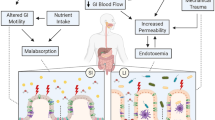
Abstract
To improve performance and recovery faster, athletes are advised to eat more often than usual and consume higher doses of simple carbohydrates, during and after exercise. Sports energetic supplements contain food additives, such as artificial sweeteners, emulsifiers, acidity regulators, preservatives, and salts, which could be harmful to the gut microbiota and impair the intestinal barrier function. The intestinal barrier plays a critical function in bidirectionally regulation of the selective transfer of nutrients, water, and electrolytes, while preventing at the same time, the entrance of harmful substances (selective permeability). The gut microbiota helps to the host to regulate intestinal homeostasis through metabolic, protective, and immune functions. Globally, the gut health is essential to maintain systemic homeostasis in athletes, and to ensure proper digestion, metabolization, and substrate absorption. Gastrointestinal complaints are an important cause of underperformance and dropout during endurance events. These complications are directly related to the loss of gut equilibrium, mainly linked to microbiota dysbiosis and leaky gut. In summary, athletes must be cautious with the elevated intake of ultra-processed foods and specifically those contained on sports nutrition supplements. This review points out the specific nutritional interventions that should be implemented and/or discontinued depending on individual gut functionality.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afzaal M, Saeed F, Shah YA et al (2022) Human gut microbiota in health and disease: unveiling the relationship. Front Microbiol 13:999001. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.999001
Allaband C, McDonald D, Vázquez-Baeza Y et al (2019) Microbiome 101: studying, analyzing, and interpreting gut microbiome data for clinicians. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 17:218–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2018.09.017
Allam-Ndoul B, Castonguay-Paradis S, Veilleux A (2020) Gut microbiota and intestinal trans-epithelial permeability. Int J Mol Sci 21:6402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176402
Almutairi R, Basson AR, Wearsh P et al (2022) Validity of food additive maltodextrin as placebo and effects on human gut physiology: systematic review of placebo-controlled clinical trials. Eur J Nutr 61:2853–2871. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-022-02802-5
Álvarez-Herms J, Julià-Sánchez S, Gatterer H et al (2016) Anaerobic training in hypoxia: a new approach to stimulate the rating of effort perception. Physiol Behav 163:37–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2016.04.035
Álvarez-Herms J, González A, Corbi F, Odriozola I, Odriozola A (2023) Possible relationship between the gut leaky syndrome and musculoskeletal injuries: the important role of gut microbiota as indirect modulator[J]. AIMS Public Health 10(3):710–738. https://doi.org/10.3934/publichealth.2023049
Aoi W, Naito Y, Yoshikawa T (2006) Exercise and functional foods. Nutr J 5:15. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-5-15
Arida A, Protogerou AD, Kitas GD, Sfikakis PP (2018) Systemic inflammatory response and atherosclerosis: the paradigm of chronic inflammatory rheumatic diseases. Int J Mol Sci 19:1890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19071890
Bäckhed F, Ding H, Wang T et al (2004) The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:15718–15723. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0407076101
Bäckhed F, Ley RE, Sonnenburg JL et al (2005) Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science 307:1915–1920. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1104816
Ballard ST, Hunter JH, Taylor AE (1995) Regulation of tight-junction permeability during nutrient absorption across the intestinal epithelium. Annu Rev Nutr 15:35–55. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.nu.15.070195.000343
Bansil R, Turner BS (2018) The biology of mucus: composition, synthesis and organization. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 124:3–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2017.09.023
Barcenilla A, Pryde SE, Martin JC et al (2000) Phylogenetic relationships of butyrate-producing bacteria from the human gut. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:1654–1661. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.66.4.1654-1661.2000
Baska RS, Moses FM, Graeber G, Kearney G (1990) Gastrointestinal bleeding during an ultramarathon. Dig Dis Sci 35:276–279. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01536777
Bautista LE, Herrán OF, Pryer JA (2005) Development and simulated validation of a food-frequency questionnaire for the Colombian population. Public Health Nutr 8:181–188. https://doi.org/10.1079/phn2004672
Baxter NT, Schmidt AW, Venkataraman A et al (2019) Dynamics of human gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acids in response to dietary interventions with three fermentable fibers. Mbio 10:e02566-e2618. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.02566-18
Bengmark S (2013) Gut microbiota, immune development and function. Pharmacol Res 69:87–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2012.09.002
Bergman EN (1990) Energy contributions of volatile fatty acids from the gastrointestinal tract in various species. Physiol Rev 70:567–590. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.1990.70.2.567
Bian X, Chi L, Gao B et al (2017) Gut microbiome response to sucralose and its potential role in inducing liver inflammation in mice. Front Physiol 8:487. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.00487
Bischoff SC (2011) “Gut health”: a new objective in medicine? BMC Med 9:24. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7015-9-24
Bjarnason I, MacPherson A, Hollander D (1995) Intestinal permeability: an overview. Gastroenterology 108:1566–1581. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-5085(95)90708-4
Blaut M, Clavel T (2007) Metabolic diversity of the intestinal microbiota: implications for health and disease. J Nutr 137:751S-S755. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/137.3.751S
Boer CG, Radjabzadeh D, Medina-Gomez C et al (2019) Intestinal microbiome composition and its relation to joint pain and inflammation. Nat Commun 10:4881. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12873-4
Boets E, Gomand SV, Deroover L et al (2017) Systemic availability and metabolism of colonic-derived short-chain fatty acids in healthy subjects: a stable isotope study. J Physiol 595:541–555. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP272613
Bosenberg AT, Brock-Utne JG, Gaffin SL et al (1988) Strenuous exercise causes systemic endotoxemia. J Appl Physiol (1985) 65:106–108. https://doi.org/10.1152/jappl.1988.65.1.106
Bragina TV, Elizarova EV, Sheveleva SA (2021) Intestinal microbiote of athletes. Vopr Pitan 90:36–52. https://doi.org/10.33029/0042-8833-2021-90-4-36-52
Brock-Utne JG, Gaffin SL, Wells MT et al (1988) Endotoxaemia in exhausted runners after a long-distance race. S Afr Med J 73:533–536
Burke LM, Hawley JA, Jeukendrup A et al (2018) Toward a common understanding of diet-exercise strategies to manipulate fuel availability for training and competition preparation in endurance sport. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 28:451–463. https://doi.org/10.1123/ijsnem.2018-0289
Burke LM, Castell LM, Casa DJ et al (2019a) International association of athletics federations consensus statement 2019: nutrition for athletics. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 29:73–84. https://doi.org/10.1123/ijsnem.2019-0065
Burke LM, Jeukendrup AE, Jones AM, Mooses M (2019b) Contemporary nutrition strategies to optimize performance in distance runners and race walkers. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 29:117–129. https://doi.org/10.1123/ijsnem.2019-0004
Bycura D, Santos AC, Shiffer A et al (2021) Impact of different exercise modalities on the human gut microbiome. Sports (basel) 9:14. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports9020014
Cabiè A, Farkas JC, Fitting C et al (1993) High levels of portal TNF-alpha during abdominal aortic surgery in man. Cytokine 5:448–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/1043-4666(93)90034-3
Calabrese EJ (2008) Hormesis: why it is important to toxicology and toxicologists. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:1451–1474. https://doi.org/10.1897/07-541.1
Camilleri M (2019) Leaky gut: mechanisms, measurement and clinical implications in humans. Gut 68:1516–1526. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318427
Cani PD (2015) Metabolism: Dietary emulsifiers–sweepers of the gut lining? Nat Rev Endocrinol 11:319–320. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2015.59
Carding S, Verbeke K, Vipond DT et al (2015) Dysbiosis of the gut microbiota in disease. Microb Ecol Health Dis 26:26191. https://doi.org/10.3402/mehd.v26.26191
Casazza GA, Tovar AP, Richardson CE et al (2018) Energy availability, macronutrient intake, and nutritional supplementation for improving exercise performance in endurance athletes. Curr Sports Med Rep 17:215–223. https://doi.org/10.1249/JSR.0000000000000494
Castro GA, Arntzen CJ (1993) Immunophysiology of the gut: a research frontier for integrative studies of the common mucosal immune system. Am J Physiol 265:G599-610. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.1993.265.4.G599
Chassaing B, Gewirtz AT (2018) Not so splendid for the gut microbiota. Inflamm Bowel Dis 24:1055–1056. https://doi.org/10.1093/ibd/izy072
Chassaing B, Koren O, Goodrich JK et al (2015) Dietary emulsifiers impact the mouse gut microbiota promoting colitis and metabolic syndrome. Nature 519:92–96. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14232
Chazaud B (2020) Inflammation and skeletal muscle regeneration: leave it to the macrophages! Trends Immunol 41:481–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2020.04.006
Cheeseman M (2014) Global regulation of food additives. In: Komolprasert V, Turowski P (eds) ACS symposium series. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, pp 3–9
Chisari E, Rehak L, Khan WS, Maffulli N (2021) Tendon healing is adversely affected by low-grade inflammation. J Orthop Surg Res 16:700. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-021-02811-w
Clark A, Mach N (2016) Exercise-induced stress behavior, gut-microbiota-brain axis and diet: a systematic review for athletes. J Int Soc Sports Nutr 13:43. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12970-016-0155-6
Clauss M, Gérard P, Mosca A, Leclerc M (2021) Interplay between exercise and gut microbiome in the context of human health and performance. Front Nutr 8:637010. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2021.637010
Clemente JC, Ursell LK, Parfrey LW, Knight R (2012) The impact of the gut microbiota on human health: an integrative view. Cell 148:1258–1270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.01.035
Cone RA (2009) Barrier properties of mucus. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 61(2):75–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2008.09.008
Cook SI, Sellin JH (1998) Review article: short chain fatty acids in health and disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 12:499–507. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2036.1998.00337.x
Corbo MR, Bevilacqua A, Petruzzi L et al (2014) Functional beverages: the emerging side of functional foods. Comprehensive Rev Food Sci Food Saf 13:1192–1206. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12109
Corfield AP (2015) Mucins: a biologically relevant glycan barrier in mucosal protection. Biochim Biophys Acta 1850:236–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.05.003
Costa RJS, Snipe RMJ, Kitic CM, Gibson PR (2017) Systematic review: exercise-induced gastrointestinal syndrome-implications for health and intestinal disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 46:246–265. https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.14157
Costa RJS, Knechtle B, Tarnopolsky M, Hoffman MD (2019) Nutrition for ultramarathon running: trail, track, and road. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 29:130–140. https://doi.org/10.1123/ijsnem.2018-0255
Costigan M, Scholz J, Woolf CJ (2009) Neuropathic pain: a maladaptive response of the nervous system to damage. Annu Rev Neurosci 32:1–32. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.051508.135531
Cotter PD (2011) Small intestine and microbiota. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 27:99–105. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOG.0b013e328341dc67
Crost EH, Tailford LE, Le Gall G et al (2013) Utilisation of mucin glycans by the human gut symbiont Ruminococcus gnavus is strain-dependent. PLoS ONE 8:e76341. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0076341
Crowson MM, McClave SA (2020) Does the intestinal microbiome impact athletic performance? Curr Gastroenterol Rep 22:53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-020-00790-2
Csáki KF (2011) Synthetic surfactant food additives can cause intestinal barrier dysfunction. Med Hypotheses 76:676–681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2011.01.030
Cummings JH, Macfarlane GT (1991) The control and consequences of bacterial fermentation in the human colon. J Appl Bacteriol 70:443–459. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.1991.tb02739.x
Das B, Nair GB (2019) Homeostasis and dysbiosis of the gut microbiome in health and disease. J Biosci 44:117
de Oliveira EP, Burini RC, Jeukendrup A (2014) Gastrointestinal complaints during exercise: prevalence, etiology, and nutritional recommendations. Sports Med 44(Suppl 1):S79-85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-014-0153-2
de Sire A, de Sire R, Petito V et al (2020) Gut-joint axis: the role of physical exercise on gut microbiota modulation in older people with osteoarthritis. Nutrients 12:574. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12020574
Deitch EA (1990) The role of intestinal barrier failure and bacterial translocation in the development of systemic infection and multiple organ failure. Arch Surg 125:403–404. https://doi.org/10.1001/archsurg.1990.01410150125024
Derrien M, Vaughan EE, Plugge CM, de Vos WM (2004) Akkermansia muciniphila gen. nov., sp. nov., a human intestinal mucin-degrading bacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:1469–1476. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.02873-0
Dhurandhar D, Bharihoke V, Kalra S (2018) A histological assessment of effects of sucralose on liver of albino rats. Morphologie 102:197–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.morpho.2018.07.003
Dicken SJ, Batterham RL (2022) Ultra-processed food: a global problem requiring a global solution. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 10:691–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(22)00248-0
Do MH, Lee E, Oh M-J et al (2018) High-glucose or -fructose diet cause changes of the gut microbiota and metabolic disorders in mice without body weight change. Nutrients 10:761. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10060761
Donati Zeppa S, Agostini D, Gervasi M et al (2019) Mutual interactions among exercise, sport supplements and microbiota. Nutrients 12:17. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010017
Ebi KL, Capon A, Berry P et al (2021) Hot weather and heat extremes: health risks. Lancet 398:698–708. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01208-3
El Aidy S, van den Bogert B, Kleerebezem M (2015) The small intestine microbiota, nutritional modulation and relevance for health. Curr Opin Biotechnol 32:14–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2014.09.005
El Kaoutari A, Armougom F, Gordon JI et al (2013) The abundance and variety of carbohydrate-active enzymes in the human gut microbiota. Nat Rev Microbiol 11:497–504. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro3050
Emhoff C-AW, Messonnier LA, Horning MA et al (2013) Gluconeogenesis and hepatic glycogenolysis during exercise at the lactate threshold. J Appl Physiol 1985(114):297–306. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.01202.2012
Erickson J, Wang Q, Slavin J (2017) White grape juice elicits a lower breath hydrogen response compared with apple juice in healthy human subjects: a randomized controlled trial. J Acad Nutr Diet 117:908–913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jand.2017.01.020
Fajstova A, Galanova N, Coufal S et al (2020) Diet rich in simple sugars promotes pro-inflammatory response via gut microbiota alteration and TLR4 signaling. Cells 9:2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122701
Fasano A, Not T, Wang W et al (2000) Zonulin, a newly discovered modulator of intestinal permeability, and its expression in coeliac disease. Lancet 355:1518–1519. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02169-3
Fernández J, Fernández-Sanjurjo M, Iglesias-Gutiérrez E et al (2021) Resistance and endurance exercise training induce differential changes in gut microbiota composition in murine models. Front Physiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2021.748854
Frampton J, Murphy KG, Frost G, Chambers ES (2020) Short-chain fatty acids as potential regulators of skeletal muscle metabolism and function. Nat Metab 2:840–848. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-020-0188-7
Fu X, Liu Z, Zhu C et al (2019) Nondigestible carbohydrates, butyrate, and butyrate-producing bacteria. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 59:S130–S152. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2018.1542587
Furber MJW, Young GR, Holt GS et al (2022) Gut microbial stability is associated with greater endurance performance in athletes undertaking dietary periodization. mSystems 7:e0012922. https://doi.org/10.1128/msystems.00129-22
Furman D, Campisi J, Verdin E et al (2019) Chronic inflammation in the etiology of disease across the life span. Nat Med 25:1822–1832. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-019-0675-0
Gieryńska M, Szulc-Dąbrowska L, Struzik J et al (2022) Integrity of the intestinal barrier: the involvement of epithelial cells and microbiota-a mutual relationship. Animals (basel) 12:145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12020145
Gluckman PD, Hanson MA, Spencer HG (2005) Predictive adaptive responses and human evolution. Trends Ecol Evol 20:527–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2005.08.001
Gokoglu N (2019) Novel natural food preservatives and applications in seafood preservation: a review. J Sci Food Agric 99:2068–2077. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.9416
Goodrich JK, Waters JL, Poole AC et al (2014) Human genetics shape the gut microbiome. Cell 159:789–799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.053
Grootjans J, Lenaerts K, Buurman WA et al (2016) Life and death at the mucosal-luminal interface: New perspectives on human intestinal ischemia-reperfusion. World J Gastroenterol 22:2760–2770. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i9.2760
Guarner F, Malagelada J-R (2003) Gut flora in health and disease. Lancet 361:512–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12489-0
Guillochon M, Rowlands DS (2017) Solid, gel, and liquid carbohydrate format effects on gut comfort and performance. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 27:247–254. https://doi.org/10.1123/ijsnem.2016-0211
Halmos EP, Mack A, Gibson PR (2019) Review article: emulsifiers in the food supply and implications for gastrointestinal disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 49:41–50. https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.15045
Han M, Yang K, Yang P et al (2020) Stratification of athletes’ gut microbiota: the multifaceted hubs associated with dietary factors, physical characteristics and performance. Gut Microbes 12:1842991. https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2020.1842991
Hansson GC (2019) Mucus and mucins in diseases of the intestinal and respiratory tracts. J Intern Med 285:479–490. https://doi.org/10.1111/joim.12910
Hawley JA (2020) Microbiota and muscle highway—two way traffic. Nat Rev Endocrinol 16:71–72. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-019-0291-6
Hawrelak JA, Myers SP (2004) The causes of intestinal dysbiosis: a review. Altern Med Rev 9:180–197
Heumann D, Roger T (2002) Initial responses to endotoxins and Gram-negative bacteria. Clin Chim Acta 323:59–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0009-8981(02)00180-8
Hiippala K, Jouhten H, Ronkainen A et al (2018) The potential of gut commensals in reinforcing intestinal barrier function and alleviating inflammation. Nutrients 10:988. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10080988
Hoffman MD, Wegelin JA (2009) The Western States 100-Mile Endurance Run: participation and performance trends. Med Sci Sports Exerc 41:2191–2198. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181a8d553
Hooper LV, Wong MH, Thelin A et al (2001) Molecular analysis of commensal host-microbial relationships in the intestine. Science 291:881–884. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.291.5505.881
Hrncirova L, Machova V, Trckova E et al (2019) Food preservatives induce proteobacteria dysbiosis in human-microbiota associated Nod2-Deficient mice. Microorganisms 7:383. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7100383
Hu J, Zhou S, Ryu S et al (2023) Effects of long-term endurance exercise on cardiac morphology, function, and injury indicators among amateur marathon runners. Int J Environ Res Public Health 20:2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20032600
Huang JY, Lee SM, Mazmanian SK (2011) The human commensal Bacteroides fragilis binds intestinal mucin. Anaerobe 17:137–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anaerobe.2011.05.017
Huang W-C, Chen Y-H, Chuang H-L et al (2019) Investigation of the Effects of Microbiota on Exercise Physiological Adaption, Performance, and Energy Utilization Using a Gnotobiotic Animal Model. Front Microbiol 10:1906. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.01906
Hughes RL (2019) A Review of the Role of the Gut Microbiome in Personalized Sports Nutrition. Front Nutr 6:191. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2019.00191
Human Microbiome Project Consortium (2012) Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Nature 486:207–214. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11234
Ilbäck N-G, Nyblom M, Carlfors J et al (2004) Do surface-active lipids in food increase the intestinal permeability to toxic substances and allergenic agents? Med Hypotheses 63:724–730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2003.10.037
Jandhyala SM, Talukdar R, Subramanyam C et al (2015) Role of the normal gut microbiota. World J Gastroenterol 21:8787–8803. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i29.8787
Jang L-G, Choi G, Kim S-W et al (2019) The combination of sport and sport-specific diet is associated with characteristics of gut microbiota: an observational study. J Int Soc Sports Nutr 16:21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12970-019-0290-y
Jeukendrup AE, Vet-Joop K, Sturk A et al (2000) Relationship between gastro-intestinal complaints and endotoxaemia, cytokine release and the acute-phase reaction during and after a long-distance triathlon in highly trained men. Clin Sci (lond) 98:47–55
Johansson MEV, Hansson GC (2016) Immunological aspects of intestinal mucus and mucins. Nat Rev Immunol 16:639–649. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2016.88
Johnston M (2016) Joshua Lederberg on Bacterial Recombination. Genetics 203:613–614. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.116.190637
Joyner MJ, Coyle EF (2008) Endurance exercise performance: the physiology of champions. J Physiol 586:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2007.143834
Kararli TT (1995) Comparison of the gastrointestinal anatomy, physiology, and biochemistry of humans and commonly used laboratory animals. Biopharm Drug Dispos 16:351–380. https://doi.org/10.1002/bdd.2510160502
Karhu E, Forsgård RA, Alanko L et al (2017) Exercise and gastrointestinal symptoms: running-induced changes in intestinal permeability and markers of gastrointestinal function in asymptomatic and symptomatic runners. Eur J Appl Physiol 117:2519–2526. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-017-3739-1
Keohane DM, Woods T, O’Connor P et al (2019) Four men in a boat: ultra-endurance exercise alters the gut microbiome. J Sci Med Sport 22:1059–1064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsams.2019.04.004
Kim D, Yoo S-A, Kim W-U (2016) Gut microbiota in autoimmunity: potential for clinical applications. Arch Pharm Res 39:1565–1576. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-016-0796-7
Kim S, Goel R, Kumar A et al (2018) Imbalance of gut microbiome and intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction in patients with high blood pressure. Clin Sci (lond) 132:701–718. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20180087
Knoth C, Knechtle B, Rüst CA et al (2012) Participation and performance trends in multistage ultramarathons-the “Marathon des Sables” 2003–2012. Extrem Physiol Med 1:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/2046-7648-1-13
Koh A, De Vadder F, Kovatcheva-Datchary P, Bäckhed F (2016) From dietary fiber to host physiology: short-chain fatty acids as key bacterial metabolites. Cell 165:1332–1345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.041
Kralova I, Sjöblom J (2009) Surfactants used in food industry: a review. J Dispersion Sci Technol 30:1363–1383. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932690902735561
Lambert GP (2008) Intestinal barrier dysfunction, endotoxemia, and gastrointestinal symptoms: the “canary in the coal mine” during exercise-heat stress? Med Sport Sci 53:61–73. https://doi.org/10.1159/000151550
Laudisi F, Di Fusco D, Dinallo V et al (2019a) the food additive maltodextrin promotes endoplasmic reticulum stress-driven mucus depletion and exacerbates intestinal inflammation. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 7:457–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmgh.2018.09.002
Laudisi F, Stolfi C, Monteleone G (2019b) Impact of food additives on gut homeostasis. Nutrients 11:2334. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102334
Lepage P, Leclerc MC, Joossens M et al (2013) A metagenomic insight into our gut’s microbiome. Gut 62:146–158. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2011-301805
Lerner A, Matthias T (2015) Changes in intestinal tight junction permeability associated with industrial food additives explain the rising incidence of autoimmune disease. Autoimmun Rev 14:479–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2015.01.009
Li C, Li Y, Wang N et al (2022) Intestinal permeability associated with the loss of skeletal muscle strength in middle-aged and older adults in rural area of Beijing. China Healthcare (basel) 10:1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10061100
Liu C-W, Chi L, Tu P et al (2019) Quantitative proteomics reveals systematic dysregulations of liver protein metabolism in sucralose-treated mice. J Proteomics 196:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2019.01.011
Louis P, Flint HJ (2009) Diversity, metabolism and microbial ecology of butyrate-producing bacteria from the human large intestine. FEMS Microbiol Lett 294:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2009.01514.x
Luo M-J, Rao S-S, Tan Y-J et al (2020) Fasting before or after wound injury accelerates wound healing through the activation of pro-angiogenic SMOC1 and SCG2. Theranostics 10:3779–3792. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.44115
Mach N, Fuster-Botella D (2017) Endurance exercise and gut microbiota: a review. J Sport Health Sci 6:179–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jshs.2016.05.001
Mahmud N, Weir DG (2001) The urban diet and Crohn’s disease: is there a relationship? Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 13:93–95. https://doi.org/10.1097/00042737-200102000-00001
Malik M, Subedi S, Marques CNH, Mahler GJ (2020) Bacteria remediate the effects of food additives on intestinal function in an in vitro model of the gastrointestinal tract. Front Nutr 7:131. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2020.00131
Malinen E, Krogius-Kurikka L, Lyra A et al (2010) Association of symptoms with gastrointestinal microbiota in irritable bowel syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 16:4532–4540. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i36.4532
Marion-Letellier R, Amamou A, Savoye G, Ghosh S (2019) Inflammatory bowel diseases and food additives: to add fuel on the flames! Nutrients 11:1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11051111
Martínez-Carrillo BE, Rosales-Gómez CA, Ramírez-Durán N et al (2019) Effect of chronic consumption of sweeteners on microbiota and immunity in the small intestine of young mice. Int J Food Sci 2019:e9619020. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/9619020
Martino JV, Van Limbergen J, Cahill LE (2017) The role of carrageenan and carboxymethylcellulose in the development of intestinal inflammation. Front Pediatr 5:96. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2017.00096
Mata F, Valenzuela PL, Gimenez J et al (2019) Carbohydrate availability and physical performance: physiological overview and practical recommendations. Nutrients 11:1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11051084
McNeil NI (1984) The contribution of the large intestine to energy supplies in man. Am J Clin Nutr 39:338–342. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/39.2.338
McOmber ME, Ou C-N, Shulman RJ (2010) Effects of timing, sex, and age on site-specific gastrointestinal permeability testing in children and adults. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 50:269–275. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0b013e3181aa3aa9
Miller SI, Ernst RK, Bader MW (2005) LPS, TLR4 and infectious disease diversity. Nat Rev Microbiol 3:36–46. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro1068
Minihane AM, Vinoy S, Russell WR et al (2015) Low-grade inflammation, diet composition and health: current research evidence and its translation. Br J Nutr 114:999–1012. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114515002093
Miranda-Comas G, Petering RC, Zaman N, Chang R (2022) Implications of the gut microbiome in sports. Sports Health 14:894–898. https://doi.org/10.1177/19417381211060006
Mishra A, Makharia GK (2012) Techniques of functional and motility test: how to perform and interpret intestinal permeability. J Neurogastroenterol Motil 18:443–447. https://doi.org/10.5056/jnm.2012.18.4.443
Mohr AE, Jäger R, Carpenter KC et al (2020) The athletic gut microbiota. J Int Soc Sports Nutr 17:24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12970-020-00353-w
Monteiro C, Cannon G, Jaime P, et al (2016) Food classification. Public health NOVA. The star shines bright
Morishima S, Aoi W, Kawamura A et al (2021) Intensive, prolonged exercise seemingly causes gut dysbiosis in female endurance runners. J Clin Biochem Nutr 68:253–258. https://doi.org/10.3164/jcbn.20-131
Moses FM (1990) The effect of exercise on the gastrointestinal tract. Sports Med 9:159–172. https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-199009030-00004
Murray R, Bartoli W, Stofan J et al (1999) A comparison of the gastric emptying characteristics of selected sports drinks. Int J Sport Nutr 9:263–274. https://doi.org/10.1123/ijsn.9.3.263
Naito Y, Ito M, Watanabe T, Suzuki H (2005) Biomarkers in patients with gastric inflammation: a systematic review. Digestion 72:164–180. https://doi.org/10.1159/000088396
Nay K, Jollet M, Goustard B et al (2019) Gut bacteria are critical for optimal muscle function: a potential link with glucose homeostasis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 317:E158–E171. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00521.2018
Nickerson KP, McDonald C (2012) Crohn’s disease-associated adherent-invasive Escherichia coli adhesion is enhanced by exposure to the ubiquitous dietary polysaccharide maltodextrin. PLoS ONE 7:e52132. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0052132
Nickerson KP, Homer CR, Kessler SP et al (2014) The dietary polysaccharide maltodextrin promotes Salmonella survival and mucosal colonization in mice. PLoS ONE 9:e101789. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0101789
Nusrat A, Turner JR, Madara JL (2000) Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of tight junctions. IV. Regulation of tight junctions by extracellular stimuli: nutrients, cytokines, and immune cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 279:G851-857. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.2000.279.5.G851
O’Brien MT, O’Sullivan O, Claesson MJ, Cotter PD (2022) The athlete gut microbiome and its relevance to health and performance: a review. Sports Med 52:119–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-022-01785-x
Ockner RK, Manning JA (1974) Fatty acid-binding protein in small intestine. Identification, isolation, and evidence for its role in cellular fatty acid transport. J Clin Invest 54:326–338. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI107768
Okamoto T, Morino K, Ugi S et al (2019) Microbiome potentiates endurance exercise through intestinal acetate production. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 316:E956–E966. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00510.2018
Ortega RM, Pérez-Rodrigo C, López-Sobaler AM (2015) Dietary assessment methods: dietary records. Nutr Hosp 31(Suppl 3):38–45. https://doi.org/10.3305/nh.2015.31.sup3.8749
Ouellette AJ, Hsieh MM, Nosek MT et al (1994) Mouse Paneth cell defensins: primary structures and antibacterial activities of numerous cryptdin isoforms. Infect Immun 62:5040–5047. https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.62.11.5040-5047.1994
Paone P, Cani PD (2020) Mucus barrier, mucins and gut microbiota: the expected slimy partners? Gut 69:2232–2243. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322260
Parada Venegas D, De la Fuente MK, Landskron G, et al (2019) Short Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)-Mediated Gut Epithelial and Immune Regulation and Its Relevance for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Frontiers in Immunology 10:
Partridge D, Lloyd KA, Rhodes JM et al (2019) Food additives: assessing the impact of exposure to permitted emulsifiers on bowel and metabolic health—introducing the FADiets study. Nutr Bull 44:329–349. https://doi.org/10.1111/nbu.12408
Pasiakos SM, Karl JP, Margolis LM (2021) Challenging traditional carbohydrate intake recommendations for optimizing performance at high altitude. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 24:483–489. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCO.0000000000000782
Patterson RE, Sears DD (2017) Metabolic effects of intermittent fasting. Annu Rev Nutr 37:371–393. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-nutr-071816-064634
Payne AN, Chassard C, Lacroix C (2012) Gut microbial adaptation to dietary consumption of fructose, artificial sweeteners and sugar alcohols: implications for host-microbe interactions contributing to obesity. Obes Rev 13:799–809. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-789X.2012.01009.x
Peng Q, Chang H, Wang R et al (2019) Potassium sorbate suppresses intestinal microbial activity and triggers immune regulation in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Food Funct 10:7164–7173. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9FO01237K
Peters EM, Goetzsche JM, Grobbelaar B, Noakes TD (1993) Vitamin C supplementation reduces the incidence of postrace symptoms of upper-respiratory-tract infection in ultramarathon runners. Am J Clin Nutr 57:170–174. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/57.2.170
Peters HP, Bos M, Seebregts L et al (1999) Gastrointestinal symptoms in long-distance runners, cyclists, and triathletes: prevalence, medication, and etiology. Am J Gastroenterol 94:1570–1581. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.1999.01147.x
Peterson LW, Artis D (2014) Intestinal epithelial cells: regulators of barrier function and immune homeostasis. Nat Rev Immunol 14:141–153. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3608
Pfeiffer B, Stellingwerff T, Hodgson AB et al (2012) Nutritional intake and gastrointestinal problems during competitive endurance events. Med Sci Sports Exerc 44:344–351. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0b013e31822dc809
Piper JD, Piper PW (2017) Benzoate and sorbate salts: a systematic review of the potential hazards of these invaluable preservatives and the expanding spectrum of clinical uses for sodium benzoate. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 16:868–880. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12284
Pires W, Veneroso CE, Wanner SP et al (2017) Association between exercise-induced hyperthermia and intestinal permeability: a systematic review. Sports Med 47:1389–1403. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-016-0654-2
Podlogar T, Wallis GA (2022) New horizons in carbohydrate research and application for endurance athletes. Sports Med 52:5–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-022-01757-1
Puértolas-Balint F, Schroeder BO (2020) Does an apple a day also keep the microbes away? The interplay between diet, microbiota, and host defense peptides at the intestinal mucosal barrier. Front Immunol 11:1164. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.01164
Qamar MI, Read AE (1987) Effects of exercise on mesenteric blood flow in man. Gut 28:583–587. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.28.5.583
Qi Y, Goel R, Kim S et al (2017) Intestinal permeability biomarker Zonulin is elevated in healthy aging. J Am Med Dir Assoc 18:810.e1-810.e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2017.05.018
Raoul P, Cintoni M, Palombaro M et al (2022) Food additives, a key environmental factor in the development of IBD through Gut dysbiosis. Microorganisms 10:167. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10010167
Rehrer NJ, Brouns F, Beckers EJ et al (1992) Physiological changes and gastro-intestinal symptoms as a result of ultra-endurance running. Europ J Appl Physiol 64:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00376431
Ren C, Dokter-Fokkens J, Figueroa Lozano S et al (2018) Lactic acid bacteria may impact intestinal barrier function by modulating goblet cells. Mol Nutr Food Res 62:e1700572. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201700572
Ribeiro FM, Petriz B, Marques G et al (2021) Is there an exercise-intensity threshold capable of avoiding the leaky gut? Front Nutr 8:627289. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2021.627289
Rinninella E, Cintoni M, Raoul P et al (2019) Food components and dietary habits: keys for a healthy gut microbiota composition. Nutrients 11:2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102393
Roberts CL, Rushworth SL, Richman E, Rhodes JM (2013) Hypothesis: increased consumption of emulsifiers as an explanation for the rising incidence of Crohn’s disease. J Crohns Colitis 7:338–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crohns.2013.01.004
Rodriguez-Palacios A, Harding A, Menghini P et al (2018) The artificial sweetener splenda promotes gut proteobacteria, dysbiosis, and myeloperoxidase reactivity in crohn’s disease-like ileitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 24:1005–1020. https://doi.org/10.1093/ibd/izy060
Romo-Romo A, Aguilar-Salinas CA, Brito-Córdova GX et al (2018) Sucralose decreases insulin sensitivity in healthy subjects: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr 108:485–491. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/nqy152
Rothschild JA, Kilding AE, Plews DJ (2020) Prevalence and determinants of fasted training in endurance athletes: a survey analysis. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 30:345–356. https://doi.org/10.1123/ijsnem.2020-0109
Ruiz-Ojeda FJ, Plaza-Díaz J, Sáez-Lara MJ, Gil A (2019) Effects of sweeteners on the gut microbiota: a review of experimental studies and clinical trials. Adv Nutr 10:S31–S48. https://doi.org/10.1093/advances/nmy037
Russo F, Chimienti G, Riezzo G et al (2018) Adipose tissue-derived biomarkers of intestinal barrier functions for the characterization of diarrhoea-predominant IBS. Dis Markers 2018:1827937. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1827937
Sancho E, Batlle E, Clevers H (2003) Live and let die in the intestinal epithelium. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15:763–770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2003.10.012
Satokari R (2020) High intake of sugar and the balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory gut bacteria. Nutrients 12:1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051348
Schnabel L, Buscail C, Sabate J-M et al (2018) Association between ultra-processed food consumption and functional gastrointestinal disorders: results from the French NutriNet-Santé cohort. Am J Gastroenterol 113:1217–1228. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41395-018-0137-1
Schumann RR, Leong SR, Flaggs GW et al (1990) Structure and function of lipopolysaccharide binding protein. Science 249:1429–1431. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.2402637
Shah YM (2016) The role of hypoxia in intestinal inflammation. Mol Cell Pediatrics 3:1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40348-016-0030-1
Shah V, Lambeth SM et al (2015) Composition diversity and abundance of gut microbiome in prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Obes 2:108–114
Shi X, Horn MK, Osterberg KL et al (2004) Gastrointestinal discomfort during intermittent high-intensity exercise: effect of carbohydrate-electrolyte beverage. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 14:673–683. https://doi.org/10.1123/ijsnem.14.6.673
Shimizu K, Ogura H, Goto M et al (2006) Altered gut flora and environment in patients with severe SIRS. J Trauma 60:126–133. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ta.0000197374.99755.fe
Shing CM, Peake JM, Lim CL et al (2014) Effects of probiotics supplementation on gastrointestinal permeability, inflammation and exercise performance in the heat. Eur J Appl Physiol 114:93–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-013-2748-y
Shiro Y, Arai Y-C, Ikemoto T et al (2021) Correlation between gut microbiome composition and acute pain perception in young healthy male subjects. Pain Med 22:1522–1531. https://doi.org/10.1093/pm/pnaa401
Simon M-C, Sina C, Ferrario PG et al (2023) Gut microbiome analysis for personalized nutrition: the state of science. Mol Nutr Food Res 67:e2200476. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.202200476
Simpson RJ, Campbell JP, Gleeson M et al (2020) Can exercise affect immune function to increase susceptibility to infection? Exerc Immunol Rev 26:8–22
Singh RK, Chang H-W, Yan D et al (2017) Influence of diet on the gut microbiome and implications for human health. J Transl Med 15:73. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-017-1175-y
Sinisgalli R, de Lira CAB, Vancini RL et al (2021) Impact of training volume and experience on amateur Ironman triathlon performance. Physiol Behav 232:113344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2021.113344
Smith KA, Pugh JN, Duca FA et al (2021) Gastrointestinal pathophysiology during endurance exercise: endocrine, microbiome, and nutritional influences. Eur J Appl Physiol 121:2657–2674. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-021-04737-x
Soffritti M, Padovani M, Tibaldi E et al (2016) Sucralose administered in feed, beginning prenatally through lifespan, induces hematopoietic neoplasias in male Swiss mice. Int J Occup Environ Health 22:7–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/10773525.2015.1106075
Staudacher HM, Loughman A (2021) Gut health: definitions and determinants. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 6:269. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2468-1253(21)00071-6
Stellingwerff T, Cox GR (2014) Systematic review: carbohydrate supplementation on exercise performance or capacity of varying durations. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 39:998–1011. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2014-0027
Stuempfle KJ, Valentino T, Hew-Butler T et al (2016) Nausea is associated with endotoxemia during a 161-km ultramarathon. J Sports Sci 34:1662–1668. https://doi.org/10.1080/02640414.2015.1130238
Suzuki T (2013) Regulation of intestinal epithelial permeability by tight junctions. Cell Mol Life Sci 70:631–659. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1070-x
Swidsinski A, Ung V, Sydora BC et al (2009) Bacterial overgrowth and inflammation of small intestine after carboxymethylcellulose ingestion in genetically susceptible mice. Inflamm Bowel Dis 15:359–364. https://doi.org/10.1002/ibd.20763
Tailford LE, Crost EH, Kavanaugh D, Juge N (2015) Mucin glycan foraging in the human gut microbiome. Front Genet 6:81. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2015.00081
Temesi J, Johnson NA, Raymond J et al (2011) Carbohydrate ingestion during endurance exercise improves performance in adults. J Nutr 141:890–897. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.110.137075
ter Steege RWF, Van der Palen J, Kolkman JJ (2008) Prevalence of gastrointestinal complaints in runners competing in a long-distance run: an internet-based observational study in 1281 subjects. Scand J Gastroenterol 43:1477–1482. https://doi.org/10.1080/00365520802321170
Terjung RL, Clarkson P, Eichner ER et al (2000) American College of Sports Medicine roundtable. The physiological and health effects of oral creatine supplementation. Med Sci Sports Exerc 32:706–717. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005768-200003000-00024
Thomas DT, Erdman KA, Burke LM (2016) American College of Sports Medicine Joint Position Statement. Nutrition and athletic performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc 48:543–568. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0000000000000852
Thomas S, Izard J, Walsh E et al (2017) The host microbiome regulates and maintains human health: a primer and perspective for non-microbiologists. Cancer Res 77:1783–1812. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-2929
Thuijls G, van Wijck K, Grootjans J et al (2011) Early diagnosis of intestinal ischemia using urinary and plasma fatty acid binding proteins. Ann Surg 253:303–308. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0b013e318207a767
Tlaskalová-Hogenová H, Stěpánková R, Kozáková H et al (2011) The role of gut microbiota (commensal bacteria) and the mucosal barrier in the pathogenesis of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases and cancer: contribution of germ-free and gnotobiotic animal models of human diseases. Cell Mol Immunol 8:110–120. https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2010.67
Turner JR (2009) Intestinal mucosal barrier function in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 9:799–809. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2653
Uebanso T, Ohnishi A, Kitayama R et al (2017) Effects of low-dose non-caloric sweetener consumption on gut microbiota in mice. Nutrients 9:560. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9060560
Urdampilleta A, Arribalzaga S, Viribay A et al (2020) Effects of 120 vs. 60 and 90 g/h carbohydrate intake during a trail marathon on neuromuscular function and high intensity run capacity recovery. Nutrients 12:2094. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12072094
van der Flier LG, Clevers H (2009) Stem cells, self-renewal, and differentiation in the intestinal epithelium. Annu Rev Physiol 71:241–260. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.physiol.010908.163145
van Wijck K, Lenaerts K, van Loon LJC et al (2011) Exercise-induced splanchnic hypoperfusion results in gut dysfunction in healthy men. PLoS ONE 6:e22366. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0022366
Vandenbogaerde TJ, Hopkins WG (2011) Effects of acute carbohydrate supplementation on endurance performance: a meta-analysis. Sports Med 41:773–792. https://doi.org/10.2165/11590520-000000000-00000
von Martels JZH, Bourgonje AR, Harmsen HJM et al (2019) Assessing intestinal permeability in Crohn’s disease patients using orally administered 52Cr-EDTA. PLoS ONE 14:e0211973. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0211973
Wang L, Llorente C, Hartmann P et al (2015) Methods to determine intestinal permeability and bacterial translocation during liver disease. J Immunol Methods 421:44–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jim.2014.12.015
Wells JM, Brummer RJ, Derrien M et al (2017) Homeostasis of the gut barrier and potential biomarkers. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 312:G171–G193. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00048.2015
Wiącek J, Karolkiewicz J (2023) Different approaches to ergogenic, pre-, and probiotic supplementation in sports with different metabolism characteristics: a mini review. Nutrients 15:1541. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061541
Wolters M, Ahrens J, Romaní-Pérez M et al (2019) Dietary fat, the gut microbiota, and metabolic health—a systematic review conducted within the MyNewGut project. Clin Nutr 38:2504–2520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2018.12.024
Wong JMW, de Souza R, Kendall CWC et al (2006) Colonic health: fermentation and short chain fatty acids. J Clin Gastroenterol 40:235–243. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004836-200603000-00015
Yan J, Charles JF (2018) Gut Microbiota and IGF-1. Calcif Tissue Int 102:406–414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-018-0395-3
Yatsunenko T, Rey FE, Manary MJ et al (2012) Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature 486:222–227. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11053
Yeh YJ, Law LYL, Lim CL (2013) Gastrointestinal response and endotoxemia during intense exercise in hot and cool environments. Eur J Appl Physiol 113:1575–1583. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-013-2587-x
Yu Q, Wang Z, Li P, Yang Q (2013) The effect of various absorption enhancers on tight junction in the human intestinal Caco-2 cell line. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 39:587–592. https://doi.org/10.3109/03639045.2012.692376
Zhao J, Bai M, Ning X et al (2022) Expansion of Escherichia-Shigella in gut is associated with the onset and response to immunosuppressive therapy of IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 33:2276. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2022020189
Zoetendal EG, Raes J, van den Bogert B et al (2012) The human small intestinal microbiota is driven by rapid uptake and conversion of simple carbohydrates. ISME J 6:1415–1426. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2011.212
Zuo Y, Zhang M, Si Y et al (2021) Prediction of health risk preventative behavior of amateur marathon runners: a cross-sectional study. Risk Manag Healthc Policy 14:2929–2944. https://doi.org/10.2147/RMHP.S305937
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr Mikel Berdud and Dr Francisco Corbi for their advice on writing and editing this article. With the support of the National Institute of Physical Education of Catalonia, INEFC.
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contributed to the study. JÁ-H had the idea for the article and was the writer of the first version of the manuscript. AG and AO wrote specifically about intestinal permeability. FC collaborates supervising the manuscript. All the authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. Finally, all the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest to disclose. All the authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Human and animal rights
This article contains no studies on human or animal subjects conducted by the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by Michael I Lindinger.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Álvarez-Herms, J., González-Benito, A., Corbi, F. et al. What if gastrointestinal complications in endurance athletes were gut injuries in response to a high consumption of ultra-processed foods? Please take care of your bugs if you want to improve endurance performance: a narrative review. Eur J Appl Physiol 124, 383–402 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-023-05331-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-023-05331-z