Abstract
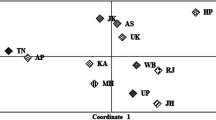
Linguistic and ethnic diversity throughout the Himalayas suggests that this mountain range played an important role in shaping the genetic landscapes of the region. Previous Y-chromosome work revealed that the Himalayas acted as a biased bidirectional barrier to gene flow across the cordillera. In the present study, 17 Y-chromosomal short tandem repeat (Y-STR) loci included in the AmpFlSTR® Yfiler kit were analyzed in 344 unrelated males from three Nepalese populations (Tamang, Newar, and Kathmandu) and a general collection from Tibet. The latter displays the highest haplotype diversity (0.9990) followed by Kathmandu (0.9977), Newar (0.9570), and Tamang (0.9545). The overall haplotype diversity for the Himalayan populations at 17 Y-STR loci was 0.9973, and the corresponding values for the extended (11 loci) and minimal (nine loci) haplotypes were 0.9955 and 0.9942, respectively. No Y-STR profiles are shared across the four Himalayan collections at the 17-, 11-, and nine-locus resolutions considered, indicating a lack of recent gene flow among them. Phylogenetic analyses support our previous findings that Kathmandu, and to some extent Newar, received significant genetic influence from India while Tamang and Tibet exhibit limited or no gene flow from the subcontinent. A median-joining network of haplogroup O3a3c-M134 based on 15 Y-STR loci from our four Himalayan populations suggests either a male founder effect in Tamang, possibly from Tibet, or a recent bottleneck following their arrival south of the Himalayas from Tibet leading to their highly reduced Y single-nucleotide polymorphism and Y-STR diversity. The genetic uniqueness of the four Himalayan populations examined in this study merits the creation of separate databases for individual identification, parentage analysis, and population genetic studies.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Willuweit S, Roewer L, International Forensic Y Chromosome User Group (2007) Y chromosome haplotype reference database (YHRD): update. Forensic Sci Int Genet 1:83–87
Jobling MA, Tyler-Smith C (1993) The human Y chromosome: an evolutionary marker comes of age. Nat Rev Genet 8:598–612
Kwak KD, Jin HJ, Shin DJ, Kim JM, Roewer L, Krawczak M, Tyler-Smith C, Kim W (2005) Y-chromosomal STR haplotypes and their applications to forensic and population studies in east Asia. Int J Leg Med 119:195–201
Gayden T, Regueiro M, Martinez L, Cadenas AM, Herrera RJ (2008) Human Y-chromosome haplotyping by allele-specific polymerase chain reaction. Electrophoresis 29:2419–2423
Iida R, Kishi K (2005) Identification, characterization and forensic application of novel Y-STRs. Leg Med 7:255–258
Hanson EK, Ballantyne J (2007) An ultra-high discrimination Y chromosome short tandem repeat multiplex DNA typing system. PLoS ONE 8:e688
Budowle B, Ge J, Low J, Lai C, Yee WH, Law G, Tan WF, Chang YM, Perumal R, Keat PY, Mizuno N, Kasai K, Sekiguchi K, Chakraborty R (2009) The effects of Asian population substructure on Y STR forensic analyses. Leg Med 11:64–69
Alves C, Gusmão L, Barbosa J, Amorim A (2003) Evaluating the informative power of Y-STRs: a comparative study using European and new African haplotype data. Forensic Sci Int 34:126–133
Roewer L, Croucher PJ, Willuweit S, Lu TT, Kayser M, Lessig R, de Knijff P, Jobling MA, Tyler-Smith C, Krawczak M (2005) Signature of recent historical events in the European Y-chromosomal STR haplotype distribution. Hum Genet 116:279–291
Immel UD, Krawczak M, Udolph J, Richter A, Rodig H, Kleiber M, Klintschar M (2006) Y-chromosomal STR haplotype analysis reveals surname-associated strata in the East-German population. Eur J Hum Genet 14:577–582
Rebała K, Mikulich AI, Tsybovsky IS, Siváková D, Dzupinková Z, Szczerkowska-Dobosz A, Szczerkowska Z (2007) Y-STR variation among Slavs: evidence for the Slavic homeland in the middle Dnieper basin. J Hum Genet 52:406–414
Rodríguez V, Tomàs C, Sánchez JJ, Castro JA, Ramon MM, Barbaro A, Morling N, Picornell A (2009) Genetic sub-structure in western Mediterranean populations revealed by 12 Y chromosome STR loci. Int J Leg Med 123:137–141
Roewer L, Krawczak M, Willuweit S et al (2001) Online reference database of European Y-chromosomal short tandem repeat (STR) haplotypes. Forensic Sci Int 118:106–113
Kayser M, Brauer S, Willuweit S et al (2002) Online Y-chromosomal short tandem repeat haplotype reference database (YHRD) for U.S. populations. J Forensic Sci 47:513–519
Lessig R, Willuweit S, Krawczak M et al (2003) Asian online Y-STR haplotype reference database. Leg Med 5:S160–S163
Gayden T, Cadenas AM, Regueiro M, Singh NB, Zhivotovsky LA, Underhill PA, Cavalli-Sforza LL, Herrera RJ (2007) The Himalayas as a directional barrier to gene flow. Am J Hum Genet 80:884–894
Gayden T, Mirabal S, Cadenas AM, Lacau H, Simms TM, Morlote D, Chennakrishnaiah S, Herrera RJ (2009) Genetic insights into the origins of Tibeto-Burman populations in the Himalayas. J Hum Genet 54:216–223
Thangaraj K, Chaubey G, Kivisild T et al (2008) Maternal footprints of Southeast Asians in North India. Hum Hered 66:1–6
Fornarino S, Pala M, Battaglia V, Maranta R, Achilli A, Modiano G, Torroni A, Semino O, Santachiara-Benerecetti SA (2009) Mitochondrial and Y-chromosome diversity of the Tharus (Nepal): a reservoir of genetic variation. BMC Evol Biol 9:154
Qian Y, Qian B, Su B et al (2000) Multiple origins of Tibetan Y chromosomes. Hum Genet 106:453–454
Su B, Xiao C, Deka R et al (2000) Y chromosome haplotypes reveal prehistorical migrations to the Himalayas. Hum Genet 107:582–590
Hammer MF, Karafet TM, Park H, Omoto K, Harihara S, Stoneking M, Horai S (2006) Dual origins of the Japanese: common ground for hunter–gatherer and farmer Y chromosomes. J Hum Genet 51:47–58
Zhang Q, Yan J, Tang H, Jiao Z, Liu Y (2006) Genetic polymorphisms of 17 Y-STRs haplotypes in Tibetan ethnic minority group of China. Leg Med 8:300–305
Zhu B, Liu S, Ci D et al (2006) Population genetics for Y-chromosomal STRs haplotypes of Chinese Tibetan ethnic minority group in Tibet. Forensic Sci Int 161:78–83
Kang LL, Liu K, Ma Y (2007) Y chromosome STR haplotypes of Tibetan living Tibet Lassa. Forensic Sci Int 172:79–83
Zhu B, Wu Y, Shen C et al (2008) Genetic analysis of 17 Y-chromosomal STRs haplotypes of Chinese Tibetan ethnic group residing in Qinghai province of China. Forensic Sci Int 175:238–243
Parkin EJ, Kraaijenbrink T, Opgenort JRML, van Driem GL, Tuladhar NM, de Knijff P, Jobling MA (2007) Diversity of 26-locus Y-STR haplotypes in a Nepalese population sample: isolation and drift in the Himalayas. Forensic Sci Int 166:176–181
Antunez de Mayolo G, Antúñez de Mayolo A, Antúñez de Mayolo P (2002) Phylogenetics of worldwide human populations as determined by polymorphic Alu insertions. Electrophoresis 23:3346–3356
Applied Biosystems (2006) AmpFlSTR Yfiler PCR amplification kit user’s manual. Applied Biosystems, Foster City
Gusmão L, Butler JM, Carracedo A, Gill P, Kayser M, Mayr WR, Morling N, Prinz M, Roewer L, Tyler-Smith C, Schneider PM, DNA Commission of the International Society of Forensic Genetics (2006) DNA Commission of the International Society of Forensic Genetics (ISFG): an update of the recommendations on the use of Y-STRs in forensic analysis. Forensic Sci Int 157:187–197
Y Chromosome Consortium (2002) A nomenclature system for the tree of human Y-chromosomal binary haplogroups. Genome Res 12:339–348
Karafet TM, Mendez FL, Meilerman MB, Underhill PA, Zegura SL, Hammer MF (2008) New binary polymorphisms reshape and increase resolution of the human Y chromosomal haplogroup tree. Genome Res 18:830–838
Excoffier L, Laval LG, Schneider S (2005) Arlequin ver. 3.0: an integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evol Bioinform Online 1:47–50
Brinkmann C, Forster P, Schürenkamp M, Horst J, Rolf B, Brinkmann B (1999) Human Y-chromosomal STR haplotypes in a Kurdish population sample. Int J Leg Med 112:181–183
Pfeiffer H, Brinkmann B, Hühne J, Rolf B, Morris AA, Steighner R, Holland MM, Forster P (1999) Expanding the forensic German mitochondrial DNA control region database: genetic diversity as a function of sample size and microgeography. Int J Leg Med 112:291–298
Hashiyada M, Umetsu K, Yuasa I et al (2008) Population genetics of 17 Y-chromosomal STR loci in Japanese. Forensic Sci Int Genet 2:e69–e70
Yan J, Tang H, Liu Y et al (2007) Genetic polymorphisms of 17 Y-STRs haplotypes in Chinese Han population residing in Shandong province of China. Leg Med 94:196–202
Chang YM, Perumal R, Keat PY, Kuehn DL (2007) Haplotype diversity of 16 Y-chromosomal STRs in three main ethnic populations (Malays, Chinese and Indians) in Malaysia. Forensic Sci Int 167:70–76
Huang TY, Hsu YT, Li JM, Chung JH, Shun CT (2008) Polymorphism of 17 Y-STR loci in Taiwan population. Forensic Sci Int 174:249–254
Dobashi Y, Kido A, Fujitani N, Susukida R, Hara M, Oya M (2005) Y-chromosome STR haplotypes in a Bangladeshi population. Leg Med 7:122–126
Nagy M, Henke L, Henke J et al (2007) Searching for the origin of Romanies: Slovakian Romani, Jats of Haryana and Jat Sikhs Y-STR data in comparison with different Romani populations. Forensic Sci Int 169:19–26
Woźniak M, Derenko M, Malyarchuk B et al (2006) Allelic and haplotypic frequencies at 11 Y-STR loci in Buryats from South-East Siberia. Forensic Sci Int 164:271–275
Parkin EJ, Kraayenbrink T, van Driem GL, Tshering Of Gaselô K, de Knijff P, Jobling MA (2006) 26-Locus Y-STR typing in a Bhutanese population sample. Forensic Sci Int 161:1–7
Rohlf F (2002) NTSYSpc. Exter, Setauket
Felsentein J (2002) Phylogeny inference package (PHYLIP), version 3.6a3. Department of Genetics, University of Washington, Seattle, distributed by author
Kayser M, Brauer S, Weiss G et al (2003) Reduced Y-chromosome, but not mitochondrial DNA, diversity in human populations from West New Guinea. Am J Hum Genet 72:281–302
Polzin T, Daneschmand SV (2002) On Steiner trees and minimum spanning trees in hypergraphs. Oper Res Lett 31:12–20
Ferri G, Robino C, Alù M et al. (2008) Molecular characterisation and population genetics of the DYS458.2 allelic variant. Forensic Sci Int Genet: Genetics Supplement Series, Progress in Forensic Genetics 12—Proceedings of the 22nd International ISFG Congress, vol. 1, pp 203–205
Cadenas AM, Regueiro M, Gayden T, Singh N, Zhivotovsky LA, Underhill PA, Herrera RJ (2007) Male amelogenin dropouts: phylogenetic context, origins and implications. Forensic Sci Int 166:155–163
Thangaraj K, Reddy AG, Singh L (2002) Is the amelogenin gene reliable for gender identification in forensic casework and prenatal diagnosis? Int J Leg Med 116:121–123
Santos FR, Pandya A, Tyler-Smith C (1998) Reliability of DNA-based sex tests. Nat Genet 18:103
Wen B, Xie X, Gao S (2004) Analyses of genetic structure of Tibeto-Burman populations reveals sex-biased admixture in southern Tibeto-Burmans. Am J Hum Genet 74:856–865
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge Sheyla Mirabal and Kristian J. Herrera for their constructive criticism of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table 1
Y-STR data of the four Himalayan populations studied. (XLS 104 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
Allele frequencies of the 17 Y-STR loci studied for Tamang, Newar, Kathmandu, and Tibet populations. (DOC 58 kb)
Supplementary Table 3
Allele frequencies of the 17 Y-STR loci studied for Tamang, Newar, Kathmandu, and Tibet populations. (DOC 71 kb)
Supplementary Table 4
Allele frequencies of the 17 Y-STR loci studied for Tamang, Newar, Kathmandu, and Tibet populations. (DOC 77 kb)
Supplementary Table 5
Allele frequencies of the 17 Y-STR loci studied for Tamang, Newar, Kathmandu, and Tibet populations. (DOC 102 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gayden, T., Chennakrishnaiah, S., La Salvia, J. et al. Y-STR diversity in the Himalayas. Int J Legal Med 125, 367–375 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-010-0485-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-010-0485-x