Abstract
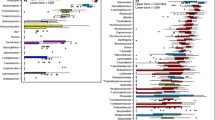
Obesity and overweight are health problems of multifactorial etiology, which may include changes in the microbiome. In Mexico, more than 30 % of the child population between 5 and 11 years of age suffer from being overweight or are obese, which makes it a public health issue in progress. The purpose of this work was to measure the short-chain fatty acid concentration by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and to characterize the bacterial diversity by ion torrent semiconductor sequencing, of 16S rDNA libraries prepared from stools collected from a sample of well-characterized Mexican children for normal weight, overweight, and obese conditions by anthropometric and biochemical criteria. We found that triglyceride levels are increased in overweight and obese children, who presented altered propionic and butyric acid concentrations in feces. In addition, although the colon microbiota did not show a clear bacterial dysbiosis among the three conditions, the abundance of some particular bacteria was changed with respect to normal controls. We conclude from our results that the imbalance in the abundance of at least nine different bacteria as well as altered short-chain fatty acid concentration in feces is associated to the overweight and obese conditions of Mexican children.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SCFAs:
-
Short-chain fatty acids
- NGS:
-
Next-generation sequencing
- nt:
-
Nucleotides
References
Waalen J (2014) The genetics of human obesity. Transl Res 164(4):293–301
James WPT (2008) The epidemiology of obesity: the size of the problem. J Intern Med 263(4):336–352
Ng M, Fleming T, Robinson M, Thomson B, Graetz N, Margono C et al (2014) Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2013. Lancet 384(9945):766–781
Holub CK, Elder JP, Arredondo EM, Barquera S, Eisenberg CM, Sánchez Romero LM et al (2013) Obesity control in Latin American and U.S. Latinos: a systematic review. Am J Prev Med 44(5):529–537
World Health Organization (WHO) (2008) The global burden of disease: 2004 update. WHO, Geneva, Switzerland
Latnovic L, Rodriguez Cabrera L (2013) Public health strategy against overweight and obesity in Mexico’s national agreement for nutritional health. Int J Obes Supp 3:S12–S14
Encuesta Nacional de Salud y Nutrición. Resultados Nacionales 2012. Instituto Nacional de Salud Pública. Available online at: http://ensanut.insp.mx/informes/ENSANUT2012ResultadosNacionales.pdf
Kannel WB, D’Agostino RB, Cobb JL (1996) Effect of weight on cardiovascular disease. Am J Clin Nutr 63(3 Suppl):419S–422S
Carey VJ, Walters EE, Colditz GA, Solomon CG, Willett WC, Rosner BA et al (1997) Body fat distribution and risk of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in women. The Nurses’ Health Study. Am J Epidemiol 145(7):614–619
Wild SH, Byrne CD (2006) ABC of obesity. Risk factors for diabetes and coronary heart disease. BMJ 333:1009–1011
Devaraj S, Hemarajata P, Versalovic J (2013) The human gut microbiome and body metabolism: implications for obesity and diabetes. Clin Chem 59(4):617–628
Ursell LK, Metcalf JL, Parfrey LW, Knight R (2012) Defining the human microbiome. Nutr Rev 70(Suppl 1):S38–S44
Ley RE (2010) Obesity and the human microbiome. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 26(1):5–11
Caricilli AM, Castoldi A, Câmara NOS (2014) Intestinal barrier: a gentlemen’s agreement between microbiota and immunity. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 5(1):18–32
Michelsen KS, Arditi M (2007) Toll-like receptors and innate immunity in gut homeostasis and pathology. Curr Opin Hematol 14(1):48–54
Rooks MG, Garrett WS (2011) Bacteria, food, and cancer. F1000 Biol Rep 3:12
Whelan K, Judd PA, Preedy VR, Taylor MA (2004) Enteral feeding: the effect on faecal output, the faecal microflora and SCFA concentrations. Proc Nutr Soc 63(1):105–113
Segain J-P, Raingeard de la Blétière D, Bourreille A, Leray V, Gervois N, Rosales C et al (2000) Butyrate inhibits inflammatory responses through NFκB inhibition: implications for Crohn’s disease. Gut 47:397–403
Dengler F, Rackwitz R, Benesch F, Pfannkuche H, Gäbel G (2014) Both butyrate incubation and hypoxia upregulate genes involved in the ruminal transport of SCFA and their metabolites. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). doi:10.1111/jpn.12201
Clemente JC, Ursell LK, Parfrey LW, Knight R (2012) The impact of the gut microbiota on human health: an integrative view. Cell 148(6):1258–1270
Bäckhed F, Ding H, Wang T, Hooper LV, Koh GY, Nagy A et al (2004) The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101(44):15718–15723
DiBaise JK, Zhang H, Crowell MD, Krajmalnik-Brown R, Decker GA, Rittmann BE (2008) Gut microbiota and its possible relationship with obesity. Mayo Clin Proc 83(4):460–469
Flint HJ (2011) Obesity and the gut microbiota. J Clin Gastroenterol 45(Suppl):S128–S132
Gill SR, Pop M, DeBoy RT, Eckburg PB, Turnbaugh PJ, Samuel BS et al (2006) Metagenomic analysis of the human distal gut microbiome. Science 312(5778):1355–1359
Eckburg PB, Bik EM, Bernstein CN, Purdom E, Dethlefsen L, Sargent M et al (2005) Diversity of the human intestinal microbial flora. Science 308(5728):1635–1638
Palmer C, Bik EM, DiGiulio DB, Relman DA, Brown PO (2007) Development of the human infant intestinal microbiota. PLoS Biol 5(7):e177
Qin J, Li R, Raes J, Arumugam M, Burgdorf KS, Manichanh C et al (2010) A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 464(7285):59–65
Tremaroli V, Bäckhed F (2012) Functional interactions between the gut microbiota and host metabolism. Nature 489(7415):242–249
de Onis M, Onyango AW, Borghi E, Siyam A, Nishida C, Siekmann J (2007) Development of a WHO growth reference for school-aged children and adolescents. Bull World Health Organ 85(9):660–667
Arimond M, Ruel MT (2004) Dietary diversity is associated with child nutritional status: evidence from 11 demographic and health surveys. J Nutr 134(10):2579–2585
García Cuartero B, García Lacalle C, Jiménez Lobo C, González Vergaz A, Calvo Rey C, Alcázar Villar MJ et al (2007) Índice HOMA y QUICKI, insulina y péptido C en niños sanos. Puntos de corte de riesgo cardiovascular. An Pediatr (Barc) 66(5):481–490
Fierer N, Hamady M, Lauber CL, Knight R (2008) The influence of sex, handedness, and washing on the diversity of hand surface bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(46):17994–17999
Whiteley AS, Jenkins S, Waite I, Kresoje N, Payne H, Mullan B et al (2012) Microbial 16S rRNA Ion Tag and community metagenome sequencing using the Ion Torrent (PGM) Platform. J Microbiol Methods 91(1):80–88
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK et al (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7(5):335–336
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26(19):2460–2461
Haas BJ, Gevers D, Earl AM, Feldgarden M, Ward DV, Giannoukos G et al (2011) Chimeric 16S rRNA sequence formation and detection in Sanger and 454-pyrosequenced PCR amplicons. Genome Res 21:494–504
DeSantis TZ, Hugenholtz P, Larsen N, Rojas M, Brodie EL, Keller K et al (2006) Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(7):5069–5072
Vázquez-Baeza Y, Pirrung M, Gonzalez A, Knight R (2013) EMPeror: a tool for visualizing high-throughput microbial community data. Gigascience 2:16
De Baere S, Eeckhaut V, Steppe M, De Maesschalck C, De Backer P, Van Immerseel F et al (2013) Development of a HPLC-UV method for the quantitative determination of four short-chain fatty acids and lactic acid produced by intestinal bacteria during in vitro fermentation. J Pharm Biomed Anal 80:107–115
Samuel BS, Gordon JI (2006) A humanized gnotobiotic mouse model of host–archaeal–bacterial mutualism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(26):10011–10016
Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Mahowald MA, Magrini V, Mardis ER, Gordon JI (2006) An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 444(7122):1027–1031
Larsen N, Vogensen FK, van den Berg FW, Nielsen DS, Andreasen AS, Pedersen BK et al (2010) Gut microbiota in human adults with type 2 diabetes differs from non-diabetic adults. PLoS One 5(2):e9085
Turnbaugh PJ, Gordon JI (2009) The core gut microbiome, energy balance and obesity. J Physiol 587(Pt 17):4153–4158
Turnbaugh PJ, Ridaura VK, Faith JJ, Rey FE, Knight R, Gordon JI (2009) The effect of diet on the human gut microbiome: a metagenomic analysis in humanized gnotobiotic mice. Sci Transl Med 1(6):6ra14
Scheppach W (1994) Effects of short chain fatty acids on gut morphology and function. Gut 35(1 Suppl):S35–S38
Kotzampassi K, Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ, Stavrou G (2014) Obesity as a consequence of gut bacteria and diet interactions. ISRN Obes 2014:651895. doi:10.1155/2014/651895
Wolever TMS, Spadafora P, Eshuis H (1991) Interaction between colonic acetate and propionate in humans. Am J Clin Nutr 53(3):681–687
Vogt JA, Wolever TMS (2003) Fecal acetate is inversely related to acetate absorption from the human rectum and distal colon. J Nutr 133:3145–3148
Frost G, Sleeth ML, Sahuri-Arisoylu M, Lizarbe B, Cerdan S, Brody L et al (2014) The short-chain fatty acid acetate reduces appetite via a central homeostatic mechanism. Nat Commun 5:3611. doi:10.1038/ncomms4611
Duncan SH, Belenguer A, Holtrop G, Johnstone AM, Flint HJ, Lobley GE (2007) Reduced dietary intake of carbohydrates by obese subjects results in decreased concentrations of butyrate and butyrate-producing bacteria in feces. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(4):1073–1078
Gostner A, Blaut M, Schäffer V, Kozianowski G, Theis S, Klingeberg M et al (2006) Effect of isomalt consumption on faecal microflora and colonic metabolism in healthy volunteers. Br J Nutr 95(1):40–50
Goodrich JK, Waters JL, Poole AC, Sutter JL, Koren O, Blekhman R et al (2014) Human genetics shape the gut microbiome. Cell 159:789–799
David LA, Maurice CF, Carmody RN, Gootenberg DB, Button JE, Wolfe BE et al (2014) Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature 505(7484):559–563
Looft T, Johnson TA, Allen HK, Bayles DO, Alt DP, Stedtfeld RD et al (2012) In-feed antibiotic effects on the swine intestinal microbiome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(5):1691–1696
Truesdell SJ, Sims JC, Boerman PA, Seymour JL, Lazarus RA (1991) Pathways for metabolism of ketoaldonic acids in an Erwinia sp. J Bacteriol 173(21):6651–6656
Tims S, Derom C, Jonkers DM, Vlietinck R, Saris WH, Kleerebezem M et al (2013) Microbiota conservation and BMI signatures in adult monozygotic twins. ISME J 7(4):707–717
Balamurugan R, George G, Kabeerdoss J, Hepsiba J, Chandragunasekaran AMS, Ramakrishna BS (2010) Quantitative differences in intestinal Faecalibacterium prausnitzii in obese Indian children. Br J Nutr 103(3):335–338
Sotos M, Nadal I, Marti A, Martínez A, Martin-Matillas M, Campoy C et al (2008) Gut microbes and obesity in adolescents. Proc Nutr Soc 67(OCE):E20. doi:10.1017/S0029665108006290
Ravussin Y, Koren O, Spor A, LeDuc C, Gutman R, Stombaugh J et al (2012) Responses of gut microbiota to diet composition and weight loss in lean and obese mice. Obesity (Silver Spring) 20(4):738–747
Kameyama K, Itoh K (2014) Intestinal colonization by a lachnospiraceae bacterium contributes to the development of diabetes in obese mice. Microbes Environ. 2014 Oct 4. [Epub ahead of print]
Zhao L (2013) The gut microbiota and obesity: from correlation to causality. Nat Rev Microbiol 11(9):639–647
Becker N, Kunath J, Loh G, Blaut M (2011) Human intestinal microbiota: characterization of a simplified and stable gnotobiotic rat model. Gut Microbes 2(1):25–33
Lee SM, Han HW, Yim SY (2015) Beneficial effects of soy milk and fiber on high cholesterol diet-induced alteration of gut microbiota and inflammatory gene expression in rats. Food Funct 6(2):492–500
Reichardt N, Duncan SH, Young P, Belenguer A, McWilliam Leitch C, Scott KP et al (2014) Phylogenetic distribution of three pathways for propionate production within the human gut microbiota. ISME J 8(6):1323–1335
Karlsson CLJ, Önnerfält J, Xu J, Molin G, Ahrné S, Thorngren-Jerneck K (2012) The microbiota of the gut in preschool children with normal and excessive body weight. Obesity 20:2257–2261
Xu P, Li M, Zhang J, Zhang T (2012) Correlation of intestinal microbiota with overweight and obesity in Kazakh school children. BMC Microbiol 12:283
Abdallah Ismail N, Ragab SH, Abd Elbaky A, Shoeib AR, Alhosary Y, Fekry D (2011) Frequency of Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes in gut microbiota in obese and normal weight Egyptian children and adults. Arch Med Sci 7(3):501–507
Martinez-Marignac VL, Valladares A, Cameron E, Chan A, Perera A, Globus-Goldberg R et al (2007) Admixture in Mexico City: implications for admixture mapping of type 2 diabetes genetic risk factors. Hum Genet 120:807–819
Silva-Zolezzi I, Hidalgo-Miranda A, Estrada-Gil J, Fernandez-Lopez JC, Uribe-Figueroa L, Contreras A et al (2009) Analysis of genomic diversity in Mexican Mestizo populations to develop genomic medicine in Mexico. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:8611–8616
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Cinvestav-IPN, Estimulos a Investigaciones Médicas, Fundación Miguel Alemán A. C., and FONSEC SS/IMSS/ISSSTE-CONACYT-233361 granted to JGM. We thank Mario Arturo Cruz Montiel, Angel Antonio Martínez Gomez, Jakeline Leon Bernal, Jessica Jazmín Bárcenas García, and Rodrigo García Gutiérrez for technical assistance in the laboratory; Antonia López Salazar for administrative assistance; Suresh Thenozhi for technical assistance in bioinformatics analysis; and Caterina R. Venturelli as well as Sathish Kumar Kamaraj for the careful reading and correction of this text. The authors are deeply indebted to all parents and children who participated in this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
The authors declare that all procedures were performed in accordance with the ethical standards approved by the Local Ethical Committee Board of Health from the Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social R-2011–1402 1402–10, Mexico City, and with the Helsinki Declaration revised in 2000.
Informed consent
The authors declare that informed consent was signed by all parents and children in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration revised in 2000.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Table S1
(DOCX 38 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murugesan, S., Ulloa-Martínez, M., Martínez-Rojano, H. et al. Study of the diversity and short-chain fatty acids production by the bacterial community in overweight and obese Mexican children. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 34, 1337–1346 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-015-2355-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-015-2355-4