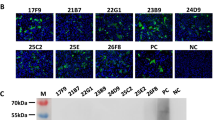
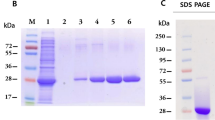
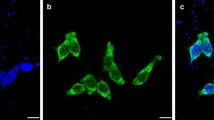
Abstract
Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) is endemic in East Asia and Europe. This study was initiated to investigate the reactivity of antibodies in sera of Chinese HFRS patients with the recombinant nucleocapsid proteins (rNPs) of Hantaan virus (HTNV), Dobrava-Belgrade virus (DOBV), and Puumala virus (PUUV), which are the prevalent hantavirus strains in Europe. Forty-eight pairs of acute and convalescent sera were collected from HFRS patients in Hubei, China (1985-2002) and tested by indirect IgG, IgA, and IgM enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays with six rNPs of European hantaviruses as coated antigens, respectively. The results showed that the sensitivity of rNPs against IgG was HTNV-rNP > DOBV-rNP > PUUV-rNP, while the sensitivity against IgA was DOBV-rNP > HTNV-rNP > PUUV-rNP. Quantitative analysis revealed both acute and convalescent sera from HFRS patients predominantly exhibit high levels of IgA. Although PUUV-rNPs showed very weak reactivity to the three kinds of immunoglobulins in all samples, three pairs of sera unexpectedly cross-reacted strongly to all three PUUV-rNP subtypes. We first observe that HFRS patients’ sera from Hubei Province show new prevalent characteristics of cross-reacting with PUUV-rNPs and continued high level of IgA in convalescent phase, as well as in China.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Niklasson BS (1992) Haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome, virological and epidemiological aspects. Pediatr Nephrol 6(2):201–204
Zeier M, Handermann M, Bahr U, Rensch B, Muller S, Kehm R, Muranyi W, Darai G (2005) New ecological aspects of hantavirus infection: a change of a paradigm and a challenge of prevention—a review. Virus Genes 30(2):157–180
Kariwa H, Yoshimatsu K, Arikawa J (2007) Hantavirus infection in East Asia. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 30(5–6):341–356
Kruger DH, Ulrich R, Lundkvist AA (2001) Hantavirus infections and their prevention. Microbes Infect 3(13):1129–1144
Maes P, Clement J, Gavrilovskaya I, Van Ranst M (2004) Hantaviruses: immunology, treatment, and prevention. Viral Immunol 17(4):481–497
Plyusnin A, Kruger DH, Lundkvist A (2001) Hantavirus infections in Europe. Adv Virus Res 57:105–136
Childs JE, Kaufmann AF, Peters CJ, Ehrenberg RL (1993) Hantavirus infection—southwestern United States: interim recommendations for risk reduction. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. MMWR Recomm Rep 42(RR-11):1–13
Lee HW, van der Groen G (1989) Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. Prog Med Virol 36:62–102
Schmaljohn C, Hjelle B (1997) Hantaviruses: a global disease problem. Emerg Infect Dis 3(2):95–104
Vapalahti O, Mustonen J, Lundkvist A, Henttonen H, Plyusnin A, Vaheri A (2003) Hantavirus infections in Europe. Lancet Infect Dis 3(10):653–661
Nemirov K, Vapalahti O, Lundkvist A, Vasilenko V, Golovljova I, Plyusnina A, Niemimaa J, Laakkonen J, Henttonen H, Vaheri A, Plyusnin A (1999) Isolation and characterization of Dobrava hantavirus carried by the striped field mouse (Apodemus agrarius) in Estonia. J Gen Virol 80(Pt 2):371–379
Sibold C, Ulrich R, Labuda M, Lundkvist A, Martens H, Schutt M, Gerke P, Leitmeyer K, Meisel H, Kruger DH (2001) Dobrava hantavirus causes hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in central Europe and is carried by two different Apodemus mice species. J Med Virol 63(2):158–167
Song G (1999) Epidemiological progresses of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in China. Chin Med J (Engl) 112((5):472–477
Tang LY, Yu T, Liu WX, Chen HX (2000) Study on types of hemorragic fever with renal syndrome in Chinese epidemic areas. Disease Surveillance 15(7):248–250
Chen HX, Luo CW, Chen F, Wang XH, Yang JH, Ma LJ, Hu JY, Sun HY, Yao ZH, Qiu JC (1999) Study and surveillance of HFRS (hemorrhage fever with renal syndrome) in China. Chinese Journal of Public Health 15(7):616–623
Wang H, Yoshimatsu K, Ebihara H, Ogino M, Araki K, Kariwa H, Wang Z, Luo Z, Li D, Hang C, Arikawa J (2000) Genetic diversity of hantaviruses isolated in china and characterization of novel hantaviruses isolated from Niviventer confucianus and Rattus rattus. Virology 278(2):332–345
Liu G, Li C, Hu GW, Li Y, Yao LS, Chen YQ, Huang B, Ren M, Chen YZ, Guan SX, Yu CY, Na BZ, Zhong XD, Sun YX, Li WX, Li DX (2003) Identification of Puumala like viruses in China. Zhonghua shi yan he lin chuang bing du xue za zhi 17(1):55–57
Zhang YZ, Zou Y, Yan YZ, Hu GW, Yao LS, Du ZS, Jin LZ, Liu YY, Li MH, Chen HX, Fu ZF (2007) Detection of phylogenetically distinct Puumala-like viruses from red-grey vole Clethrionomys rufocanus in China. J Med Virol 79(8):1208–1218
Zou Y, Xiao QY, Dong X, Lv W, Zhang SP, Li MH, Plyusnin A, Zhang YZ (2008) Genetic analysis of hantaviruses carried by reed voles Microtus fortis in China. Virus Res 137(1):122–128
Zou Y, Wang JB, Gaowa HS, Yao LS, Hu GW, Li MH, Chen HX, Plyusnin A, Shao R, Zhang YZ (2008) Isolation and genetic characterization of hantaviruses carried by Microtus voles in China. J Med Virol 80(4):680–688
Cohen MS, Casals J, Hsiung GD, Kwei HE, Chin CC, Ge HC, Hsiang CM, Lee PW, Gibbs CJ Jr, Gajdusek DC (1981) Epidemic hemorrhagic fever in Hubei Province, The People's Republic of China: a clinical and serological study. Yale J Biol Med 54(1):41–55
Xiao SY, Liang M, Schmaljohn CS (1993) Molecular and antigenic characterization of HV114, a hantavirus isolated from a patient with haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in China. J Gen Virol 74(Pt 8):1657–1659
Fang Y, Huang XH, Zhou Q, Hu EP, Guan HX (1995) The trend of epidemic situation changes of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) in early 1990s in Hubei Province. Chinese Journal of Vector Biology and Control 6(2):111–113
Yang ZQ, Zhang TM, Zhang MY, Zheng ZM, Hu ZJ, Qu CF, Zhu BL, Xiang JM, Huggins JW, Cosgriff TM, Smith JI (1989) A study on early viremia in patients with epidemic hemorrhagic fever (EHF) and the blockade therapy. National Medical Journal of China 69(11):621–624
Elgh F, Lundkvist A, Alexeyev OA, Stenlund H, Avsic-Zupanc T, Hjelle B, Lee HW, Smith KJ, Vainionpaa R, Wiger D, Wadell G, Juto P (1997) Serological diagnosis of hantavirus infections by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay based on detection of immunoglobulin G and M responses to recombinant nucleocapsid proteins of five viral serotypes. J Clin Microbiol 35(5):1122–1130
Petraityte R, Yang H, Hunjan R, Razanskiene A, Dhanilall P, Ulrich RG, Sasnauskas K, Jin L (2008) Development and evaluation of serological assays for detection of Hantaanvirus-specific antibodies in human sera using yeast-expressed nucleocapsid protein. J Virol Methods 148(1–2):89–95
Meisel H, Wolbert A, Razanskiene A, Marg A, Kazaks A, Sasnauskas K, Pauli G, Ulrich R, Kruger DH (2006) Development of novel immunoglobulin G (IgG), IgA, and IgM enzyme immunoassays based on recombinant Puumala and Dobrava hantavirus nucleocapsid proteins. Clin Vaccine Immunol 13(12):1349–1357
Razanskiene A, Schmidt J, Geldmacher A, Ritzi A, Niedrig M, Lundkvist A, Kruger DH, Meisel H, Sasnauskas K, Ulrich R (2004) High yields of stable and highly pure nucleocapsid proteins of different hantaviruses can be generated in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biotechnol 111(3):319–333
Elgh F, Linderholm M, Wadell G, Juto P (1996) The clinical usefulness of a Puumalavirus recombinant nucleocapsid protein based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in the diagnosis of nephropathia epidemica as compared with an immunofluorescence assay. Clin Diagn Virol 6(1):17–26
Groen J, Gerding M, Jordans JG, Clement JP, Osterhaus AD (1994) Class and subclass distribution of hantavirus-specific serum antibodies at different times after the onset of nephropathia epidemica. J Med Virol 43(1):39–43
Meng XS, Chen YP, Li C, Yu JS, Guo YM, Zhang QF, Sun YL, Li DX (2003) Using recombinant antigens of Hantavirus to study the kinetics of serum IgA, IgG, IgM antibodies in the acute-phase of hemorrhagic fever renal syndrome. Zhonghua shi yan he lin chuang bing du xue za zhi 17(3):254–257
de Carvalho NC, Bjorling E, Lundkvist A (2000) Immunoglobulin A responses to Puumala hantavirus. J Gen Virol 81(Pt 6):1453–1461
Elgh F, Linderholm M, Wadell G, Tarnvik A, Juto P (1998) Development of humoral cross-reactivity to the nucleocapsid protein of heterologous hantaviruses in nephropathia epidemica. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 22(4):309–315
Kato H, Kato R, Fujihashi K, McGhee JR (2001) Role of mucosal antibodies in viral infections. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 260:201–228
Dzagurova T, Tkachenko E, Slonova R, Ivanov L, Ivanidze E, Markeshin S, Dekonenko A, Niklasson B, Lundkvist A (1995) Antigenic relationships of hantavirus strains analysed by monoclonal antibodies. Arch Virol 140(10):1763–1773
Geldmacher A, Schmaler M, Kruger DH, Ulrich R (2004) Yeast-expressed hantavirus Dobrava nucleocapsid protein induces a strong, long-lasting, and highly cross-reactive immune response in mice. Viral Immunol 17(1):115–122
Li Q, Yang ZQ, Qu H, Xiao H (2005) Variability of G1 gene of hantaviruses occurring in the Hubei Province, P.R. China from 1985 to 2000. Acta Virol 49(1):51–57
Zhang Y, Zhang H, Dong X, Yuan J, Zhang H, Yang X, Zhou P, Ge X, Li Y, Wang LF, Shi Z (2010) Hantavirus outbreak associated with laboratory rats in Yunnan, China. Infect Genet Evol 10(5):638–644
Zou Y, Hu J, Wang ZX, Wang DM, Yu C, Zhou JZ, Fu ZF, Zhang YZ (2008) Genetic characterization of hantaviruses isolated from Guizhou, China: evidence for spillover and reassortment in nature. J Med Virol 80(6):1033–1041
Acknowledgements
We thank the physicians who assisted in the sample collection and Dr. K. Sasnauskas, Institute of Biotechnology, Vilnius, Lithuania for providing S. cerevisiae strains expressing N proteins. We would like to thank Dr. Rhea-Beth Markowitz, Medical College of Georgia, Augusta, Georgia, USA and Dr. Ying Lin, Second Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China for editing assistance. This work was supported by the National High Technology Research and Development 863 Program of China (No. 2007AA02Z465), a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC project No. 30770096) and the Open Grant of State Key Laboratory of Virology (2007-05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Hai-Rong Xiong and Qing Li contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, HR., Li, Q., Chen, W. et al. Specific humoral reaction of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) patients in China to recombinant nucleocapsid proteins from European hantaviruses. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 30, 645–651 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-010-1134-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-010-1134-5