction with the murine host environment. Front. Physiol. 5:1–13, 2014.
Perniconi, B., A. Costa, P. Aulino, L. Teodori, S. Adamo, and D. Coletti. The pro-myogenic environment provided by whole organ scale acellular scaffolds from skeletal muscle. Biomaterials 32:7870–7882, 2011.
Price, A. P., K. A. England, A. M. Matson, B. R. Blazar, and A. Panoskaltsis-Mortari. Development of a decellularized lung bioreactor system for bioengineering the lung: The matrix reloaded. Tissue Eng. Part A 16:2581–2591, 2010.
Quarti, A., S. Nardone, M. Colaneri, G. Santoro, and M. Pozzi. Preliminary experience in the use of an extracellular matrix to repair congenital heart diseases. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 13:569–572, 2011.
Rajabi-Zeleti, S., S. Jalili-Firoozinezhad, M. Azarnia, F. Khayyatan, S. Vahdat, S. Nikeghbalian, A. Khademhosseini, H. Baharvand, and N. Aghdami. The behavior of cardiac progenitor cells on macroporous pericardium-derived scaffolds. Biomaterials 35:970–982, 2014.
Reddy, P. P., D. J. Barrieras, G. Wilson, D. J. Bagli, G. A. McLorie, A. E. Khoury, and P. A. Merguerian. Regeneration of functional bladder substitutes using large segment acellular matrix allografts in a porcine model. J. Urol. 164:936–941, 2000.
Reing, J. E., B. N. Brown, K. A. Daly, J. M. Freund, T. W. Gilbert, S. X. Hsiong, A. Huber, K. E. Kullas, S. Tottey, M. T. Wolf, and S. F. Badylak. The effects of processing methods upon mechanical and biologic properties of porcine dermal extracellular matrix scaffolds. Biomaterials 31:8626–8633, 2010.
Reing, J. E., L. Zhang, J. Myers-Irvin, K. E. Cordero, D. O. Freytes, E. Heber-Katz, K. Bedelbaeva, D. McIntosh, A. Dewilde, S. J. Braunhut, and S. F. Badylak. Degradation products of extracellular matrix affect cell migration and proliferation. Tissue Eng. Part A 15:605–614, 2009.
Rieder, E., M. T. Kasimir, G. Silberhumer, G. Seebacher, E. Wolner, P. Simon, and G. Weigel. Decellularization protocols of porcine heart valves differ importantly in efficiency of cell removal and susceptibility of the matrix to recellularization with human vascular cells. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 127:399–405, 2004.
Rommer, E. A., M. Peric, and A. Wong. Urinary bladder matrix for the treatment of recalcitrant nonhealing radiation wounds. Adv. Skin Wound Care 26:450–455, 2013.
Rosario, D. J., G. C. Reilly, E. A. Salah, M. Glover, A. J. Bullock, and S. MacNeil. Decellularization and sterilization of porcine urinary bladder matrix for tissue engineering in the lower urinary tract. Regen. Med. 3:145–156, 2008.
Ross, E. A., M. J. Williams, T. Hamazaki, N. Terada, W. L. Clapp, C. Adin, G. W. Ellison, M. Jorgensen, and C. D. Batich. Embryonic stem cells proliferate and differentiate when seeded into kidney scaffolds. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 20:2338–2347, 2009.
Sadtler, K., B. W. Allen, K. Estrellas, F. Housseau, D. M. Pardoll, and J. H. Elisseeff. The scaffold immune microenvironment: Biomaterial-mediated immune polarization in traumatic and nontraumatic applications. Tissue Eng. Part A 23:1044–1053, 2017.
Sadtler, K., K. Estrellas, B. W. Allen, M. T. Wolf, H. Fan, A. J. Tam, C. H. Patel, B. S. Luber, H. Wang, K. R. Wagner, J. D. Powell, F. Housseau, D. M. Pardoll, and J. H. Elisseeff. Developing a pro-regenerative biomaterial scaffold microenvironment requires T helper 2 cells. Science 352:366–370, 2016.
Sadtler, K., M. T. Wolf, S. Ganguly, C. A. Moad, L. Chung, S. Majumdar, F. Housseau, D. M. Pardoll, and J. H. Elisseeff. Divergent immune responses to synthetic and biological scaffolds. Biomaterials 192:405–415, 2019.
Saldin, L. T., M. C. Cramer, S. S. Velankar, L. J. White, and S. F. Badylak. Extracellular matrix hydrogels from decellularized tissues: Structure and function. Acta Biomater. 49:1–15, 2017.
Sandor, M., H. Xu, J. Connor, J. Lombardi, J. R. Harper, R. P. Silverman, and D. J. McQuillan. Host response to implanted porcine-derived biologic materials in a primate model of abdominal wall repair. Tissue Eng. Part A 14:2021–2031, 2008.
Santoso, E. G., K. Yoshida, Y. Hirota, M. Aizawa, O. Yoshino, A. Kishida, Y. Osuga, S. Saito, T. Ushida, and K. S. Furukawa. Application of detergents or high hydrostatic pressure as decellularization processes in uterine tissues and their subsequent effects on in vivo uterine regeneration in murine models. PLoS ONE 9:e103201, 2014.
Sarathchandra, P., R. T. Smolenski, A. H. Y. Yuen, A. H. Chester, S. Goldstein, A. E. Heacox, M. H. Yacoub, and P. M. Taylor. Impact of γ-irradiation on extracellular matrix of porcine pulmonary valves. J. Surg. Res. 176:376–385, 2012.
Sasikumar, S., S. Chameettachal, B. Cromer, F. Pati, and P. Kingshott. Decellularized extracellular matrix hydrogels– cell behavior as function of matrix stiffness. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 10:123–133, 2019.
Sawada, K., D. Terada, T. Yamaoka, S. Kitamura, and T. Fujisato. Cell removal with supercritical carbon dioxide for acellular artificial tissue. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 83:943–949, 2008.
Sawai, T., N. Usui, K. Sando, Y. Fukui, S. Kamata, A. Okada, N. Taniguchi, N. Itano, and K. Kimata. Hyaluronic acid of wound fluid in adult and fetal rabbits. J. Pediatr. Surg. 32:41–43, 1997.
Schoen, F. J., and R. J. Levy. Calcification of tissue heart valve substitutes: Progress toward understanding and prevention. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 79:1072–1080, 2005.
Scholl, F. G., M. M. Boucek, K.-C. Chan, L. Valdes-Cruz, and R. Perryman. Preliminary experience with cardiac reconstruction using decellularized porcine extracellular matrix scaffold: Human applications in congenital heart disease. World J. Pediatr. Congenit. Hear. Surg. 1:132–136, 2010.
Sclamberg, S. G., J. E. Tibone, J. M. Itamura, and S. Kasraeian. Six-month magnetic resonance imaging follow-up of large and massive rotator cuff repairs reinforced with porcine small intestinal submucosa. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 13:538–541, 2004.
Sellaro, T. L., A. K. Ravindra, D. B. Stolz, and S. F. Badylak. Maintenance of hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cell phenotype in vitro using organ-specific extracellular matrix scaffolds. Tissue Eng. 13:2301–2310, 2007.
Seo, Y., Y. Jung, and S. H. Kim. Decellularized heart ECM hydrogel using supercritical carbon dioxide for improved angiogenesis. Acta Biomater. 67:270–281, 2018.
Shah, M., P. Kc, K. M. Copeland, J. Liao, and G. Zhang. A thin layer of decellularized porcine myocardium for cell delivery. Sci. Rep. 8:1–11, 2018.
Shah, B. C., M. M. Tiwari, M. R. Goede, M. J. Eichler, R. R. Hollins, C. L. McBride, J. S. Thompson, and D. Oleynikov. Not all biologics are equal!. Hernia 15:165–171, 2011.
Shamis, Y., E. Hasson, A. Soroker, E. Bassat, Y. Shimoni, T. Ziv, R. V. Sionov, and E. Mitrani. Organ-specific scaffolds for in vitro expansion, differentiation, and organization of primary lung cells. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 17:861–870, 2011.
Shin, K., K. H. Koo, J. Jeong, S. J. Park, D. J. Choi, Y.-G. Ko, and H. Kwon. Three-dimensional culture of salivary gland stem cell in orthotropic decellularized extracellular matrix hydrogels. Tissue Eng. Part A 2019. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.tea.2018.0308.
Shojaie, S., L. Ermini, C. Ackerley, J. Wang, S. Chin, B. Yeganeh, M. Bilodeau, M. Sambi, I. Rogers, J. Rossant, C. E. Bear, and M. Post. Acellular lung scaffolds direct differentiation of endoderm to functional airway epithelial cells: Requirement of matrix-bound HS proteoglycans. Stem Cell Rep. 4:419–430, 2015.
Sicari, B. M., V. Agrawal, B. F. Siu, C. J. Medberry, C. L. Dearth, N. J. Turner, and S. F. Badylak. A murine model of volumetric muscle loss and a regenerative medicine approach for tissue replacement. Tissue Eng. Part A 18:1941–1948, 2012.
Sicari, B. M., J. L. Dziki, B. F. Siu, C. J. Medberry, C. L. Dearth, and S. F. Badylak. The promotion of a constructive macrophage phenotype by solubilized extracellular matrix. Biomaterials 35:8605–8612, 2014.
Sicari, B. M., S. A. Johnson, B. F. Siu, P. M. Crapo, K. A. Daly, H. Jiang, C. J. Medberry, S. Tottey, N. J. Turner, and S. F. Badylak. The effect of source animal age upon the in vivo remodeling characteristics of an extracellular matrix scaffold. Biomaterials 33:5524–5533, 2012.
Sicari, B. M., J. P. Rubin, C. L. Dearth, M. T. Wolf, F. Ambrosio, M. Boninger, N. J. Turner, D. J. Weber, T. W. Simpson, A. Wyse, E. H. P. Brown, J. L. Dziki, L. E. Fisher, S. Brown, and S. F. Badylak. An acellular biologic scaffold promotes skeletal muscle formation in mice and humans with volumetric muscle loss. Sci. Transl. Med. 6:234ra58, 2014.
Sikin, A. M., and S. S. H. Rizvi. Recent patents on food, nutrition, and agriculture. Preface. Recent. Pat. Food Nutr. Agric 5:1, 2013.
Silva, A. C., S. C. Rodrigues, J. Caldeira, A. M. Nunes, V. Sampaio-Pinto, T. P. Resende, M. J. Oliveira, M. A. Barbosa, S. Thorsteinsdóttir, D. S. Nascimento, and P. Pinto-do-Ó. Three-dimensional scaffolds of fetal decellularized hearts exhibit enhanced potential to support cardiac cells in comparison to the adult. Biomaterials 104:52–64, 2016.
Simsa, R., A. M. Padma, P. Heher, M. Hellström, A. Teuschl, L. Jenndahl, N. Bergh, and P. Fogelstrand. Systematic in vitro comparison of decellularization protocols for blood vessels. PLoS ONE 13:1–19, 2018.
Singelyn, J. M., and J. A. DeQuach. Naturally derived myocardial matrix as an injectable scaffold for cardiac tissue engineering. Biomaterials 30:5409–5416, 2009.
Sinha, P., D. Zurakowski, T. K. S. Kumar, D. He, C. Rossi, and R. A. Jonas. Effects of glutaraldehyde concentration, pretreatment time, and type of tissue (porcine versus bovine) on postimplantation calcification. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 143:224–227, 2012.
Slaughter, M. S., K. G. Soucy, R. G. Matheny, B. C. Lewis, M. F. Hennick, Y. Choi, G. Monreal, M. A. Sobieski, G. A. Giridharan, and S. C. Koenig. Development of an extracellular matrix delivery system for effective intramyocardial injection in ischemic tissue. ASAIO J. 60:730–736, 2014.
Soler, J. A., S. Gidwani, and M. J. Curtis. Early complications from the use of porcine dermal collagen implants (Permacol ™) as bridging constructs in the repair of massive rotator cuff tears: A report of 4 cases. Acta Orthop. Belg. 73:432–436, 2007.
Sonnenschein, C., and A. M. Soto. The society of cells—Cancer and control of cell proliferation. New York: Springer Verlag, pp. 99–133, 1999.
Soto, A. M., and C. Sonnenschein. The tissue organization field theory of cancer: A testable replacement for the somatic mutation theory. Bioessays 33:332–340, 2011.
Soucy, K. G., E. F. Smith, G. Monreal, G. Rokosh, B. B. Keller, F. Yuan, R. G. Matheny, A. M. Fallon, B. C. Lewis, L. C. Sherwood, M. A. Sobieski, G. A. Giridharan, S. C. Koenig, and M. S. Slaughter. Feasibility study of particulate extracellular matrix (P-ECM) and left ventricular assist device (HVAD) therapy in chronic ischemic heart failure bovine model. ASAIO J. 61:161–169, 2015.
Spang, M. T., and K. L. Christman. Extracellular matrix hydrogel therapies: In vivo applications and development. Acta Biomater. 68:1–14, 2018.
Sun, Y., G. Chen, and Y. Lv. Effects of hypoxia on the biological behavior of MSCs seeded in demineralized bone scaffolds with different stiffness. Acta Mech. Sin. Xuebao 35:309–320, 2019.
Sun, W. Q., and P. Leung. Calorimetric study of extracellular tissue matrix degradation and instability after gamma irradiation. Acta Biomater. 4:817–826, 2008.
Sung, H. W., Y. Chang, C. T. Chiu, C. N. Chen, and H. C. Liang. Crosslinking characteristics and mechanical properties of a bovine pericardium fixed with a naturally occurring crosslinking agent. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 47:116–126, 1999.
Sutherland, A. J., E. C. Beck, S. C. Dennis, G. L. Converse, R. A. Hopkins, C. J. Berkland, and M. S. Detamore. Decellularized cartilage may be a chondroinductive material for osteochondral tissue engineering. PLoS ONE 10:1–13, 2015.
Toole, B. P., T. N. Wight, and M. I. Tammi. Hyaluronan-cell interactions in cancer and vascular disease. J. Biol. Chem. 277:4593–4596, 2002.
Tottey, S., S. A. Johnson, P. M. Crapo, J. E. Reing, L. Zhang, H. Jiang, C. J. Medberry, B. Reines, and S. F. Badylak. The effect of source animal age upon extracellular matrix scaffold properties. Biomaterials 32:128–136, 2011.
Turner, N. J., J. S. Badylak, D. J. Weber, and S. F. Badylak. Biologic scaffold remodeling in a dog model of complex musculoskeletal injury. J. Surg. Res. 176:490–502, 2012.
Uriarte, J. J., P. N. Nonaka, N. Campillo, R. K. Palma, E. Melo, L. V. F. de Oliveira, D. Navajas, and R. Farré. Mechanical properties of acellular mouse lungs after sterilization by gamma irradiation. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 40:168–177, 2014.
Uriel, S., D. Ph, E. Labay, M. Francis-sedlak, M. L. Moya, R. R. Weichselbaum, N. Ervin, Z. Cankova, E. M. Brey, and D. Ph. Extraction and assembly of tissue-derived gels for cell culture and tissue engineering. Tissue Eng. Part C. Methods 15:309–321, 2009.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for industry: Current good tissue practice (CGTP) and additional requirements for manufacturers of human cells, tissues, and cellular and tissue-based products (HCT/Ps)., 2011.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Medical devices containing materials derived from animal sources (Except for in vitro diagnostic devices): Guidance for industry and Food and Drug Administration staff., 2019.
Utomo, L., M. Pleumeekers, L. Nimeskern, S. Nürnberger, K. S. Stok, F. Hildner, and G. J. V. M. Van Osch. Preparation and characterization of a decellularized cartilage scaffold for ear cartilage reconstruction. Biomed. Mater. 10:015010, 2015.
Valentin, J. E., J. S. Badylak, G. P. McCabe, and S. F. Badylak. Extracellular matrix bioscaffolds for orthopaedic applications: A comparative histologic study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 88A:2673–2686, 2006.
Valentin, J. E., A. M. Stewart-Akers, T. W. Gilbert, and S. F. Badylak. Macrophage participation in the degradation and remodeling of extracellular matrix scaffolds. Tissue Eng. Part A 15:1687–1694, 2009.
Valentin, J. E., N. J. Turner, T. W. Gilbert, and S. F. Badylak. Functional skeletal muscle formation with a biologic scaffold. Biomaterials 31:7475–7484, 2010.
Van Der Merwe, Y., A. E. Faust, E. T. Sakalli, C. C. Westrick, G. Hussey, I. P. Con, V. L. N. Fu, S. F. Badylak, and M. B. Steketee. Matrix-bound nanovesicles prevent ischemia-induced retinal ganglion cell axon degeneration and death and preserve visual function. Sci. Rep. 9:3482, 2019.
VeDepo, M. C., E. E. Buse, R. W. Quinn, T. D. Williams, M. S. Detamore, R. A. Hopkins, and G. L. Converse. Species-specific effects of aortic valve decellularization. Acta Biomater. 50:249–258, 2017.
Visser, J., P. A. Levett, N. C. R. Te Moller, J. Besems, K. W. M. Boere, M. H. P. Van Rijen, J. C. De Grauw, W. J. A. Dhert, P. R. Van Weeren, and J. Malda. Crosslinkable hydrogels derived from cartilage, meniscus, and tendon tissue. Tissue Eng. Part A 21:1195–1206, 2015.
Voytik-Harbin, S. L., A. O. Brightman, B. Z. Waisner, J. P. Robinson, and C. H. Lamar. Small intestinal submucosa: A tissue-derived extracellular matrix that promotes tissue-specific growth and differentiation of cells in vitro. Tissue Eng. 4:157–174, 1998.
Walton, J. R., N. K. Bowman, Y. Khatib, J. Linklater, and G. A. C. Murrell. Restore orthobiologic implant: Not recommended for augmentation of rotator cuff repairs. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Ser. A 89:786–791, 2007.
Wang, Y., J. Bao, X. Wu, Q. Wu, Y. Li, Y. Zhou, L. Li, and H. Bu. Genipin crosslinking reduced the immunogenicity of xenogeneic decellularized porcine whole-liver matrices through regulation of immune cell proliferation and polarization. Sci. Rep. 6:1–16, 2016.
Wang, R. M., and K. L. Christman. Decellularized myocardial matrix hydrogels: In basic research and preclinical studies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 96:77–82, 2016.
Wang, L., J. A. Johnson, D. W. Chang, and Q. Zhang. Decellularized musculofascial extracellular matrix for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 34:2641–2654, 2013.
Wang, R. M., T. D. Johnson, J. He, Z. Rong, M. Wong, V. Nigam, A. Behfar, Y. Xu, and K. L. Christman. Humanized mouse model for assessing the human immune response to xenogeneic and allogeneic decellularized biomaterials. Biomaterials 129:98–110, 2017.
Wang, Z., D. W. Long, Y. Huang, W. C. W. Chen, K. Kim, and Y. Wang. Decellularized neonatal cardiac extracellular matrix prevents widespread ventricular remodeling in adult mammals after myocardial infarction. Acta Biomater. 87:140–151, 2019.
Wang, J. K., B. Luo, V. Guneta, L. Li, S. E. M. Foo, Y. Dai, T. T. Y. Tan, N. S. Tan, C. Choong, and M. T. C. Wong. Supercritical carbon dioxide extracted extracellular matrix material from adipose tissue. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 75:349–358, 2017.
Wang, Q., C. Zhang, L. Zhang, W. Guo, G. Feng, S. Zhou, Y. Zhang, T. Tian, Z. Li, and F. Huang. The preparation and comparison of decellularized nerve scaffold of tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 102:4301–4308, 2014.
Wassenaar, J. W., R. L. Braden, K. G. Osborn, and K. L. Christman. Modulating in vivo degradation rate of injectable extracellular matrix hydrogels. J. Mater. Chem. B 4:2794–2802, 2016.
Wassenaar, J. W., R. Gaetani, J. J. Garcia, R. L. Braden, C. G. Luo, D. Huang, A. N. DeMaria, J. H. Omens, and K. L. Christman. Evidence for mechanisms underlying the functional benefits of a myocardial matrix hydrogel for post-MI treatment. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 67:1074–1086, 2016.
Wei, H. J., H. C. Liang, M. H. Lee, Y. C. Huang, Y. Chang, and H. W. Sung. Construction of varying porous structures in acellular bovine pericardia as a tissue-engineering extracellular matrix. Biomaterials 26:1905–1913, 2005.
West, D. C., D. M. Shaw, P. Lorenz, N. S. Adzick, and M. T. Longaker. Fibrotic healing of adult and late gestation fetal wounds correlates with increased hyaluronidase activity and removal of hyaluronan. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 29:201–210, 1997.
Whitby, D. J., and M. W. J. Ferguson. The extracellular matrix of lip wounds in fetal, neonatal and adult mice. Development 112:651–668, 1991.
White, L. J., T. J. Keane, A. Smoulder, L. Zhang, A. A. Castleton, J. E. Reing, N. J. Turner, C. L. Dearth, and S. F. Badylak. The impact of sterilization upon extracellular matrix hydrogel structure and function. J. Immunol. Regen. Med. 2:11–20, 2018.
White, L. J., A. J. Taylor, D. M. Faulk, T. J. Keane, L. T. Saldin, J. E. Reing, I. T. Swinehart, N. J. Turner, B. D. Ratner, and S. F. Badylak. The impact of detergents on the tissue decellularization process: A ToF-SIMS study. Acta Biomater. 50:207–219, 2017.
Williams, C., K. P. Quinn, I. Georgakoudi, and L. D. Black. Young developmental age cardiac extracellular matrix promotes the expansion of neonatal cardiomyocytes in vitro. Acta Biomater. 10:194–204, 2014.
Wolf, M. T., K. A. Daly, E. P. Brennan-Pierce, S. A. Johnson, C. Carruthers, A. D. Amore, S. P. Nagarkar, S. S. Velankar, and S. F. Badylak. A hydrogel derived from decellularized dermal extracellular matrix. Biomaterials 33:7028–7038, 2012.
Wolf, M. T., K. A. Daly, J. E. Reing, and S. F. Badylak. Biologic scaffold composed of skeletal muscle extracellular matrix. Biomaterials 33:2916–2925, 2012.
Wolf, M. T., S. Ganguly, T. L. Wang, C. W. Anderson, K. Sadtler, R. Narain, C. Cherry, A. J. Parrillo, B. V. Park, G. Wang, F. Pan, S. Sukumar, D. M. Pardoll, and J. H. Elisseeff. A biologic scaffold–associated type 2 immune microenvironment inhibits tumor formation and synergizes with checkpoint immunotherapy. Sci. Transl. Med. 11:eaat7973, 2019.
Wolf, M. T., Y. Vodovotz, S. Tottey, B. N. Brown, and S. F. Badylak. Predicting in vivo responses to biomaterials via combined in vitro and in silico analysis. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 21:148–159, 2015.
Wood, J. D., A. Simmons-Byrd, A. R. Spievack, and S. F. Badylak. Use of a particulate extracellular matrix bioscaffold for treatment of acquired urinary incontinence in dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 226:1095–1097, 2005.
Yang, Q., J. Peng, Q. Guo, J. Huang, L. Zhang, J. Yao, F. Yang, S. Wang, W. Xu, A. Wang, and S. Lu. A cartilage ECM-derived 3-D porous acellular matrix scaffold for in vivo cartilage tissue engineering with PKH26-labeled chondrogenic bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials 29:2378–2387, 2008.
Yang, G., B. B. Rothrauff, H. Lin, R. Gottardi, P. G. Alexander, and R. S. Tuan. Enhancement of tenogenic differentiation of human adipose stem cells by tendon-derived extracellular matrix. Biomaterials 34:9295–9306, 2013.
Yin, Z., X. Chen, T. Zhu, J. J. Hu, H. X. Song, W. L. Shen, L. Y. Jiang, B. C. Heng, J. F. Ji, and H. W. Ouyang. The effect of decellularized matrices on human tendon stem/progenitor cell differentiation and tendon repair. Acta Biomater. 9:9317–9329, 2013.
Young, D. A., V. Bajaj, and K. L. Christman. Decellularized adipose matrix hydrogels stimulate in vivo neovascularization and adipose formation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 102:1641–1651, 2014.
Young, D. A., Y. S. Choi, A. J. Engler, and K. L. Christman. Stimulation of adipogenesis of adult adipose-derived stem cells using substrates that mimic the stiffness of adipose tissue. Biomaterials 34:8581–8588, 2013.
Young, D. A., K. C. McGilvray, N. Ehrhart, and T. W. Gilbert. Comparison of in vivo remodeling of urinary bladder matrix and acellular dermal matrix in an ovine model. Regen. Med. 13:759–773, 2018.
Youngstrom, D. W., I. Rajpar, D. L. Kaplan, and J. G. Barrett. A bioreactor system for in vitro tendon differentiation and tendon tissue engineering. J. Orthop. Res. 33:911–918, 2015.
Zambon, A., M. Vetralla, L. Urbani, M. F. Pantano, G. Ferrentino, M. Pozzobon, N. Pugno, P. De Coppi, N. Elvassore, and S. Spilimbergo. Dry acellular oesophageal matrix prepared by supercritical carbon dioxide. J. Supercrit. Fluids 115:33–41, 2016.
Zantop, T., T. W. Gilbert, M. Yoder, and S. F. Badylak. Extracellular matrix scaffolds are repopulated by bone marrow-derived cells in a mouse model of achilles tendon reconstruction. J. Orthop. Res. 24:1299–1309, 2006.
Zhang, X., and J. Dong. Direct comparison of different coating matrix on the hepatic differentiation from adipose-derived stem cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 456:938–944, 2015.
Zhang, J., B. Li, and J. H.-C. Wang. The role of engineered tendon matrix in the stemness of tendon stem cells in vitro and the promotion of tendon-like tissue formation in vivo. Biomaterials 32:6972–6981, 2011.
Zhao, Z. Q., J. D. Puskas, D. Xu, N. P. Wang, M. Mosunjac, R. A. Guyton, J. Vinten-Johansen, and R. Matheny. Improvement in cardiac function with small intestine extracellular matrix is associated with recruitment of C-kit cells, myofibroblasts, and macrophages after myocardial infarction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 55:1250–1261, 2010.
Zhou, Q., X. Ye, R. Sun, Y. Matsumoto, M. Moriyama, Y. Asano, Y. Ajioka, and Y. Sauo. Differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent stem cells into alveolar epithelial cells in vitro for use in vivo. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 3:675–685, 2014.
Zhu, T., Q. Tang, Y. Shen, H. Tang, L. Chen, and J. Zhu. An acellular cerebellar biological scaffold: Preparation, characterization, biocompatibility and effects on neural stem cells. Brain Res. Bull. 113:48–57, 2015.
Zuo, H., D. Peng, B. Zheng, X. Liu, Y. Wang, L. Wang, X. Zhou, and J. Liu. Regeneration of mature dermis by transplanted particulate acellular dermal matrix in a rat model of skin defect wound. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 23:2933–2944, 2012.
Conflict of interest
SF Badylak is the Chief Scientific Officer of ECM Therapeutics, Inc. MC Cramer has nothing to disclose.
Funding
MC Cramer was supported by the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health (5T32HL076124-12).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Jennifer West oversaw the review of this article.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cramer, M.C., Badylak, S.F. Extracellular Matrix-Based Biomaterials and Their Influence Upon Cell Behavior. Ann Biomed Eng 48, 2132–2153 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-019-02408-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-019-02408-9