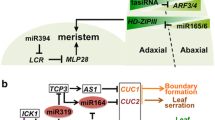
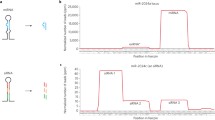
Abstract
Plant and animal microRNAs (miRNAs) are evolutionarily ancient small RNAs, ∼19–24 nucleotides in length, that are generated by cleavage from larger highly structured precursor molecules. In both plants and animals, miRNAs posttranscriptionally regulate gene expression through interactions with their target mRNAs, and these targets are often genes involved with regulating key developmental events. Despite these similarities, plant and animal miRNAs exert their control in fundamentally different ways. Generally, animal miRNAs repress gene expression by mediating translational attenuation through (multiple) miRNA-binding sites located within the 3′ untranslated region of the target gene. In contrast, almost all plant miRNAs regulate their targets by directing mRNA cleavage at single sites in the coding regions. These and other differences suggest that the two systems may have originated independently, possibly as a prerequisite to the development of complex body plans.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altuvia S (2004) Regulatory small RNAs: the key to co-ordinating global regulatory circuits. J Bacteriol 186:6679–6680
Ambros V (2004) The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431:244–350
Ambros V, Lee RC, Lavanway A, Williams PT, Jewell D (2003) MicroRNAs and other tiny endogenous RNAs in C. elegans. Curr Biol 13:807–818
Aravin AA, Lagos-Quintana M, Yalcin A, Zavolan M, Marks D, Snyder B, Gaasterland T, Meyer J, Tuschl T (2003) The small RNA profile during Drosophila melanogaster development. Dev Cell 5:337–350
Aukerman MJ, Sakai H (2003) Regulation of flowering time and floral organ identity by a microRNA and its APETALA2-like target genes. Plant Cell 15:2730–2741
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Bartel B, Bartel DP (2003) MicroRNAs—at the root of plant development? Plant Physiol 132:709–717
Bonnet E, Wuyts J, Rouze P, Van de Peer Y (2004) Detection of 91 potential conserved plant microRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana and Oryza sativa identifies important target genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:11511–11516
Chen X (2004) A microRNA as a translational repressor of APETALA2 in Arabidopsis flower development. Science 303:2022–2025
Doench JG, Sharp PA (2004) Specificity of microRNA target selection in translational repression. Genes Dev 18:504–511
Doench JG, Peterson CP, Sharp PA (2003) siRNAs can function as miRNAs. Genes Dev 17:438–442
Enright AJ, John B, Gaul U, Tuschl T, Sander C, Marks DS (2003) MicroRNA targets in Drosophila. Genome Biol 5:R1
Floyd SF, Bowman JL (2004) Ancient microRNA target sequences in plants. Nature 428:485–486
John B, Enright AJ, Aravin A, Tuschl T, Sander C, Marks DS (2004) Human microRNA targets. PLOS Biol 2:e363
Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP (2004) Computational identification of plant microRNAs and their targets, including a stress-induced miRNA. Mol Cell 14:787–799
Kasschau KD, Xie Z, Allen E, Llave C, Chapman EJ, Krizan KA, Carrington JC (2003) P1/HC-Pro, a viral suppressor of RNA silencing, interferes with Arabidopsis development and miRNA function. Dev Cell 4:205–217
Kuersten S, Goodwin EB (2003) The power of the 3′ UTR-translational control and development. Nat Rev Genet 4:626–637
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T (2001) Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs. Science 294:853–858
Lau NC, Lim LP, Weinstein EG, Bartel DP (2001) An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 294:858–862
Lee RC, Feinbaum R, Ambros V (1993) The heterochronic gene lin-4 of C. elegans encodes two small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin41. Cell 75:843–854
Lewis BP, Shih I, Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP, Burge CB (2003) Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell 115:787–798
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2005) Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 120:15–20
Lim LP, Lau NC, Weinstein EG, Abdelhakim A, Yekta S, Rhoades MW, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2003a) The microRNAs of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genes Dev 17:991–1008
Lim LP, Glasner ME, Yekta S, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2003b) Vertebrate microRNA genes. Science 299:1540
Llave C, Kasschau KD, Rector MA, Carrington JC (2002a) Endogenous and silencing-associated small RNAs in plants. Plant Cell 14:1605–1619
Llave C, Xie Z, Kasschau KD, Carrington JC (2002b) Cleavage of scarecrow-like mRNA targets directed by a class of Arabidopsis miRNA. Science 297:2053–2056
Meyerowitz EM (2002) Plants compared to animals: the broadest comparative study of development. Science 295:1482–1485
Millar AA, Gubler F (2005) The Arabidopsis GAMYB-like genes, MYB33 and MYB65, are microRNA-regulated genes that redundantly facilitate anther development. Plant Cell 17:705–721
Olsen PH, Ambros V (1999) The lin-4 regulatory RNA controls developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans by blocking LIN-14 protein synthesis after the initiation of translation. Dev Biol 216:671–680
Palatnik JF, Allen E, Wu X, Schommer C, Schwab R, Carrington JC, Weigel D (2003) Control of leaf morphogenesis by microRNAs. Nature 425:257–263
Parizotto EA, Dunoyer P, Rahm N, Himber C, Voinnet O (2004) In vivo investigation of the transcription, processing, endonucleolytic activity, and functional relevance of the spatial distribution of a plant miRNA. Genes Dev 18:2237–2242
Park W, Li J, Song R, Messing J, Chen X (2002) CARPEL FACTORY, a Dicer homolog, and HEN1, a novel protein, act in microRNA metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr Biol 12:1484–1495
Pasquinelli AE, Reinhart BJ, Slack F, Martindale MQ, Kuroda M, Maller B, Srinivasan A, Fishman M, Hayward D, Ball E et al (2000) Conservation across animal phylogeny of the sequence and temporal regulation of the 21 nucleotide let-7 heterochronic regulatory RNA. Nature 408:86–89
Reinhart BJ, Weinstein EG, Rhoades MW, Bartel B, Bartel DP (2002) MicroRNAs in plants. Genes Dev 16:1616–1626
Rhoades MW, Reinhart BJ, Lim LP, Burge CB, Bartel B, Bartel DP (2002) Prediction of plant microRNA targets. Cell 110:513–520
Seggerson K, Tang L, Moss EG (2002) Two genetic circuits repress the Caenorhabditis elegans heterochronic gene lin-28 after translation initiation. Dev Biol 243:215–225
Seitz H, Royo H, Bortolin ML, Lin SP, Ferguson-Smith AC, Cavaille J (2004) A large imprinted microRNA gene cluster at the mouse Dlk1–Gtl2 domain. Genome Res 9:1741–1748
Stark A, Brennecke J, Russell RB, Cohen SM (2003) Identification of Drosophila microRNA targets. PLOS Biol 1:E60
Sunkar R, Zhu JK (2004) Novel and stress-regulated microRNAs and other small RNAs from Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16:2001–2019
Tang G, Reinhart BJ, Bartel DP, Zamore PD (2003) A biochemical framework for RNA silencing in plants. Genes Dev 17:49–63
Voinnet O (2003) RNA silencing bridging the gaps in wheat extracts. Trends Plant Sci 8:307–309
Wrightman B, Burglin TR, Gatto J, Arasu P, Ruvkun G (1991) Negative regulatory sequences in the lin-14 3′-untranslated region are necessary to generate a temporal switch during Caenorhabditis elegans development. Genes Dev 5:1813–1824
Xie Z, Kasschau KD, Carrington JC (2003) Negative feedback regulation of Dicer-like1 in Arabidopsis by microRNA-guided mRNA degradation. Curr Biol 13:784–789
Yekta S, Shih I-H, Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNA-directed cleavage of HOXB8 mRNA. Science 304:594–596
Zeng Y, Yi R, Cullen BR (2003) MicroRNAs and small interfering RNAs can inhibit mRNA expression by similar mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:9779–9784
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Millar, A.A., Waterhouse, P.M. Plant and animal microRNAs: similarities and differences. Funct Integr Genomics 5, 129–135 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-005-0145-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-005-0145-2