Abstract
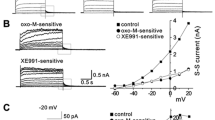
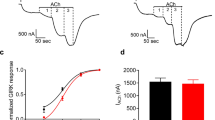
Inwardly rectifying potassium channels Kir2.1–Kir2.3 are important regulators of membrane potential and, thus, control cellular excitability. However, little is known about the regulation of these channels. Therefore, we studied the mechanisms mediating the regulation of Kir2.1–Kir2.3 by the G-protein-coupled m1 muscarinic receptor using the whole-cell patch-clamp technique and recombinant expression in the tsA201 mammalian cell line. Stimulation of the m1 muscarinic receptor inhibited all subtypes of inward rectifier tested, Kir2.1–Kir2.3. The inhibition of each channel subtype was reversible and was attenuated by the muscarinic receptor antagonist, atropine. The protein kinase C activator phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) mimicked the effects of m1 receptor activation by inhibiting Kir2.1 currents. However, PMA had no effect on Kir2.2 or Kir2.3. Inclusion of 200-μM guanosine 5′-O-(2-thiodiphosphate) (GDPβS) in the patch pipette solution prevented the effects of m1 muscarinic receptor stimulation on all three of the channel subtypes tested, confirming the mediation of the responses by G-proteins. Cotransfection with the activated mutant of the small GTPase Rho reduced current density, while C3 exoenzyme, a selective inhibitor of Rho, attenuated the m1 muscarinic receptor-induced inhibition of Kir2.1–Kir2.3. Also, buffering the intracellular calcium concentration with a high concentration of EGTA abolished the m1 receptor-induced inhibition of Kir2.1–Kir2.3, implicating a role for calcium in these responses. These results indicate that all three of the Kir2 channels are similarly inhibited by m1 muscarinic receptor stimulation through calcium-dependent activation of the small GTPase Rho.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ariano MA, Cepeda C, Calvert CR, Flores-Hernandez J, Hernandez-Echeagaray E, Klapstein GJ, Chandler SH, Aronin N, DiFiglia M, Levine MS (2005) Striatal potassium channel dysfunction in Huntington’s disease transgenic mice. J Neurophysiol 93:2565–2574
Braun AP, Fedida D, Giles WR (1992) Activation of alpha 1-adrenoceptors modulates the inwardly rectifying potassium currents of mammalian atrial myocytes. Pflugers Arch 421:431–439
Cachero TG, Morielli AD, Peralta EG (1998) The small GTP-binding protein RhoA regulates a delayed rectifier potassium channel. Cell 93:1077–1085
Chen C, Okayama H (1987) High efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol 8:2745–2752
Chikumi H, Vazquez-Prado J, Servitja JM, Miyazaki H, Gutkind JS (2002) Potent activation of RhoA by Galpha q and Gq-coupled receptors. J Biol Chem 277:27130–27134
Chuang H, Jan YN, Jan LY (1997) Regulation of IRK3 inward rectifier K± channel by m1 acetylcholine receptor and intracellular magnesium. Cell 89:1121–1132
Cohen NA, Sha Q, Makhina EN, Lopatin AN, Linder ME, Snyder SH, Nichols CG (1996) Inhibition of an inward rectifier potassium channel (Kir 2.3) by G-protein βγ subunits. J Biol Chem 271:32301–32305
Coso OA, Chiariello M, Yu JC, Teramoto H, Crespo P, Xu N, Miki T, Gutkind JS (1995) The small GTP-binding proteins Rac1 and Cdc42 regulate the activity of the JNK/SAPK signaling pathway. Cell 81:1137–1146
Du X, Zhang H, Lopes C, Mirshahi T, Rohacs T, Logothetis DE (2004) Characteristic interactions with phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate determine regulation of kir channels by diverse modulators. J Biol Chem 279:37271–37281
Fakler B, Brandle U, Glowatzki E, Zenner H-P, Ruppersberg JP (1994) Kir 2.1 inward rectifier K± channels are regulated independently by protein kinases and ATP hydrolysis. Neuron 13:1413–1420
Fedida D, Braun AP, Giles WR (1991) Alpha 1-adrenoceptors reduce background K± current in rabbit ventricular myocytes. J Physiol 441:673–684
Firth TA, Jones SVP (2001) GTP-binding protein Gq mediates muscarinic receptor-induced inhibition of the inwardly rectifying potassium channel IRK1 (Kir 2.1). Neuropharmacology 40:358–365
Gilman AG (1987) G-proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem 56:615–649
Giovannardi S, Forlani G, Balestrini M, Bossi E, Tonini R, Sturani E, Peres A, Zippel R (2002) Modulation of the inward rectifier potassium channel IRK1 by the Ras signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 277:12158–12163
Henry P, Pearson WL, Nichols CG (1996) Protein kinase C inhibition of cloned inward rectifier (HRK1/KIR2.3) K± channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol 495:681–688
Hill CS, Wynne J, Treisman R (1995) The Rho family GTPases RhoA, Rac1 and Cdc42Hs regulate transcriptional activation by SRF. Cell 81:1159–1170
Hoang QV, Zhao P, Nakajima S, Nakajima Y (2004) Orexin (hypocretin) effects on constitutively active inward rectifier K± channels in cultured nucleus basalis neurons. J Neurophysiol 92:3183–3191
Holinstat M, Mehta D, Kozasa T, Minshall RD, Malik AB (2003) Protein kinase C alpha-induced p115RhoGEF phosphorylation signals endothelial cytoskeletal rearrangement. J Biol Chem 278:28793–28798
Inanobe A, Fujita A, Ito M, Tomoike H, Inageda K, Kurachi Y (2002) Inward rectifier K± channel Kir2.3 is localized at the postsynaptic membrane of excitatory synapses. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 282:C1396–C1403
Jones SVP (1996) Modulation of the inwardly rectifying potassium channel IRK1 by the m1 muscarinic receptor. Mol Pharmacol 49:662–667
Jones SVP (1997) Dual modulation of an inwardly rectifying potassium conductance. Neuropharmacology 36:209–215
Jones SVP (2003) Role of small GTPases in modulation of inwardly rectifying potassium channels. Mol Pharmacol 64:987–993
Kamouchi M, Van Den Bremt K, Eggermont J, Droogmans G, Nilius B (1997) Modulation of inwardly rectifying potassium channels in cultured bovine pulmonary artery endothelial cells. J Physiol 504:545–556
Kanazirska MV, Vassilev PM, Quinn SJ, Tillotson DL, Williams GH (1992) Single potassium channels in adrenal zona glomerulosa cells. II. Inhibition by angiotensin II. Am J Physiol 263:E760–E765
Karle CA, Zitron E, Zhang W, Wendt-Nordahl G, Kathofer S, Thomas D, Gut B, Scholz E, Vahl C-F, Katus HA, Kiehn J (2002) Human cardiac inwardly-rectifying K± channel Kir2.1b is inhibited by direct protein kinase C-dependent regulation in human isolated cardiomyocytes and in an expression system. Circulation 106:1493–1499
Koyano K, Velimirovic BM, Grigg JJ, Nakajima S, Nakajima Y (1993) Two signal transduction mechanisms of substance P-induced depolarisation in locus coeruleus neurons. Eur J Neurosci 5:1189–1197
Kubo Y, Baldwin TJ, Jan YN, Jan LY (1993) Primary structure and functional expression of a mouse inward rectifier potassium channel. Nature 362:127–133
Morishige K-I, Takahashi N, Jahangir A, Yamada M, Koyama H, Zanelli JS, Kurachi Y (1994) Molecular cloning and functional expression of a novel brain-specific inward rectfier potassium channel. FEBS Lett 346:251–256
Nilius B, Voets T, Barth H, Aktories K, Kaibuchi K, Droogmans G, Eggermont J (1999) Role of Rho and Rho kinase in the activation of volume regulated anion channels in bovine endothelial cells. J Physiol 516:67–74
Nishizuka Y (1995) Protein kinase C and lipid signaling for sustained cellular responses. FASEB J 9:484–496
Pan ZZ, Williams JT (1994) Muscarine hyperpolarizes a subpopulation of neurons by activating an M2 muscarinic receptor in rat nucleus raphe magnus in vitro. J Neurosci 14:1332–1338
Perillan PR, Chen M, Potts EA, Simard JM (2002) Transforming growth factor-beta 1 regulates Kir2.3 inward rectifier K± channels via phospholipase C and protein kinase C-delta in reactive astrocytes from adult rat brain. J Biol Chem 277:1974–1980
Plaster NM, Tawil R, Tristani-Firouzi M, Canun S, Bendahhou S, Tsunoda A, Donaldson MR, Iannaccone ST, Brunt E, Barohn R et al (2001) Mutations in Kir2.1 cause the developmental and episodic electrical phenotypes of Andersen’s syndrome. Cell 105:511–519
Pruss H, Derst C, Lommel R, Veh RW (2005) Differential distribution of individual subunits of strongly inwardly rectifying potassium channels (Kir2 family) in rat brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 139:63–79
Roy ML, Sontheimer H (1995) β-Adrenergic modulation of glial inwardly rectifying potassium channels. J Neurochem 64:1576–1584
Ruppersberg JP (2000) Intracellular regulation of inward rectifier K± channels. Pflugers Arch 441:1–11
Shen K-Z, North RA (1992) Substance P opens cation channels and closes potassium channels in rat locus coeruleus neurons. Neuroscience 50:345–353
Stanfield PR, Nakajima S, Nakajima Y (2002) Constitutively active and G-protein coupled inward rectifier K± channels: Kir2 and Kir3.0. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 145:47–179
Stonehouse AH, Pringle JH, Norman RI, Stanfield PR, Conley EC, Brammar WJ (1999) Co-localization of the inwardly rectifying potassium ion channel, Kir2.2, and the substance P receptor in single locus coeruleus neurons. Ann N Y Acad Sci 897:429–431
Stonehouse AH, Pringle JH, Norman RI, Stanfield PR, Conley EC, Brammmar WJ (1999) Characterisation of Kir2 proteins in the rat cerebellum and hippocampus by polyclonal antibodies. Histochem Cell Biol 112:457–465
Storey NM, O’Bryan JP, Armstrong DL (2002) Rac and Rho mediate opposing hormonal regulation of the ether-a-go-go-related potassium channel. Curr Biol 12:27–33
Takahashi N, Morishige K-I, Jahangir A, Yamada M, Findlay I, Koyama H, Kurachi Y (1994) Molecular cloning and functional expression of cDNA encoding a second class of inward rectifier potassium channels in the mouse brain. J Biol Chem 37:23274–23279
Takano K, Stanfield PR, Nakajima S, Nakajima Y (1995) Protein kinase C-mediated inhibition of an inward rectifier potassium channel by substance P in nucleus basalis neurons. Neuron 14:999–1008
Takano M, Kuratomi S (2003) Regulation of cardiac inwardly rectifying potassium channels by membrane lipid metabolism. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 81:67–79
Tang W, Yang X-C (1994) Cloning a novel human inward rectifier potassium channel and its functional expression in Xenopus oocytes. FEBS Lett 348:239–243
Tang W, Qin CL, Yang X-C (1995) Cloning, localization, and functional expression of a human brain inward rectifier potassium channel (hIRK1). Recept Channels 3:175–183
Uchimura N, North RA (1990) Muscarine reduces inwardly rectifying potassium conductance in rat nucleus accumbens neurones. J Physiol 422:369–380
Wang H, Yang B, Zhang Y, Han H, Wang J, Shi H, Wang Z (2001) Different subtypes of alpha-1-adrenoceptor modulate different K± currents via different signaling pathways in canine ventricular myocytes. J Biol Chem 276:40811–40816
Wischmeyer E, Karschin A (1996) Receptor stimulation causes slow inhibition of IRK1 inwardly rectifying potassium channels by direct protein kinase A-mediated phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:5819–5823
Wischmeyer E, Doring F, Karschin A (1998) Acute suppression of inwardly rectifying Kir 2.1 channels by direct tyrosine kinase phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 273:34063–34068
Womble MD, Moises HC (1993) Hyperpolarization-activated currents in neurons of the rat basolateral amygdala. J Neurophysiol 70:2056–2065
Yatani A, Irie K, Otani T, Abdellatif M, Wei L (2005) RhoA GTPase regulates l-type Ca2± currents in cardiac myocytes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 288:H650–H659
Zaritsky JJ, Redell JB, Tempel BL, Schwarz TL (2001) The consequences of disrupting cardiac inwardly rectifying K(±) current (I(K1)) as revealed by the targeted deletion of the murine Kir2.1 and Kir2.2 genes. J Physiol 533:697–710
Zhu G, Qu Z, Cui N, Jiang C (1999) Suppression of Kir2.3 activity by protein kinase C phosphorylation of the channel protein at threonine 53. J Biol Chem 274:11643–11646
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Drs. Y. Kubo and L.Y. Jan for the kind gift of mKir2.1 cDNA, Dr. W. Tang for the kind gifts of hKir2.1 and hKir2.2 cDNAs, Dr. Y. Kurachi for the kind gifts mKir2.2 and mKir2.3 cDNAs, Dr. J.S. Gutkind for the Rho mutants, and Dr. Treisman for the EFC3 plasmid. This work was funded in part by National Institutes of Health grant NS29634 and by the National Science Foundation Office of Experimental Program to Stimulate Competitive Research (NSF EPSCor).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rossignol, T.M., Jones, S.V.P. Regulation of a family of inwardly rectifying potassium channels (Kir2) by the m1 muscarinic receptor and the small GTPase Rho. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 452, 164–174 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-005-0014-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-005-0014-9