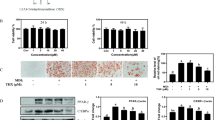
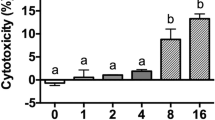
Abstract
The effects of parthenolide (PL), a sesquiterpene lactone obtained from feverfew plant, on lipid accumulation and signaling pathway in adipocytes were investigated. PL significantly inhibited lipid accumulation and adipogenic factors during adipogenesis. In particular, PL exerted its inhibitory effects in early adipogenic stage by regulating the early adipogenic factors. In addition, PL regulated the expression of adipokines; leptin, retinol binding protein, and resistin mRNAs were downregulated, whereas adiponectin gene expression was increased. Furthermore, PL significantly reduced intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) production during adipogenesis. This PL-mediated regulation of ROS production was associated with the regulation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor (Nrf2)-kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1) pathway. PL effectively increased the abundance of Nrf2 and its target proteins, heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and NADPH dehydrogenase 1 (NQO1), by promoting the nuclear translocation of Nrf2, indicating that PL-mediated anti-adipogenic effects are associated with the Nrf2/Keap1 pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banerjee SS, Feinberg MW, Watanabe M, Gray S, Haspel RL, Denkinger DJ, Kawahara R, Hauner H, Jain MK. The Krüppel-like factor KLF2 inhibits peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ expression and adipogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 2581-2584 (2003)
Birsoy K, Chen Z, Friedman J. Transcriptional regulation of adipogenesis by KLF4. Cell Metab. 7: 339-347 (2008)
Chan RS, Woo J. Prevention of overweight and obesity: how effective is the current public health approach. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 7: 765-783 (2010)
Choi KM, Lee YS, Sin DM, Lee S, Lee MK, Lee YM, Hong JT, Yun YP, Yoo HS. Sulforaphane inhibits mitotic clonal expansion during adipogenesis through cell cycle arrest. Obesity 20: 1365-1371 (2012)
Denu RA, Hematti P. Effects of oxidative stress on mesenchymal stem cell biology. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2016: 2989076 (2016)
Desprès JP, Lemieux I. Abdominal obesity and metabolic syndrome. Nature 444: 881-887 (2006)
Duntas LH, Biondi B. The interconnections between obesity, thyroid function, and autoimmunity: the multifold role of leptin. Thyroid 23: 646-653 (2013)
Feltenstein MW, Schühly W, Warnick JE, Fischer NH, Sufka KJ. Anti-inflammatory and anti-hyperalgesic effects of sesquiterpene lactones from Magnolia and Bear’s foot. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 79: 299-302 (2004)
Fernández-Sánchez A, Madrigal-Santillán E, Bautista M, Esquivel-Soto J, Morales-González A, Esquivel-Chirino C, Durante-Montiel I, Sánchez-Rivera G, Valadez-Vega C, Morales-González JA. Inflammation, oxidative stress, and obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 12: 3117-3132 (2011)
Festi D, Colecchia A., Sacco T, Bondi M, Roda E, Marchesini G. Hepatic steatosis in obese patients: clinical aspects and prognostic significance. Obesity Rev. 5: 27-42 (2004)
Furukawa S, Fujita T, Shimabukuro M, Iwaki M, Yamada Y, Nakajima Y, Nakayama O, Makishima M, Matsuda M, Shimomura I. Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact on metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Invest. 114: 1752-1761 (2004)
Gaikwad A, Long DJ 2nd, Stringer JL, Jaiswal AK. In vivo role of NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) in the regulation of intracellular redox state and accumulation of abdominal adipose tissue. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 22559-22564 (2001)
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JM, Cross CE. Free radicals, antioxidants, and human disease: where are we now? J. Lab. Clin. Med. 119: 598-620 (1992)
Hill JO, Wyatt HR, Peters JC. Energy balance and obesity. Circulation 126: 126-132 (2012)
Kersten S. Mechanisms of nutritional and hormonal regulation of lipogenesis. EMBO Rep. 2: 282-286 (2001)
Kim JH, Kim CY, Kang B, Hong J, Choi HS. Dibenzoylmethane suppresses lipid accumulation and reactive oxygen species production through regulation of nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 and insulin signaling in adipocytes. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 41: 680-689 (2018)
Klok M, Jakobsdottir S, Drent M. The role of leptin and ghrelin in the regulation of food intake and body weight in humans: a review. Obesity Rev. 8: 21-34 (2007)
Kobayashi M, Yamamoto M. Molecular mechanisms activating the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway of antioxidant gene regulation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 7: 385-394 (2005)
Kusminski CM, McTernan PG, Kumar S. Role of resistin in obesity, insulin resistance and Type II diabetes. Clin. Sci. 109: 243-256 (2005)
Moraes-vieira PM, Yore MM, Dwyer PM, Syed I, Aryal P, Kahn BB. RBP4 activates antigen-presenting cells, leading to adipose tissue inflammation and systemic insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 19: 512-526 (2014)
Moseti D, Regassa A, Kim WK. Molecular regulation of adipogenesis and potential anti-adipogenic bioactive molecules. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 17: 124 (2016)
Nelson MH, Cobb SE, Shelton J. Variations in parthenolide content and daily dose of feverfew products. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 59: 1527-1531 (2002)
Pan H, Guo J, Su Z. Advances in understanding the interrelations between leptin resistance and obesity. Physiol. Behav. 130: 157-169 (2014)
Pareek A, Suthar M, Rathore GS, Bansal V. Feverfew (Tanacetum parthenium L.): a systematic review. Pharmacogn. Rev. 5: 103-110 (2011)
Pi J, Leung L, Xue P, Wang W, Hou Y, Liu D, Yehuda-shinaidman E, Lee C, Lau J, Kurtz T W, CHAN JY. Deficiency in the nuclear factor E2-related factor-2 transcription factor results in impaired adipogenesis and protects against diet-induced obesity. J. Biol. Chem. 285: 9292-9300 (2010)
Pieralisi A, Martini C, Soto D, Vila MC, Calvo JC, Guerra LN. N-acetylcysteine inhibits lipid accumulation in mouse embryonic adipocytes. Redox Biol. 9: 39-44 (2016)
Ryter SW, Choi AM. Heme oxygenase-1: redox regulation of a stress protein in lung and cell culture models. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 7: 80-91 (2005)
Schroder K, Wandzioch K, Helmcke I, Brandes RP. Nox4 acts as a switch between differentiation and proliferation in preadipocytes. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 29: 239-245 (2009)
Shin S, Wakabayashi N, Misra V, Biswal S, Lee GH, Agoston ES, Yamamoto M, Kensler T W. NRF2 modulates aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling: influence on adipogenesis. Mol. Cell Biol. 27: 7188-7197 (2007)
Suh HJ, Cho SY, Kim EY, Choi HS. Blockade of lipid accumulation by silibinin in adipocytes and zebrafish. Chem. Biol. Interact. 227: 53-62 (2015)
Szkudelska K, Szkudelski T, Nogowski L. Daidzein, coumestrol and zearalenone affect lipogenesis and lipolysis in rat adipocytes. Phytomedicine 9: 338-345 (2002)
Tang QQ, Otto TC, Lane MD. Mitotic clonal expansion: a synchronous process required for adipogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 100: 44-49 (2003)
Tontonoz P, Hu E, Graves RA, Budavari AI, Spiegelman BM. mPPAR gamma 2: tissue-specific regulator of an adipocyte enhancer. Genes Dev. 8: 1224-1234 (1994)
Yang Q, Graham TE, Mody N, Preitner F, Peroni OD, Zabolotny JM, Kotani K, Quadro L, Kahn BB. Serum retinol binding protein 4 contributes to insulin resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nature 436: 356-362 (2005)
Zhong Y, Liu T, Lai W, Tan Y, Tian D, Guo Z. Heme oxygenase-1-mediated reactive oxygen species reduction is involved in the inhibitory effect of curcumin on lipopolysaccharide-induced monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 production in RAW264.7 macrophages. Mol. Med. Rep. 7: 242-246 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, a Grant funded by the Korea government (the Ministry of Education) (NRF‐2015R1D1A1A01059729; 2016), and a research Grant from the Seoul Women’s University (2019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights
There is no animal or human experiment in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, C.Y., Kang, B., Hong, J. et al. Parthenolide inhibits lipid accumulation via activation of Nrf2/Keap1 signaling during adipocyte differentiation. Food Sci Biotechnol 29, 431–440 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-019-00672-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-019-00672-y