Abstract
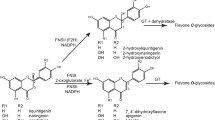
Flavonol synthase (FLS) (EC-number 1.14.11.23), the enzyme that catalyses the conversion of flavonols into dihydroflavonols, is part of the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway. In Arabidopsis thaliana, this activity is thought to be encoded by several loci. In addition to the FLAVONOL SYNTHASE1 (FLS1) locus that has been confirmed by enzyme activity assays, loci displaying similarity of the deduced amino acid sequences to FLS1 have been identified. We studied the putative A. thaliana FLS gene family using a combination of genetic and metabolite analysis approaches. Although several of the FLS gene family members are expressed, only FLS1 appeared to influence flavonoid biosynthesis. Seedlings of an A. thaliana fls1 null mutant (fls1-2) show enhanced anthocyanin levels, drastic reduction in flavonol glycoside content and concomitant accumulation of glycosylated forms of dihydroflavonols, the substrate of the FLS reaction. By using a leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase (ldox) fls1-2 double mutant, we present evidence that the remaining flavonol glycosides found in the fls1-2 mutant are synthesized in planta by the FLS-like side activity of the LDOX enzyme.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANR:
-
Anthocyanidin reductase
- CHS:
-
Chalcone synthase
- CHI:
-
Chalcone isomerase
- DFR:
-
Dihydroflavonol 4-reductase
- DHF:
-
Dihydroflavonol
- DPBA:
-
Diphenylboric acid 2-aminoethylester
- EBG:
-
Early biosynthetic gene
- ESI:
-
Electro spray ionization
- F3H:
-
Flavanone 3β-hydroxylase
- F3′H:
-
Flavonoid 3′-hydroxylase
- FLS:
-
Flavonol synthase
- GT:
-
Glycosyltransferase
- GUS:
-
β-Glucuronidase
- GUS′:
-
Standardized specific β-glucuronidase activity
- HPLC:
-
High performance liquid chromatography
- HPTLC:
-
High performance thin layer chromatography
- LBG:
-
Late biosynthetic gene
- LC:
-
Liquid chromatography
- LUC:
-
Luciferase
- LDOX:
-
Leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase
- MS:
-
Mass spectrometry
- MU:
-
4-Methylumbelliferone
- PDA:
-
Photo-diode array
- QTOF:
-
Quadrupole-time-of-flight
- 3GT:
-
Anthocyanidin 3-O-glycosyltransferase
References
Albert S, Delseny M, Devic M (1997) BANYULS, a novel negative regulator of flavonoid biosynthesis in the Arabidopsis seed coat. Plant J 11:289–299
Blount JW, Korth KL, Masoud SA, Rasmussen S, Lamb C, Dixon RA (2000) Altering expression of cinnamic acid 4-hydroxylase in transgenic plants provides evidence for a feedback loop at the entry point into the phenylpropanoid pathway. Plant Physiol 122:107–116
Bolwell GP, Cramer CL, Lamb CJ, Schuch W, Dixon RA (1986) l-Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase from Phaseolus vulgaris: modulation of the levels of active enzyme by trans-cinnamic acid. Planta 169:97–107
Bovy A, de Vos R, Kemper M, Schijlen E, Almenar Pertejo M, Muir S, Collins G, Robinson S, Verhoeyen M, Hughes S, Santos-Buelga C, van Tunen A (2002) High-flavonol tomatoes resulting from the heterologous expression of the maize transcription factor genes LC and C1. Plant Cell 14:2509–2526
Britsch L, Heller W, Grisebach H (1981) Conversion of flavanone to flavone, dihydroflavonol to flavonol with enzyme systems from cell cultures of parsley. Z Naturforsch C 36:742–750
Britsch L, Dedio J, Saedler H, Forkmann G (1993) Molecular characterization of flavanone 3 beta-hydroxylases. Consensus sequence, comparison with related enzymes and the role of conserved histidine residues. Eur J Biochem 217:745–754
Chenna R, Sugawara H, Koike T, Lopez R, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG, Thompson JD (2003) Multiple sequence alignment with the Clustal series of programs. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3497–3500
Chua CS, Biermann D, Goo KS, Sim TS (2008) Elucidation of active site residues of Arabidopsis thaliana flavonol synthase provides a molecular platform for engineering flavonols. Phytochemistry 69:66–75
Clifton IJ, McDonough MA, Ehrismann MD, Kershaw NJ, Granatino N, Schofield CJ (2006) Structural studies on 2-oxoglutarate oxygenases and related double-stranded β-helix fold proteins. J Inorg Biochem 100:644–669
De Vos RCH, Moco S, Lommen A, Keurentjes JJB, Bino RJ, Hall RD (2007) Untargeted large-scale plant metabolomics using liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Nat Protoc 2:778–791
Edwards K, Johnstone C, Thompson C (1991) A simple and rapid method for the preparation of plant genomic DNA for PCR analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 19:1349
Forkmann G (1991) Flavonoids as flower pigments: the formation of the natural spectrum and its extension by genetic engineering. Plant Breed 106:1–26
Forkmann G, De Vlaming P, Spribille R, Wiering H, Schram AW (1986) Genetic and biochemical studies on the conversion of dihydroflavonols to flavonols in flowers of Petunia hybrida. Z Naturforsch C 41:179–186
Hahlbrock K, Knobloch KH, Kreuzaler F, Potts JR, Wellmann E (1976) Coordinated induction and subsequent activity changes of two groups of metabolically interrelated enzymes. Light-induced synthesis of flavonoid glycosides in cell suspension cultures of Petroselinum hortense. Eur J Biochem 61:199–206
Harborne JB, Williams CA (2000) Advances in flavonoid research since 1992. Phytochemistry 55:481–504
Hartmann U, Sagasser M, Mehrtens F, Stracke R, Weisshaar B (2005) Differential combinatorial interactions of cis-acting elements recognized by R2R3-MYB, BZIP, and BHLH factors control light-responsive and tissue-specific activation of phenylpropanoid biosynthesis genes. Plant Mol Biol 57:155–171
Heller W, Forkmann G (1994) Biosynthesis of flavonoids. In: Harborne JB (ed) The flavonoids. Chapman & Hall, London, pp 499–535
Holton TA, Brugliera F, Tanaka Y (1993) Cloning and expression of flavonol synthase from Petunia hybrida. Plant J 4:1003–1010
Iwashina T (2003) Flavonoid function and activity to plants and other organisms. Biol Sci Space 17:24–44
Jones P, Messner B, Nakajima J, Schaffner AR, Saito K (2003) UGT73C6 and UGT78D1, glycosyltransferases involved in flavonol glycoside biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Biol Chem 278:43910–43918
Keurentjes JJ, Fu J, De Vos RCH, Lommen A, Hall RD, Bino RJ, van der Plas LH, Jansen RC, Vreugdenhil D, Koornneef M (2006) The genetics of plant metabolism. Nat Genet 38:842–849
Kubasek WL, Shirley BW, McKillop A, Goodman HM, Briggs W, Ausubel FM (1992) Regulation of flavonoid biosynthetic genes in germinating Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant Cell 4:1229–1236
Le Gall G, DuPont MS, Mellon FA, Davis AL, Collins GJ, Verhoeyen ME, Colquhoun IJ (2003) Characterization and content of flavonoid glycosides in genetically modified tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) fruits. J Agric Food Chem 51:2438–2446
Leonard E, Yan Y, Koffas MA (2006) Functional expression of a P450 flavonoid hydroxylase for the biosynthesis of plant-specific hydroxylated flavonols in Escherichia coli. Metab Eng 8:172–181
Lillo C, Lea US, Ruoff P (2008) Nutrient depletion as a key factor for manipulating gene expression and product formation in different branches of the flavonoid pathway. Plant Cell Environ 31:587–601
Loake GJ, Choudhary AD, Harrison MJ, Mavandad M, Lamb CJ, Dixon RJ (1991) Phenylpropanoid pathway intermediates regulate transient expression of a chalcone synthase gene promoter. Plant Cell 3:829–840
Lukacin R, Britsch L (1997) Identification of strictly conserved histidine and arginine residues as part of the active site in Petunia hybrida flavanone 3beta-hydroxylase. Eur J Biochem 249:748–757
Lukacin R, Wellmann F, Britsch L, Martens S, Matern U (2003) Flavonol synthase from Citrus unshiu is a bifunctional dioxygenase. Phytochemistry 62:287–292
Markham KR (1989) Flavones, flavonols and their glycosides. In: Dey PM, Harborne JB (eds) Methods in plant biochemistry. Academic Press, New York, pp 197–236
Martens S, Forkmann G (1999) Cloning and expression of flavone synthase II from Gerbera hybrids. Plant J 20:611–618
Martens S, Forkmann G, Matern U, Lukacin R (2001) Cloning of parsley flavone synthase I. Phytochemistry 58:43–46
Martens S, Forkmann G, Britsch L, Wellmann F, Matern U, Lukacin R (2003) Divergent evolution of flavonoid 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases in parsley. FEBS Lett 544:93–98
Martin C, Prescott A, Mackay S, Bartlett J, Vrijlandt E (1991) Control of anthocyanin biosynthesis in flowers of Antirrhinum majus. Plant J 1:37–49
Mehrtens F, Kranz H, Bednarek P, Weisshaar B (2005) The Arabidopsis transcription factor MYB12 is a flavonol-specific regulator of phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 138:1083–1096
Moco S, Bino RJ, Vorst O, Verhoeven HA, de Groot J, van Beek TA, Vervoort J, de Vos CHR (2006) A liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry-based metabolome database for tomato. J Plant Physiol 141:1205–1218
Myllylä R, Günzler V, Kivirikko KI, Kaska DD (1992) Modification of vertebrate and algal prolyl 4-hydroxylases and vertebrate lysyl hydroxylase by diethyl pyrocarbonate. Evidence for histidine residues in the catalytic site of 2-oxoglutarate-coupled dioxygenases. Biochem J 286:923–927
Owens DK, Alerding AB, Crosby KC, Bandara AB, Westwood JH, Winkel BS (2008a) Functional analysis of a predicted flavonol synthase gene family in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 147:1046–1061
Owens DK, Crosby KC, Runac J, Howard BA, Winkel BS (2008b) Biochemical and genetic characterization of Arabidopsis flavanone 3beta-hydroxylase. Plant Physiol Biochem 46:833–843
Pelletier MK, Murrell JR, Shirley BW (1997) Characterization of flavonol synthase and leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 113:1437–1445
Pelletier MK, Burbulis IE, Shirley BW (1999) Disruption of specific flavonoid genes enhances the accumulation of flavonoid enzymes and endproducts in Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant Mol Biol 40:45–54
Prescott AG, Stamford NPJ, Wheeler G, Firmin JL (2002) In vitro properties of a recombinant flavonol synthase from Arabidopsis thaliana. Phytochemistry 60:589–593
Quattrocchio F, Wing JF, Leppen HTC, Mol JNM, Koes RE (1993) Regulatory genes controlling anthocyanin pigmentation are functionally conserved among plant species and have distinct sets of target genes. Plant Cell 5:1497–1512
Quattrocchio F, Baudry A, Lepiniec L, Grotewold E (2006) The regulation of flavonoid biosynthesis. In: Grotewold E (ed) The science of flavonoids. Springer, Columbus, pp 97–122
Reddy AM, Reddy VS, Scheffler BE, Wienand U, Reddy AR (2007) Novel transgenic rice overexpressing anthocyanidin synthase accumulates a mixture of flavonoids leading to an increased antioxidant potential. Metab Eng 9:95–111
Roach PL, Clifton IJ, Fulop V, Harlos K, Barton GJ, Hajdu J, Andersson I, Schofield CJ, Baldwin JE (1995) Crystal structure of isopenicillin N synthase is the first from a new structural family of enzymes. Nature 375:700–704
Ross JA, Kasum CM (2002) Dietary flavonoids: bioavailability, metabolic effects, and safety. Annu Rev Nutr 22:19–34
Routaboul JM, Kerhoas L, Debeaujon I, Pourcel L, Caboche M, Einhorn J, Lepiniec L (2006) Flavonoid diversity and biosynthesis in seed of Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta 224:96–107
Schoenbohm C, Martens S, Eder C, Forkmann G, Weisshaar B (2000) Identification of the Arabidopsis thaliana flavonoid 3′-hydroxylase gene and functional expression of the encoded P450 enzyme. Biol Chem 381:749–753
Sheahan JJ, Rechnitz GA (1992) Flavonoid-specific staining of Arabidopsis thaliana. Biotechniques 13:880–883
Sprenger-Haussels M, Weisshaar B (2000) Transactivation properties of parsley proline rich bZIP transcription factors. Plant J 22:1–8
Spribille R, Forkmann G (1984) Conversion of dihydroflavonols to flavonols with enzyme extracts from flower buds of Matthiola incana R. Br Z Naturforsch C 39:714–719
Stracke R, Ishihara H, Huep G, Barsch A, Mehrtens F, Niehaus K, Weisshaar B (2007) Differential regulation of closely related R2R3-MYB transcription factors controls flavonol accumulation in different parts of the Arabidopsis thaliana seedling. Plant J 50:660–677
Tikunov Y, Lommen A, de Vos CH, Verhoeven HA, Bino RJ, Hall RD, Bovy AG (2005) A novel approach for nontargeted data analysis for metabolomics. Large-scale profiling of tomato fruit volatiles. Plant Physiol 139:1125–1137
Tohge T, Nishiyama Y, Hirai MY, Yano M, Nakajima J, Awazuhara M, Inoue E, Takahashi H, Goodenowe DB, Kitayama M, Noji M, Yamazaki M, Saito K (2005) Functional genomics by integrated analysis of metabolome and transcriptome of Arabidopsis plants over-expressing an MYB transcription factor. Plant J 42:218–235
Turnbull JJ, Nagle MJ, Seibel JF, Welford RW, Grant GH, Schofield CJ (2003) The C-4 stereochemistry of leucocyanidin substrates for anthocyanidin synthase affects product selectivity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13:3853–3857
Turnbull JJ, Nakajima J, Welford RW, Yamazaki M, Saito K, Schofield CJ (2004) Mechanistic studies on three 2-oxoglutarate-dependent oxygenases of flavonoid biosynthesis: anthocyanidin synthase, flavonol synthase, and flavanone 3beta-hydroxylase. J Biol Chem 279:1206–1216
van Eldik GJ, Reijnen WH, Ruiter RI, van Herpen MMA, Schrauwen JAM, Wullems GJ (1997) Regulation of flavonol biosynthesis during anther and pistil development, and during pollen tube growth in Solanum tuberosum. Plant J 11:105–113
Welford RWD, Turnbull JJ, Claridge TDW, Prescott AG, Schofield CJ (2001) Evidence for oxidation at C-3 of the flavonoid C-ring during anthocyanin biosynthesis. Chem Commun 1828–1829
Wellmann F, Lukacin R, Moriguchi T, Britsch L, Schiltz E, Matern U (2002) Functional expression and mutational analysis of flavonol synthase from Citrus unshiu. Eur J Biochem 269:4134–4142
Winkel-Shirley B (2001) Flavonoid biosynthesis. A colorful model for genetics, biochemistry, cell biology, and biotechnology. Plant Physiol 126:485–493
Wisman E, Hartmann U, Sagasser M, Baumann E, Palme K, Hahlbrock K, Saedler H, Weisshaar B (1998) Knock-out mutants from an En-1 mutagenized Arabidopsis thaliana population generate new phenylpropanoid biosynthesis phenotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:12432–12437
Yan Y, Chemler J, Huang L, Martens S, Koffas MA (2005) Metabolic engineering of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:3617–3623
Yonekura-Sakakibara K, Tohge T, Niida R, Saito K (2007) Identification of a flavonol 7-O-rhamnosyltransferase gene determining flavonoid pattern in Arabidopsis by transcriptome coexpression analysis and reverse genetics. J Biol Chem 282:14932–14941
Acknowledgements
We thank Melanie Kuhlmann for excellent technical assistance and the Sequencing Core Facility at the Bielefeld University for doing an excellent job in determining DNA sequences. This project was funded in part by the EU project FLAVO (FOOD-CT-2004-513960) and the GABI program of the Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF)/Projektträger Jülich (PTJ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Nucleotide sequence database accession numbers: GenBank accession EU287457 and EU287459.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
425_2008_841_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Fig. S1 Multiple alignment of FLS polypeptides. Result from ClustalW2 multiple sequence alignment done at EMBL-EBI (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/clustalw2/) using default parameters (Chenna et al. 2003). Protein sequence data were obtained from GenBank (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/): Petroselinum crispum PcFLS (AAP57395), Petunia x hybrida PhFLS (CAA80264), Solanum tuberosum StFLS (CAA63092), Eustoma grandiflorum EgFLS (AAF64168), Citrus unshiu CuFLS (BAA36554), Malus domestica MdFLS (AAX89401) and Camellia sinensis CsFLS (ABM88786). Amino acid residues, identical in all polypeptides are black boxed. Amino acids found at least in all polypeptides with proven FLS activity are marked in grey. The three regions of high similarity found in 2 oxoglutarate-dependent- and related enzymes (Britsch et al. 1993; Wellmann et al. 2002) are underlined. Amino acid residues, involved in iron binding (Myllylä et al. 1992; Britsch et al. 1993; Lukacin and Britsch 1997; Clifton et al. 2006) are marked with squares (■). The HxD...H motif, defining amino acids involved in 2 oxoglutarate binding (Britsch et al. 1993; Roach et al. 1995; Lukacin and Britsch 1997), is marked with circles (●). A diamond (♦) marks conserved amino acids of unknown function (Lukacin and Britsch 1997; Wellmann et al. 2002). At the bottom of the sequence alignment, the following symbols denote the degree of conservation in each column: (*) identical in all sequences, (:) conserved substitutions, (.) semi-conserved substitutions (PDF 337 kb)
425_2008_841_MOESM2_ESM.xls
Table S1 Summary of LC-PDA-QTOF-MS derived data showing differential metabolites in seedlings of analysed genotypes. Results of three independent biological samples are given. RT, retention time [min]; observed mass [m/z], averaged accurate mass ([M H] ), as mass-to-charge ratio; calc mass, calculated accurate mass; D mass [ppm], deviation between the averages of observed and calculated accurate masses, in parts per million; UV/Vis, absorbance maxima in the UV/Vis range (nd, not detectable absorbance); MS fragments, MS/MS fragments obtained through increased collision energy on indicated parent mass; mol formular, molecular formula of the metabolite; metabolite name, common name of putatively identified metabolite; mean, data represent means of results from the three given separate experiments; SD, standard deviation (XLS 68 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stracke, R., De Vos, R.C.H., Bartelniewoehner, L. et al. Metabolomic and genetic analyses of flavonol synthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana support the in vivo involvement of leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase. Planta 229, 427–445 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-008-0841-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-008-0841-y