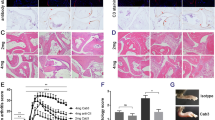
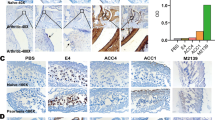
Abstract
Antibodies against cartilage proteins are highly prevalent in the sera and synovial fluids of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients and also precede disease induction in various spontaneous and induced animal models of arthritis. These antibodies play an important role in the induction and perpetuation of the clinical disease. Antibodies binding to cartilage protein(s), especially the major articular cartilage protein, collagen type II (CII) can induce, in naive mice, an acute form of arthritis that can substantially destroy the cartilage and bone architecture. More importantly, these anti-CII antibodies can also directly cause the destruction of the target tissue preceding and independently of disease development and in the absence of any other pathogenic inflammatory factors or the action of immune cells. Alternatively, antibodies to citrullinated protein antigens and rheumatoid factor are well-validated prognostic and diagnostic markers of severe erosive RA, although their arthritogenic potential is questioned. Recently, we have found that the monoclonal antibodies to citrulline-modified cartilage protein can bind cartilage and synovial tissue and mediate arthritis in mice. Similarly, one of the pathogenic anti-CII monoclonal antibodies has rheumatoid-factor-like activity, suggesting a disease-inducing role for these commonly prevalent antibodies in RA patients. Interestingly, recent findings have also shown that the enzymatic cleavage or modification of pathogenic IgG antibodies protects the cartilage surface, thereby opening up new therapeutic possibilities for protecting the cartilage from inflammatory damage.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adkison AM, Raptis SZ, Kelley DG, Pham CT (2002) Dipeptidyl peptidase I activates neutrophil-derived serine proteases and regulates the development of acute experimental arthritis. J Clin Invest 109:363–371
Amirahmadi SF, Pho MH, Gray RE, Crombie DE, Whittingham SF, Zuasti BB, Van Damme MP, Rowley MJ (2004) An arthritogenic monoclonal antibody to type II collagen, CII-C1, impairs cartilage formation by cultured chondrocytes. Immunol Cell Biol 82:427–434
Amirahmadi SF, Whittingham S, Crombie DE, Nandakumar KS, Holmdahl R, Mackay IR, Damme MP van, Rowley MJ (2005) Arthritogenic anti-type II collagen antibodies are pathogenic for cartilage-derived chondrocytes independent of inflammatory cells. Arthritis Rheum 52:1897–1906
Auger I, Sebbag M, Vincent C, Balandraud N, Guis S, Nogueira L, Svensson B, Cantagrel A, Serre G, Roudier J (2005) Influence of HLA-DR genes on the production of rheumatoid arthritis-specific autoantibodies to citrullinated fibrinogen. Arthritis Rheum 52:3424–3432
Bajtner E, Nandakumar KS, Engstrom A, Holmdahl R (2005) Chronic development of collagen-induced arthritis is associated with arthritogenic antibodies against specific epitopes on type II collagen. Arthritis Res Ther 7:R1148–R1157
Banda NK, Kraus D, Vondracek A, Huynh LH, Bendele A, Holers VM, Arend WP (2002) Mechanisms of effects of complement inhibition in murine collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 46:3065–3075
Banda NK, Kraus DM, Muggli M, Bendele A, Holers VM, Arend WP (2003) Prevention of collagen-induced arthritis in mice transgenic for the complement inhibitor complement receptor 1-related gene/protein y. J Immunol 171:2109–2115
Banda NK, Thurman JM, Kraus D, Wood A, Carroll MC, Arend WP, Holers VM (2006) Alternative complement pathway activation is essential for inflammation and joint destruction in the passive transfer model of collagen-induced arthritis. J Immunol 177:1904–1912
Banda NK, Takahashi K, Wood AK, Holers VM, Arend WP (2007) Pathogenic complement activation in collagen antibody-induced arthritis in mice requires amplification by the alternative pathway. J Immunol 179:4101–4109
Banda NK, Wood AK, Takahashi K, Levitt B, Rudd PM, Royle L, Abrahams JL, Stahl GL, Holers VM, Arend WP (2008) Initiation of the alternative pathway of murine complement by immune complexes is dependent on N-glycans in IgG antibodies. Arthritis Rheum 58:3081–3089
Burkhardt H, Koller T, Engstrom A, Nandakumar KS, Turnay J, Kraetsch HG, Kalden JR, Holmdahl R (2002) Epitope-specific recognition of type II collagen by rheumatoid arthritis antibodies is shared with recognition by antibodies that are arthritogenic in collagen-induced arthritis in the mouse. Arthritis Rheum 46:2339–2348
Burkhardt H, Sehnert B, Bockermann R, Engstrom A, Kalden JR, Holmdahl R (2005) Humoral immune response to citrullinated collagen type II determinants in early rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Immunol 35:1643–1652
Burkhardt H, Huffmeier U, Spriewald B, Bohm B, Rau R, Kallert S, Engstrom A, Holmdahl R, Reis A (2006) Association between protein tyrosine phosphatase 22 variant R620W in conjunction with the HLA-DRB1 shared epitope and humoral autoimmunity to an immunodominant epitope of cartilage-specific type II collagen in early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 54:82–89
Carlsen S, Nandakumar KS, Holmdahl R (2006) Type IX collagen deficiency enhances the binding of cartilage-specific antibodies and arthritis severity. Arthritis Res Ther 8:R102
Carlsen S, Nandakumar KS, Backlund J, Holmberg J, Hultqvist M, Vestberg M, Holmdahl R (2008) Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein induction of chronic arthritis in mice. Arthritis Rheum 58:2000–2011
Caspi D, Anouk M, Golan I, Paran D, Kaufman I, Wigler I, Levartovsky D, Litinsky I, Elkayam O (2006) Synovial fluid levels of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies and IgA rheumatoid factor in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 55:53–56
Charriere G, Hartmann DJ, Vignon E, Ronziere MC, Herbage D, Ville G (1988) Antibodies to types I, II, IX, and XI collagen in the serum of patients with rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheum 31:325–332
Collin M, Olsen A (2001) EndoS, a novel secreted protein from Streptococcus pyogenes with endoglycosidase activity on human IgG. EMBO J 20:3046–3055
Cook AD, Rowley MJ, Stockman A, Muirden KD, Mackay IR (1994) Specificity of antibodies to type II collagen in early rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 21:1186–1191
Cook AD, Rowley MJ, Mackay IR, Gough A, Emery P (1996) Antibodies to type II collagen in early rheumatoid arthritis. Correlation with disease progression. Arthritis Rheum 39:1720–1727
Cook AD, Stockman A, Brand CA, Tait BD, Mackay IR, Muirden KD, Bernard CC, Rowley MJ (1999) Antibodies to type II collagen and HLA disease susceptibility markers in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 42:2569–2576
Cook AD, Gray R, Ramshaw J, Mackay IR, Rowley MJ (2004) Antibodies against the CB10 fragment of type II collagen in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 6:R477–R483
Cremer MA, Rosloniec EF, Kang AH (1998) The cartilage collagens: a review of their structure, organization, and role in the pathogenesis of experimental arthritis in animals and in human rheumatic disease. J Mol Med 76:275–288
Crombie DE, Turer M, Zuasti BB, Wood B, McNaughton D, Nandakumar KS, Holmdahl R, Van Damme MP, Rowley MJ (2005) Destructive effects of murine arthritogenic antibodies to type II collagen on cartilage explants in vitro. Arthritis Res Ther 7:R927–R937
Daumer KM, Khan AU, Steinbeck MJ (2000) Chlorination of pyridinium compounds. Possible role of hypochlorite, N-chloramines, and chlorine in the oxidation of pyridinoline cross-links of articular cartilage collagen type II during acute inflammation. J Biol Chem 275:34681–34692
Dzhambazov B, Holmdahl M, Yamada H, Lu S, Vestberg M, Holm B, Johnell O, Kihlberg J, Holmdahl R (2005) The major T cell epitope on type II collagen is glycosylated in normal cartilage but modified by arthritis in both rats and humans. Eur J Immunol 35:357–366
Fujii K, Tsuji M, Kitamura A, Murota K (1992) The diagnostic significance of anti-type II collagen antibody assay in rheumatoid arthritis. Int Orthop 16:272–276
Goodfellow RM, Williams AS, Levin JL, Williams BD, Morgan BP (2000) Soluble complement receptor one (sCR1) inhibits the development and progression of rat collagen-induced arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol 119:210–216
Gray RE, Seng N, Mackay IR, Rowley MJ (2004) Measurement of antibodies to collagen II by inhibition of collagen fibril formation in vitro. J Immunol Methods 285:55–61
Helm-van Mil AH van der, Verpoort KN, Breedveld FC, Huizinga TW, Toes RE, Vries RR de (2006) The HLA-DRB1 shared epitope alleles are primarily a risk factor for anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies and are not an independent risk factor for development of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 54:1117–1121
Hietala MA, Jonsson IM, Tarkowski A, Kleinau S, Pekna M (2002) Complement deficiency ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis in mice. J Immunol 169:454–459
Hietala MA, Nandakumar KS, Persson L, Fahlen S, Holmdahl R, Pekna M (2004) Complement activation by both classical and alternative pathways is critical for the effector phase of arthritis. Eur J Immunol 34:1208–1216
Hoffmann MH, Tuncel J, Skriner K, Tohidast-Akrad M, Turk B, Pinol-Roma S, Serre G, Schett G, Smolen JS, Holmdahl R, Steiner G (2007) The rheumatoid arthritis-associated autoantigen hnRNP-A2 (RA33) is a major stimulator of autoimmunity in rats with pristane-induced arthritis. J Immunol 179:7568–7576
Holmdahl R, Rubin K, Klareskog L, Larsson E, Wigzell H (1986) Characterization of the antibody response in mice with type II collagen-induced arthritis, using monoclonal anti-type II collagen antibodies. Arthritis Rheum 29:400–410
Holmdahl R, Bailey C, Enander I, Mayer R, Klareskog L, Moran T, Bona C (1989) Origin of the autoreactive anti-type II collagen response. II. Specificities, antibody isotypes and usage of V gene families of anti-type II collagen B cells. J Immunol 142:1881–1886
Holmdahl R, Jansson L, Larsson A, Jonsson R (1990) Arthritis in DBA/1 mice induced with passively transferred type II collagen immune serum. Immunohistopathology and serum levels of anti-type II collagen auto-antibodies. Scand J Immunol 31:147–157
Hughes LB, Moreland LW (2001) New therapeutic approaches to the management of rheumatoid arthritis. BioDrugs 15:379–393
Jaalinoja J, Nissila M, Kauppi MJ, Hakala M, Laiho K, Karttunen R, Horkko S, Ala-Kokko L (2008) Serum antibodies against intact human collagen IX are elevated at onset of rheumatoid arthritis but are not related to development of erosions. J Rheumatol 35:745–751
Johansson AC, Sundler M, Kjellen P, Johannesson M, Cook A, Lindqvist AK, Nakken B, Bolstad AI, Jonsson R, Alarcon-Riquelme M, Holmdahl R (2001) Genetic control of collagen-induced arthritis in a cross with NOD and C57BL/10 mice is dependent on gene regions encoding complement factor 5 and FcgammaRIIb and is not associated with loci controlling diabetes. Eur J Immunol 31:1847–1856
Kagari T, Tanaka D, Doi H, Shimozato T (2003) Essential role of Fc gamma receptors in anti-type II collagen antibody-induced arthritis. J Immunol 170:4318–4324
Kerwar SS, Englert ME, McReynolds RA, Landes MJ, Lloyd JM, Oronsky AL, Wilson FJ (1983a) Type II collagen-induced arthritis. Studies with purified anticollagen immunoglobulin. Arthritis Rheum 26:1120–1131
Kerwar SS, Gordon S, McReynolds RA, Oronsky AL (1983b) Passive transfer of arthritis by purified anticollagen immunoglobulin: localization of 125I-labeled antibody. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 29:318–321
Klareskog L, Johnell O, Hulth A, Holmdahl R, Rubin K (1986) Reactivity of monoclonal anti-type II collagen antibodies with cartilage and synovial tissue in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 29:730–738
Kraetsch HG, Unger C, Wernhoff P, Schneider C, Kalden JR, Holmdahl R, Burkhardt H (2001) Cartilage-specific autoimmunity in rheumatoid arthritis: characterization of a triple helical B cell epitope in the integrin-binding-domain of collagen type II. Eur J Immunol 31:1666–1673
Krapp S, Mimura Y, Jefferis R, Huber R, Sondermann P (2003) Structural analysis of human IgG-Fc glycoforms reveals a correlation between glycosylation and structural integrity. J Mol Biol 325:979–989
Masson-Bessiere C, Sebbag M, Durieux JJ, Nogueira L, Vincent C, Girbal-Neuhauser E, Durroux R, Cantagrel A, Serre G (2000) In the rheumatoid pannus, anti-filaggrin autoantibodies are produced by local plasma cells and constitute a higher proportion of IgG than in synovial fluid and serum. Clin Exp Immunol 119:544–552
Mathsson L, Mullazehi M, Wick MC, Sjoberg O, Vollenhoven R van, Klareskog L, Ronnelid J (2008) Antibodies against citrullinated vimentin in rheumatoid arthritis: higher sensitivity and extended prognostic value concerning future radiographic progression as compared with antibodies against cyclic citrullinated peptides. Arthritis Rheum 58:36–45
Mewar D, Wilson AG (2006) Autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis: a review. Biomed Pharmacother 60:648–655
Mizuno M, Nishikawa K, Spiller OB, Morgan BP, Okada N, Okada H, Matsuo S (2001) Membrane complement regulators protect against the development of type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Arthritis Rheum 44:2425–2434
Morgan K, Clague RB, Shaw MJ, Firth SA, Twose TM, Holt PJ (1981) Native type II collagen—induced arthritis in the rat: the effect of complement depletion by cobra venom factor. Arthritis Rheum 24:1356–1362
Mullazehi M, Mathsson L, Lampa J, Ronnelid J (2006) Surface-bound anti-type II collagen-containing immune complexes induce production of tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin-1beta, and interleukin-8 from peripheral blood monocytes via Fc gamma receptor IIA: a potential pathophysiologic mechanism for humoral anti-type II collagen immunity in arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 54:1759–1771
Mullazehi M, Mathsson L, Lampa J, Ronnelid J (2007) High anti-collagen type-II antibody levels and induction of proinflammatory cytokines by anti-collagen antibody-containing immune complexes in vitro characterise a distinct rheumatoid arthritis phenotype associated with acute inflammation at the time of disease onset. Ann Rheum Dis 66:537–541
Nandakumar KS, Holmdahl R (2005) Efficient promotion of collagen antibody induced arthritis (CAIA) using four monoclonal antibodies specific for the major epitopes recognized in both collagen induced arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol Methods 304:126–136
Nandakumar KS, Holmdahl R (2008) Therapeutic cleavage of IgG: new avenues for treating inflammation. Trends Immunol 29:173–178
Nandakumar KS, Svensson L, Holmdahl R (2003a) Collagen type II-specific monoclonal antibody-induced arthritis in mice: description of the disease and the influence of age, sex, and genes. Am J Pathol 163:1827–1837
Nandakumar KS, Andren M, Martinsson P, Bajtner E, Hellstrom S, Holmdahl R, Kleinau S (2003b) Induction of arthritis by single monoclonal IgG anti-collagen type II antibodies and enhancement of arthritis in mice lacking inhibitory FcgammaRIIB. Eur J Immunol 33:2269–2277
Nandakumar KS, Backlund J, Vestberg M, Holmdahl R (2004) Collagen type II (CII)-specific antibodies induce arthritis in the absence of T or B cells but the arthritis progression is enhanced by CII-reactive T cells. Arthritis Res Ther 6:R544–R550
Nandakumar KS, Johansson BP, Bjorck L, Holmdahl R (2007a) Blocking of experimental arthritis by cleavage of IgG antibodies in vivo. Arthritis Rheum 56:3253–3260
Nandakumar KS, Collin M, Olsen A, Nimmerjahn F, Blom AM, Ravetch JV, Holmdahl R (2007b) Endoglycosidase treatment abrogates IgG arthritogenicity: importance of IgG glycosylation in arthritis. Eur J Immunol 37:2973–2982
Nandakumar KS, Bajtner E, Hill L, Bohm B, Rowley MJ, Burkhardt H, Holmdahl R (2008) Arthritogenic antibodies specific for a major type II collagen triple-helical epitope bind and destabilize cartilage independent of inflammation. Arthritis Rheum 58:184–196
Nezlin R, Ghetie V (2004) Interactions of immunoglobulins outside the antigen-combining site. Adv Immunol 82:155–215
Nimmerjahn F, Ravetch JV (2007) Fc-receptors as regulators of immunity. Adv Immunol 96:179–204
Pereira RS, Black CM, Duance VC, Jones VE, Jacoby RK, Welsh KI (1985) Disappearing collagen antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet II:501–502
Petkova SB, Konstantinov KN, Sproule TJ, Lyons BL, Awwami MA, Roopenian DC (2006) Human antibodies induce arthritis in mice deficient in the low-affinity inhibitory IgG receptor Fc gamma RIIB. J Exp Med 203:275–280
Rintisch C, Ameri J, Olofsson P, Luthman H, Holmdahl R (2008) Positional cloning of the Igl genes controlling rheumatoid factor production and allergic bronchitis in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:14005–14010
Ronnelid J, Lysholm J, Engstrom-Laurent A, Klareskog L, Heyman B (1994) Local anti-type II collagen antibody production in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid. Evidence for an HLA-DR4-restricted IgG response. Arthritis Rheum 37:1023–1029
Roughley PJ (2001) Articular cartilage and changes in arthritis: noncollagenous proteins and proteoglycans in the extracellular matrix of cartilage. Arthritis Res 3:342–347
Saxne T, Heinegard D (1992) Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein: a novel marker of cartilage turnover detectable in synovial fluid and blood. Br J Rheumatol 31:583–591
Saydain G, George L, Raoof S (2002) New therapies: plasmapheresis, intravenous immunoglobulin, and monoclonal antibodies. Crit Care Clin 18:957–975
Schellekens GA, Jong BA de, Hoogen FH van den, Putte LB van de, Venrooij WJ van (1998) Citrulline is an essential constituent of antigenic determinants recognized by rheumatoid arthritis-specific autoantibodies. J Clin Invest 101:273–281
Schulte S, Unger C, Mo JA, Wendler O, Bauer E, Frischholz S, Mark K von der, Kalden JR, Holmdahl R, Burkhardt H (1998) Arthritis-related B cell epitopes in collagen II are conformation-dependent and sterically privileged in accessible sites of cartilage collagen fibrils. J Biol Chem 273:1551–1561
Sitaru C, Zillikens D (2005) Mechanisms of blister induction by autoantibodies. Exp Dermatol 14:861–875
Sitaru C, Mihai S, Zillikens D (2007) The relevance of the IgG subclass of autoantibodies for blister induction in autoimmune bullous skin diseases. Arch Dermatol Res 299:1–8
Slatter DA, Paul RG, Murray M, Bailey AJ (1999) Reactions of lipid-derived malondialdehyde with collagen. J Biol Chem 274:19661–19669
Souto-Carneiro MM, Burkhardt H, Muller EC, Hermann R, Otto A, Kraetsch HG, Sack U, Konig A, Heinegard D, Muller-Hermelink HK, Krenn V (2001) Human monoclonal rheumatoid synovial B lymphocyte hybridoma with a new disease-related specificity for cartilage oligomeric matrix protein. J Immunol 166:4202–4208
Stuart JM, Dixon FJ (1983) Serum transfer of collagen-induced arthritis in mice. J Exp Med 158:378–392
Stuart JM, Huffstutter EH, Townes AS, Kang AH (1983a) Incidence and specificity of antibodies to types I, II, III, IV, and V collagen in rheumatoid arthritis and other rheumatic diseases as measured by 125I-radioimmunoassay. Arthritis Rheum 26:832–840
Stuart JM, Tomoda K, Yoo TJ, Townes AS, Kang AH (1983b) Serum transfer of collagen-induced arthritis. II. Identification and localization of autoantibody to type II collagen in donor and recipient rats. Arthritis Rheum 26:1237–1244
Takagishi K, Kaibara N, Hotokebuchi T, Arita C, Morinaga M, Arai K (1985) Serum transfer of collagen arthritis in congenitally athymic nude rats. J Immunol 134:3864–3867
Tarkowski A, Klareskog L, Carlsten H, Herberts P, Koopman WJ (1989a) Secretion of antibodies to types I and II collagen by synovial tissue cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 32:1087–1092
Tarkowski A, Holmdahl R, Klareskog L (1989b) Rheumatoid factors in mice. Monogr Allergy 26:214–229
Terato K, Shimozuru Y, Katayama K, Takemitsu Y, Yamashita I, Miyatsu M, Fujii K, Sagara M, Kobayashi S, Goto M, et al (1990) Specificity of antibodies to type II collagen in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 33:1493–1500
Terato K, Hasty KA, Reife RA, Cremer MA, Kang AH, Stuart JM (1992) Induction of arthritis with monoclonal antibodies to collagen. J Immunol 148:2103–2108
Terato K, Harper DS, Griffiths MM, Hasty DL, Ye XJ, Cremer MA, Seyer JM (1995) Collagen-induced arthritis in mice: synergistic effect of E. coli lipopolysaccharide bypasses epitope specificity in the induction of arthritis with monoclonal antibodies to type II collagen. Autoimmunity 22:137–147
Terato K, DeArmey DA, Ye XJ, Griffiths MM, Cremer MA (1996) The mechanism of autoantibody formation to cartilage in rheumatoid arthritis: possible cross-reaction of antibodies to dietary collagens with autologous type II collagen. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 79:142–154
Tsark EC, Wang W, Teng YC, Arkfeld D, Dodge GR, Kovats S (2002) Differential MHC class II-mediated presentation of rheumatoid arthritis autoantigens by human dendritic cells and macrophages. J Immunol 169:6625–6633
Uysal H, Sehnert B, Nandakumar KS, Boiers U, Burkhardt H, Holmdahl R, Thunnissen MM (2008) The crystal structure of the pathogenic collagen type II-specific mouse monoclonal antibody CIIC1 Fab: structure to function analysis. Mol Immunol 45:2196–2204
Uysal H, Bockermann R, Nandakumar KS, Sehnert B, Bajtner E, Engstrom A, Serre G, Burkhardt H, Thunnissen MM, Holmdahl R (2009) Structure and pathogenicity of antibodies specific for citrullinated collagen type II in experimental arthritis. J Exp Med 206:449–462
Vincents B, Pawel-Rammingen U von, Bjorck L, Abrahamson M (2004) Enzymatic characterization of the streptococcal endopeptidase, IdeS, reveals that it is a cysteine protease with strict specificity for IgG cleavage due to exosite binding. Biochemistry 43:15540–15549
Vos K, Steenbakkers P, Miltenburg AM, Bos E, Heuvel MW van den, Hogezand RA van, Vries RR de, Breedveld FC, Boots AM (2000) Raised human cartilage glycoprotein-39 plasma levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory conditions. Ann Rheum Dis 59:544–548
Vossenaar ER, Nijenhuis S, Helsen MM, Heijden A van der, Senshu T, Berg WB van den, Venrooij WJ van, Joosten LA (2003) Citrullination of synovial proteins in murine models of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 48:2489–2500
Wang Y, Rollins SA, Madri JA, Matis LA (1995) Anti-C5 monoclonal antibody therapy prevents collagen-induced arthritis and ameliorates established disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:8955–8959
Wang Y, Kristan J, Hao L, Lenkoski CS, Shen Y, Matis LA (2000) A role for complement in antibody-mediated inflammation: C5-deficient DBA/1 mice are resistant to collagen-induced arthritis. J Immunol 164:4340–4347
Watson WC, Townes AS (1985) Genetic susceptibility to murine collagen II autoimmune arthritis. Proposed relationship to the IgG2 autoantibody subclass response, complement C5, major histocompatibility complex (MHC) and non-MHC loci. J Exp Med 162:1878–1891
Wenig K, Chatwell L, Pawel-Rammingen U von, Bjorck L, Huber R, Sondermann P (2004) Structure of the streptococcal endopeptidase IdeS, a cysteine proteinase with strict specificity for IgG. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:17371–17376
Wernhoff P, Unger C, Bajtner E, Burkhardt H, Holmdahl R (2001) Identification of conformation-dependent epitopes and V gene selection in the B cell response to type II collagen in the DA rat. Int Immunol 13:909–919
Wernhoff P, Olofsson P, Holmdahl R (2003) The genetic control of rheumatoid factor production in a rat model of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 48:3584–3596
Wooley PH, Luthra HS, Singh SK, Huse AR, Stuart JM, David CS (1984) Passive transfer of arthritis to mice by injection of human anti-type II collagen antibody. Mayo Clin Proc 59:737–743
Yamada H, Dzhambazov B, Bockermann R, Blom T, Holmdahl R (2004) A transient post-translationally modified form of cartilage type II collagen is ignored by self-reactive T cells. J Immunol 173:4729–4735
Acknowledgements
I am grateful to Rikard Holmdahl for support and critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
I thank the following for financial support: the Alex and Eva Wallström Foundation, Professor Nanna Svartz Foundation, King Gustaf V’s 80-year Foundation, Åke Wiberg’s Foundation, and the Swedish Rheumatism Association.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nandakumar, K.S. Pathogenic antibody recognition of cartilage. Cell Tissue Res 339, 213–220 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-009-0816-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-009-0816-8