Summary.
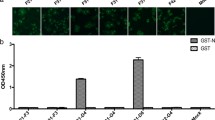
Sapovirus (SaV), a member of the genus Sapovirus in the family Caliciviridae, is an agent of human and porcine gastroenteritis. SaV strains are divided into five genogroups (GI–GV) based on their capsid (VP1) sequences. Human SaV strains are noncultivable, but expression of the recombinant capsid protein (rVP1) in a baculovirus expression system results in the self-assembly of virus-like particles (VLPs) that are morphologically similar to native SaV. In this study, rVP1 constructs of SaV GI, GII, and GV strains were expressed in a baculovirus expression system. The structures of the GI, GII, and GV VLPs, with diameters of 41–48 nm, were morphologically similar to those of native SaV. However a fraction of GV VLPs were smaller, with diameters of 26–31 nm and spikes on the outline. This is the first report of GII and GV VLP formation and the first identification of small VLPs. To examine the cross-reactivities among GI, GII, and GV rVP1, hyperimmune rabbit antisera were raised against Escherichia coli-expressed GI, GII, and GV N- and C-terminal VP1. Western blotting showed the GI antisera cross-reacted with GV rVP1 but not GII rVP1; GII antisera cross-reacted weakly with GI rVP1 but did not cross-react with GV rVP1; and GV antisera reacted only with GV rVP1. Also, hyperimmune rabbit and guinea pig antisera raised against purified GI VLPs were used to examine the cross-reactivities among GI, GII, and GV VLPs by an antigen enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The ELISA showed that the GI VLPs were antigenically distinct from GII and GV VLPs.
Article PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hansman, G., Natori, K., Oka, T. et al. Cross-reactivity among sapovirus recombinant capsid proteins. Arch Virol 150, 21–36 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-004-0406-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-004-0406-8