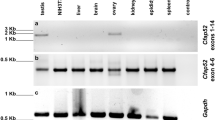
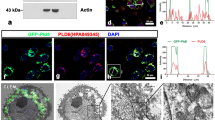
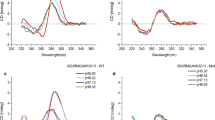
Abstract
The localization of DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box helicase 6 (DDX6) in spermatogenic cells from the mouse, rat, and guinea pig was studied by immunofluorescence (IF) and immunoelectron microscopy (IEM). Spermatogenic cells from these species yielded similar DDX6 localization pattern. IF microscopy results showed that DDX6 localizes to both the nucleus and cytoplasm. In the cytoplasm of spermatogenic cells, diffuse cytosolic and discrete granular staining was observed, with the staining pattern changing during cell differentiation. IEM revealed that DDX6 localized to the five different types of nuage structures and non-nuage structures, including small granule aggregate and late spermatid annuli. Nuclear labeling was strongest in leptotene and zygotene spermatocytes and moderately strong in the nuclear pocket of late spermatids. DDX6 also localized to the surface of outer dense fibers, which comprise of flagella. The results show that DDX6 is present in nuage and non-nuage structures as well as nuclei, suggesting that DDX6 has diverse functions in spermatogenic cells.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akao Y, Nakagawa Y (2006) Expression of the DEAD-box/RNA helicase rck/p54 in mouse tissues: implications for heterogeneous protein expression. J Histochem Cytochem 54:955–960
Andrei MA, Ingelfinger D, Heitzmann R, Achel T, Rivera-Pomar R, Lührmann R (2005) A role for elF4E and elF4E-transporter in targeting mRNPs to mammalian processing bodies. RNA 11:717–727
Aravin AA, Van der Heijden GW, Castaneda J, Vagin VV, Hannon GJ, Bortvin A (2009) Cytoplasmic compartmentalization of the fetal piRNA pathway in mice. PLoS Genet 5:1–12
Clermont Y, Oko R, Hermo L (1993) Cell biology of mammalian spermiogenesis. In: Desjardins C, Ewing LL (eds) Cell and molecular biology of the testis. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 332–376
Coller JM, Tucker M, Sheth U, Valecia-Sanchez MA, Parker R (2001) The DEAD box helicase, Dhh1p, functions in mRNA decapping and interacts with both the decapping and deadenylase complexes. RNA 7:1717–1727
Eulalio A, Behm-Ansmant L, Schweizer D, Izaurralde E (2007) P-body formation is a consequence, not the cause, of RNA-mediated gene silencing. Mol Cell Biol 27:3970–3981
Fawcett DW, Eddy EM, Phillips DM (1970) Observations on the fine structure and relationships of the chromatoid body in mammalian spermatogenesis. Biol Reprod 2:129–153
Fenger-Groen M, Fillman C, Norrild B, Lykke-Andersen J (2005) Multiple processing body factors and the ARE binding protein TTP activate mRNA decapping. Mol Cell 20:905–915
Ferraiuolo M, Basak S, Dostie J, Murray EL, Schoenberg DR, Sonnenberg N (2005) A role for the elF4E-binding protein 4E-T in P-body formation and mRNA decay. J Cell Biol 170:913–924
Franks T, Lukke-Andersen J (2008) The control of mRNA decapping and P-body formation. Mol Cell 32:605–615
Greer AE, Hearing P, Ketner G (2011) The adenovirus E4 11 k protein binds and localizes the cytoplasmic P-body component Ddx6 to aggresomes. Virology 417:161–168
Haraguchi CM, Mabuchi T, Yokota S (2003) Localization of a mitochondrial type of NADP-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase in kidney and heart of rat: an immunocytochemical and biochemical study. J Histochem Cytochem 51:215–226
Huys A, Thibault PA, Wilson JA (2013) Modulation of hepatitis C virus RNA accumulation and translation by DDX6 and miR-122 are mediated by separate mechanism. PLoS One 8(6):e67437
James V, Zhang Y, Foxler DE, de Moor CH, Kong YW, Webb TM, Self TJ, Feng Y, Lagos D, Chu CY, Rana TM, Morley SJ, Longmore GD, Bushell M, Sharp TV (2010) LIM-domain proteins, LIMD1, Ajuba, and WTIP are required for microRNA-mediated gene silencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:12499–12504
Kotaja N, Sassone-Corsi P (2007) The chromatoid body: a germ-cell-specific RNA-processing centre. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:85–90
Kotaja N, Bhattacharyya SN, Jaskiewicz L, Kimmins S, Parvinen M, Filipowicz W, Sassone-Corsi P (2006) The chromatoid body of male germ cells: similarity with processing bodies and presence of dicer and microRNA pathway components. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:2647–2652
Ladomery M, Wade E, Sommerville J (1997) Xp54, the Xenopus homologue of human RNA helicase p54, is an integral component of stored mRNP particles in oocytes. Nucleic Acids Res 25:965–973
Lalli MF, Clermont Y (1981) Structural changes of the head components of rat spermatid during spermatogenesis. Am J Anat 160:419–434
Matsumoto K, Kwon O-Y, Kim H, Akao Y (2005) Epression of rck/p54, a DEAD-box RNA helicase, in gametogenesis and early embryogenesis of mice. Dev Dyn 233:1149–1156
Meikar O, DaRos M, Korhonen H, Kotaja N (2011) Chromatoid body and small RNAs in male germ cells. Reproduction 142:195–209
Minshall N, Kress M, Weil D, Standart N (2009) Role of p54 RNA helicase activity and its C-terminal domain in translational repression, P-body localization and assembly. Mol Biol Cell 20:2464–2472
Naarmann IS, Narnisch C, Müller-Newen G, Urlaub H, Ostareck-Lederer A, Ostareck DH (2010) DDX6 recruits translational silenced human reticulocyte 15-lipoxygenase mRNA to RNP granules. RNA 16:2189–2204
Onohara Y, Yokota S (2012) Expression of DDX25 in nuage components of mammalian spermatogenic cells: immunofluorescence and immunoelectron microscopic study. Histochem Cell Biol 137:37–51
Onohara Y, Fujiwara T, Yasukochi T, Himeno M, Yokota S (2010) Localization of mouse vasa homolog protein in chromatoid body and related nuage structures of mammalian spermatogenic cells during spermatogenesis. Histochem Cell Biol 133:627–639
Rickwood D, Ford TC (1983) Preparation and fractionation of nuclei, nucleoli and deoxyribonucleoproteins. In: Rickwood D (ed) Iodinated density gradient media. A practical approach. IRL PRESS, Oxford, pp 69–89
Russell L, Frank B (1978) Ultrastructural characterization of nuage in spermatocytes of the rat testis. Anat Rec 190:79–98
Russell LD, Ettlin RA, Hikim APS, Clegg ED (1990) Histological and histopathological evaluation of the testis. Cache River Press, Florida
Smillie DA, Sommerville J (2002) RNA helicase p54 (DDX6) is a shuttling protein involved in nuclear assembly of stores mRNP particles. J Cell Sci 115:395–407
Takebe M, Onohara Y, Yokota S (2013) Miki Takebe, Expression of MAEL in Nuage and non-Nuage compartments of rat spermatogenic cells and colocalization with DDX4, DDX25 and MIWI. Histochem Cell Biol 140:169–181
Tritschler F, Braun JE, Eulalio A, Truffault V, Izaurralde E, Weichenrieder O (2009) Structural basis for the mutually exclusive anchoring of P body components EDC3 and Tral to the DEAD box protein DDX6/Me31B. Mol Cell 33:661–668
Voronina E, Seydoux G, Nagamori N, Sassone-Corsi P (2013) RNA granules in germ cells. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2011(3):1–27
Weston A, Sommerville J (2006) Xp54 and related (DDX6-like) RNA helicases: roles in messenger RNP assembly, translation regulation and RNA degradation. Nucleic Acids Res 34:3082–3094
Yokota S (2012a) Preparation of colloidal gold particles and conjugation of protein A, IgG, F(ab’)2, and streptavidin. In: Schwarzbach SD, Osafune T (eds) Immunoelectron microscopy. Methods and protocols. Springer, New York, pp 109–119
Yokota S (2012b) Nuage proteins: their localization in subcellular structures of spermatogenic cells as revealed by immunoelectron microscopy. Histochem Cell Biol 138:1–11
Yokota S, Onohara Y (2013) Expression sites of NANOS1 in rat spermatogenic cells as revealed by immunoelectron microscopy. Cell Bio 2:1–10
Yonetamari H, Onohara Y, Yokota S (2012) Localization of BRUNNOL2 in rat spermatogenic cells as revealed by immunofluorescence and immunoelectron microscopic techniques. Open J Cell Biol 2:11–20
Zhang W-J, Wu JY (1996) Functional properties of p54, a novel SR protein active in constitutive and alternative splicing. Mol Cell Biol 16:5400–5408
Acknowledgments
The work was supported in part by research funds from Nagasaki International University, a grant-in-aid from the Ministry of Education, Science, Culture and Sport, and Sport (17570158), by science research promotion fund from the Promotion and Mutual Aid Corporation for Private Schools of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawahara, C., Yokota, S. & Fujita, H. DDX6 localizes to nuage structures and the annulus of mammalian spermatogenic cells. Histochem Cell Biol 141, 111–121 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-013-1153-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-013-1153-2