Abstract
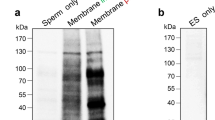
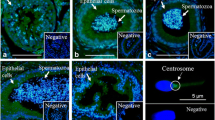
Epididymosomes (apocrine secreted epididymal vesicles) are assumed to play a crucial role in sperm maturation. Our aim has been to analyze the fusogenic properties of bovine epididymosomes and their involvement in the transfer of membrane components (lipids, proteins, plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase 4 [PMCA4]) into bovine sperm. The fusogenic properties of epididymosomes with spermatozoa were investigated in vitro by using octadecyl rhodamine-B (R18)-labeled epididymosomes. Spermatozoa isolated from the epididymal caput showed a higher fusion rate than those taken from the cauda. The fusion rate was dependent on pH and time. Furthermore, the lipid and protein content in spermatozoa changed during epididymal transit and after in vitro fusion with epididymosomes. Following the in vitro fusion of caput spermatozoa with epididymosomes, the cholesterol/total phospholipid ratio of the sperm plasma membrane decreased. The effect was comparable with the cholesterol/total phospholipid ratio of native cauda spermatozoa. Co-incubation experiments of spermatozoa with biotinylated epididymosomes additionally revealed that proteins were transferred from epididymosomes to sperm. To examine the potential transfer of epididymis-derived PMCA4 to spermatozoa, immunofluorescence analysis and Ca2+-ATPase activity assays were performed. In caput spermatozoa, the PMCA4 fluorescence signal was slightly raised and Ca2+-ATPase activity increased after in vitro fusion. Thus, our experiments indicate significant changes in the lipid and protein composition of epididymal sperm following interaction with epididymosomes. Moreover, our results substantiate the presumption that PMCA4 is transferred to spermatozoa via epididymosomes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arienti G, Carlini E, Palmerini CA (1997) Fusion of human sperm to prostasomes at acidic pH. J Membr Biol 155:89–94
Aumüller G, Wilhelm B, Seitz J (1999) Apocrine secretion—fact or artifact? Anat Anz 181:437–446
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brandenburger T, Strehler EE, Filoteo AG, Caride AJ, Aumuller G, Post H, Schwarz A, Wilhelm B (2011) Switch of PMCA4 splice variants in bovine epididymis results in altered isoform expression during functional sperm maturation. J Biol Chem 286:7938–7946
Burke RW, Diamondstone BI, Velapoldi RA, Menis O (1974) Mechanisms of the Liebermann-Burchard and Zak color reactions for cholesterol. Clin Chem 20:794–801
Caballero J, Frenette G, Sullivan R (2011) Post testicular sperm maturational changes in the bull: important role of the epididymosomes and prostasomes. Vet Med Int 2011:757194
Carlini E, Palmerini CA, Cosmi EV, Arienti G (1997) Fusion of sperm with prostasomes: effects on membrane fluidity. Arch Biochem Biophys 343:6–12
Cooper TG (1998) Interactions between epididymal secretions and spermatozoa. J Reprod Fertil Suppl 53:119–136
Cooper TG (1999) Epididymis. Encycl Reprod 2:17
Corazzi L, Pistolesi R, Arienti G (1991) The fusion of liposomes to rat brain microsomal membranes regulates phosphatidylserine synthesis. J Neurochem 56:207–212
Deng X, He Y, Martin-Deleon PA (2000) Mouse Spam1 (PH-20): evidence for its expression in the epididymis and for a new category of spermatogenic-expressed genes. J Androl 21:822–832
Eickhoff R, Wilhelm B, Renneberg H, Wennemuth G, Bacher M, Linder D, Bucala R, Seitz J, Meinhardt A (2001) Purification and characterization of macrophage migration inhibitory factor as a secretory protein from rat epididymis: evidences for alternative release and transfer to spermatozoa. Mol Med 7:27–35
Eickhoff R, Jennemann G, Hoffbauer G, Schuring MP, Kaltner H, Sinowatz F, Gabius HJ, Seitz J (2006) Immunohistochemical detection of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in fetal and adult bovine epididymis: release by the apocrine secretion mode? Cells Tissues Organs 182:22–31
Fiske CH, Subbarow Y (1925) The colormetric determination of phosphorus. J Biol Chem 66:26
Fornes MW, Barbieri A, Cavicchia JC (1995) Morphological and enzymatic study of membrane-bound vesicles from the lumen of the rat epididymis. Andrologia 27:1–5
Frenette G, Sullivan R (2001) Prostasome-like particles are involved in the transfer of P25b from the bovine epididymal fluid to the sperm surface. Mol Reprod Dev 59:115–121
Frenette G, Lessard C, Sullivan R (2002) Selected proteins of “prostasome-like particles” from epididymal cauda fluid are transferred to epididymal caput spermatozoa in bull. Biol Reprod 67:308–313
Frenette G, Girouard J, Sullivan R (2006) Comparison between epididymosomes collected in the intraluminal compartment of the bovine caput and cauda epididymidis. Biol Reprod 75:885–890
Frenette G, Girouard J, D’Amours O, Allard N, Tessier L, Sullivan R (2010) Characterization of two distinct populations of epididymosomes collected in the intraluminal compartment of the bovine cauda epididymis. Biol Reprod 83:473–480
Gatti JL, Metayer S, Belghazi M, Dacheux F, Dacheux JL (2005) Identification, proteomic profiling, and origin of ram epididymal fluid exosome-like vesicles. Biol Reprod 72:1452–1465
Girouard J, Frenette G, Sullivan R (2011) Comparative proteome and lipid profiles of bovine epididymosomes collected in the intraluminal compartment of the caput and cauda epididymidis. Int J Androl 34:e475–e486
Groos S, Wilhelm B, Renneberg H, Riva A, Reichelt R, Seitz J, Aumuller G (1999) Simultaneous apocrine and merocrine secretion in the rat coagulating gland. Cell Tissue Res 295:495–504
Hall JC, Hadley J, Doman T (1991) Correlation between changes in rat sperm membrane lipids, protein, and the membrane physical state during epididymal maturation. J Androl 12:76–87
Hermo L, Jacks D (2002) Nature’s ingenuity: bypassing the classical secretory route via apocrine secretion. Mol Reprod Dev 63:394–410
Hoekstra D, Boer T de, Klappe K, Wilschut J (1984) Fluorescence method for measuring the kinetics of fusion between biological membranes. Biochemistry 23:5675–5681
Kirchhoff C, Hale G (1996) Cell-to-cell transfer of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored membrane proteins during sperm maturation. Mol Hum Reprod 2:177–184
Legare C, Berube B, Boue F, Lefievre L, Morales CR, El-Alfy M, Sullivan R (1999) Hamster sperm antigen P26h is a phosphatidylinositol-anchored protein. Mol Reprod Dev 52:225–233
Levine N, Marsh DJ (1971) Micropuncture studies of the electrochemical aspects of fluid and electrolyte transport in individual seminiferous tubules, the epididymis and the vas deferens in rats. J Physiol (Lond) 213:557–570
Nikolopoulou M, Soucek DA, Vary JC (1985) Changes in the lipid content of boar sperm plasma membranes during epididymal maturation. Biochim Biophys Acta 815:486–498
Oh JS, Han C, Cho C (2009) ADAM7 is associated with epididymosomes and integrated into sperm plasma membrane. Mol Cells 28:441–446
Okunade GW, Miller ML, Pyne GJ, Sutliff RL, O’Connor KT, Neumann JC, Andringa A, Miller DA, Prasad V, Doetschman T, Paul RJ, Shull GE (2004) Targeted ablation of plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase (PMCA) 1 and 4 indicates a major housekeeping function for PMCA1 and a critical role in hyperactivated sperm motility and male fertility for PMCA4. J Biol Chem 279:33742–33750
Palmerini CA, Carlini E, Nicolucci A, Arienti G (1999) Increase of human spermatozoa intracellular Ca2+ concentration after fusion with prostasomes. Cell Calcium 25:291–296
Parks JE, Hammerstedt RH (1985) Development changes occurring in the lipids of ram epididymal spermatozoa plasma membrane. Biol Reprod 32:653–668
Post H, Schwarz A, Brandenburger T, Aumuller G, Wilhelm B (2010) Arrangement of PMCA4 in bovine sperm membrane fractions. Int J Androl 33:775–783
Rana AP, Majumder GC, Misra S, Ghosh A (1991) Lipid changes of goat sperm plasma membrane during epididymal maturation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1061:185–196
Rejraji H, Vernet P, Drevet JR (2002) GPX5 is present in the mouse caput and cauda epididymidis lumen at three different locations. Mol Reprod Dev 63:96–103
Rejraji H, Sion B, Prensier G, Carreras M, Motta C, Frenoux JM, Vericel E, Grizard G, Vernet P, Drevet JR (2006) Lipid remodeling of murine epididymosomes and spermatozoa during epididymal maturation. Biol Reprod 74:1104–1113
Sanchez-Luengo S, Aumuller G, Albrecht M, Sen PC, Rohm K, Wilhelm B (2004) Interaction of PDC-109, the major secretory protein from bull seminal vesicles, with bovine sperm membrane Ca2+-ATPase. J Androl 25:234–244
Schuh K, Cartwright EJ, Jankevics E, Bundschu K, Liebermann J, Williams JC, Armesilla AL, Emerson M, Oceandy D, Knobeloch KP, Neyses L (2004) Plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase 4 is required for sperm motility and male fertility. J Biol Chem 279:28220–28226
Sikdar R, Ganguly U, Pal P, Mazumder B, Sen PC (1991) Biochemical characterization of a calcium ion stimulated-ATPase from goat spermatozoa. Mol Cell Biochem 103:121–130
Sullivan R, Saez F, Girouard J, Frenette G (2005) Role of exosomes in sperm maturation during the transit along the male reproductive tract. Blood Cells Mol Dis 35:1–10
Triphan J, Aumuller G, Brandenburger T, Wilhelm B (2007) Localization and regulation of plasma membrane Ca(2+)-ATPase in bovine spermatozoa. Eur J Cell Biol 86:265–273
Wandernoth PM, Raubuch M, Mannowetz N, Becker HM, Deitmer JW, Sly WS, Wennemuth G (2010) Role of carbonic anhydrase IV in the bicarbonate-mediated activation of murine and human sperm. PLoS One 5:e15061
Wennemuth G, Babcock DF, Hille B (2003) Calcium clearance mechanisms of mouse sperm. J Gen Physiol 122:115–128
Wilhelm B, Keppler C, Hoffbauer G, Lottspeich F, Linder D, Meinhardt A, Aumuller G, Seitz J (1998) Cytoplasmic carbonic anhydrase II of rat coagulating gland is secreted via the apocrine export mode. J Histochem Cytochem 46:505–511
Wilhelm B, Meinhardt A, Renneberg H, Linder D, Gabius HJ, Aumuller G, Seitz J (1999) Serum albumin as a potential carrier for the apocrine secretion of proteins in the rat coagulating gland. Eur J Cell Biol 78:256–264
Wilhelm B, Brandenburger T, Post H, Aumuller G (2008) Expression and localization of PMCA4 in rat testis and epididymis. Histochem Cell Biol 129:331–343
Yanagimachi R, Kamiguchi Y, Mikamo K, Suzuki F, Yanagimachi H (1985) Maturation of spermatozoa in the epididymis of the Chinese hamster. Am J Anat 172:317–330
Zhang J, Xiao P, Zhang X (2009) Phosphatidylserine externalization in caveolae inhibits Ca2+ efflux through plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase in ECV304. Cell Calcium 45:177–184
Acknowledgments
The authors are greatly indebted to Anne Henkeler, Gudrun Hoffbauer and Claudia Keppler for their expert technical help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schwarz, A., Wennemuth, G., Post, H. et al. Vesicular transfer of membrane components to bovine epididymal spermatozoa. Cell Tissue Res 353, 549–561 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-013-1633-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-013-1633-7