Summary.
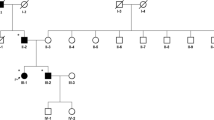
Mutations in the DJ-1 gene lead to autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism. We performed F-DOPA and FDG PET neuroimaging in two parkinsonism patients homozygous for DJ-1 mutations, three relatives heterozygous for a DJ-1 mutation and one non-carrier, all from the originally described kindred from The Netherlands. Their characteristics were compared to those of typical Parkinson’s disease patients and healthy controls. Both parkinsonism patients had reduced F-DOPA uptake concordant with typical Parkinson’s disease. In the, clinically unaffected, heterozygous relatives, F-DOPA metabolism was unremarkable, thus not suggesting a dosage effect of the DJ-1 gene.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dekker, M., Eshuis, S., Maguire, R. et al. PET neuroimaging and mutations in the DJ-1 gene. J Neural Transm 111, 1575–1581 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-004-0165-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-004-0165-4