Abstract
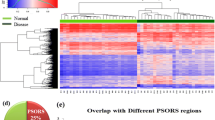
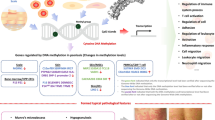
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that is characterized by aberrant cross-talk between keratinocytes and immune cells such as CD4+ T cells, resulting in keratinocyte hyperproliferation in the epidermis. DNA methylation, one of several epigenetic mechanisms, plays an important role in gene expression without changing the DNA sequence. Several studies have suggested the involvement of epigenetic regulation in skin lesions from patients with psoriasis. In this study, we investigated the genome-wide DNA methylation status of CD4+ T cells in patients with psoriasis compared with healthy subjects using methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-Seq). The results of MeDIP-Seq showed that the global methylation values of CD4+ T cells are higher in patients with psoriasis than in healthy controls, particularly in the promoter regions. Among the most hypermethylated genes in the promoter regions, we selected the genes whose expression is significantly reduced in the CD4+ T cells of psoriasis patients. Studies using the methylation inhibitor 5-azacytidine in vitro methylation assays have shown that the differential expression levels were associated with the methylation status of each gene. Bisulfite sequencing of the transcription start region of phosphatidic acid phosphatase type 2 domain containing 3 (PPAPDC3), one of the selected genes, showed hypermethylation in the CD4+ T cells of psoriasis patients. These results suggested that the methylation status, which is identified by MeDIP-Seq of the genes, was correlated with the mRNA expression level of the genes. Collectively, the DNA methylation status in CD4+ T cells might be associated with the pathogenesis of psoriasis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anders S, Huber W (2010) Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol 11:R106
Bernstein BE, Meissner A, Lander ES (2007) The mammalian epigenome. Cell 128:669–681
Brand S, Kesper DA, Teich R, Kilic-Niebergall E, Pinkenburg O, Bothur E, Lohoff M, Garn H, Pfefferle PI, Renz H (2012) DNA methylation of TH1/TH2 cytokine genes affects sensitization and progress of experimental asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 129:1602–1610
Brigati C, Banelli B, Casciano I, Di Vinci A, Matis S, Cutrona G, Forlani A, Allemanni G, Romani M (2011) Epigenetic mechanisms regulate ΔNP73 promoter function in human tonsil B cells. Mol Immunol 48:408–414
Brogdon JL, Xu Y, Szabo SJ, An S, Buxton F, Cohen D, Huang Q (2007) Histone deacetylase activities are required for innate immune cell control of Th1 but not Th2 effector cell function. Blood 109:1123–1130
Casciano I, Mazzocco K, Boni L, Pagnan G, Banelli B, Allemanni G, Ponzoni M, Tonini GP, Romani M (2002) Expression of DeltaNp73 is a molecular marker for adverse outcome in neuroblastoma patients. Cell Death Differ 9:246–251
Chandran V, Raychaudhuri SP (2010) Geoepidemiology and environmental factors of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. J Autoimmun 34:J314–J321
Datta Mitra A, Raychaudhuri SP, Abria CJ, Mitra A, Wright R, Ray R, Kundu-Raychaudhuri S (2013) 1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin-D3-3-bromoacetate regulates AKT/mTOR signaling cascades: a therapeutic agent for psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol 133:1556–1564
Enamandram M, Kimball AB (2013) Psoriasis epidemiology: the interplay of genes and the environment. J Invest Dermatol 133:287–289
Gaspari AA (2006) Innate and adaptive immunity and the pathophysiology of psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol 54:S67–S80
Han J, Park SK, Bae JB, Choi J, Lyu JM, Park SH, Kim HS, Kim YJ, Kim S, Kim TY (2012) The characteristics of genome-wide DNA methylation in naive CD4+ T cells of patients with psoriasis or atopic dermatitis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 422:157–163
Karason A, Gudjonsson JE, Upmanyu R, Antonsdottir AA, Hauksson VB, Runasdottir EH, Jonsson HH, Gudbjartsson DF, Frigge ML, Kong A, Stefansson K, Valdimarsson H, Gulcher JR (2003) A susceptibility gene for psoriatic arthritis maps to chromosome 16q: evidence for imprinting. Am J Hum Genet 72:125–131
Lew W, Bowcock AM, Krueger JG (2004) Psoriasis vulgaris: cutaneous lymphoid tissue supports T-cell activation and “Type 1” inflammatory gene expression. Trends Immunol 25:295–305
Liu GH, Guan T, Datta K, Coppinger J, Yates J 3rd, Gerace L (2009) Regulation of myoblast differentiation by the nuclear envelope protein NET39. Mol Cell Biol 29:5800–5812
Makar KW, Wilson CB (2004) DNA methylation is a nonredundant repressor of the Th2 effector program. J Immunol 173:4402–4406
Mitra A, Raychaudhuri SK, Raychaudhuri SP (2012) IL-22 induced cell proliferation is regulated by PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling cascade. Cytokine 60:38–42
Nestle FO, Kaplan DH, Barker J (2009) Psoriasis. N Engl J Med 36:496–509
Reik W (2007) Stability and flexibility of epigenetic gene regulation in mammalian development. Nature 447:425–432
Roberson EDO, Liu Y, Ryan C, Joyce CE, Duan S, Cao L, Martin A, Liao W, Mentor A, Bowcock AM (2012) A subset of methylated CpG sites differentiate psoriatic from normal skin. J Invest Dermatol 132:583–592
Robertson KD (2005) DNA methylation and human diseases. Nat Rev Genet 6:597–610
Schmidl C, Klug M, Boeld TJ, Andreesen R, Hoffmann P, Edinger M, Rehli M (2009) Lineage-specific DNA methylation in T cells correlates with histone methylation and enhancer activity. Genome Res 19:1165–1174
Selmi C, Lu Q, Humble MC (2012) Heritability versus the role of the environment in autoimmunity. J Autoimmun 39:249–252
Smith JF, Syritsyna O, Fellous M, Serres C, Mannowetz N, Kirichok Y, Lishko PV (2013) Disruption of the principal, progesterone-activated sperm Ca2+ channel in a CatSper2-deficient infertile patient. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:6823–6828
Wang H, Song W, Hu T, Zhang N, Miao S, Zong S, Wang L (2011) Fank1 interacts with Jab1 and regulates cell apoptosis via the AP-1 pathway. Cell Mol Life Sci 68:2129–2139
Wilson CB, Rowell E, Sekimata M (2009) Epigenetic control of T-helper-cell differentiation. Nat Rev Immunol 9:91–105
Zaba LC, Fuentes-Duculan J, Eungdamrong NJ, Abello MV, Novitskaya I, Pierson KC, Gonzalez J, Krueger JG, Lowes MA (2009) Psoriasis is characterized by accumulation of immunostimulatory and Th1/Th17 cell-polarizing myeloid dendritic cells. J Invest Dermatol 129:79–88
Zhang K, Zhang R, Li X, Yin G, Niu X (2009) Promoter methylation status of p15 and p21 genes in HPP-CFCs of bone marrow of patients with psoriasis. Eur J Dermatol 19:141–146
Zhang K, Zhang R, Li X, Yin G, Niu X, Hou R (2007) The mRNA expression and promoter methylation status of the p16 gene in colony-forming cells with high proliferative potential in patients with psoriasis. Clin Exp Dermatol 32:702–708
Zhang P, Su Y, Chen H, Zhao M, Lu Q (2010) Abnormal DNA methylation in skin lesions and PBMCs of patients with psoriasis vulgaris. J Dermatol Sci 60:40–42
Zhang P, Su Y, Lu Q (2012) Epigenetics and psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 26:399–403
Zhang P, Zhao M, Liang G, Yin G, Huang D, Su F, Zhai H, Wang L, Su Y, Lu Q (2013) Whole-genome DNA methylation in skin lesions from patients with psoriasis vulgaris. J Autoimmun 41:17–24
Zhou X, Hua X, Ding X, Bian Y, Wang X (2011) Trichostatin differentially regulates Th1 and Th2 responses and alleviates rheumatoid arthritis in mice. J Clin Immunol 31:395–405
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Korea government (MEST) (Nos. 20110027837 & 20100021811) and the Next-Generation BioGreen 21 Program (No. PJ007991), Rural Development Administration, Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, G.T., Han, J., Park, SG. et al. DNA methylation analysis of CD4+ T cells in patients with psoriasis. Arch Dermatol Res 306, 259–268 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-013-1432-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-013-1432-8