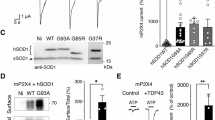
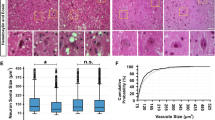
Abstract
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is an adult onset progressive motor neuron disease with no cure. Transgenic mice overexpressing familial ALS associated human mutant SOD1 are a commonly used model for examining disease mechanisms. Presently, it is well accepted that alterations in motor neuron excitability and spinal circuits are pathological hallmarks of ALS, but the underlying molecular mechanisms remain unresolved. Here, we sought to understand whether the expression of mutant SOD1 protein could contribute to altering processes governing motor neuron excitability. We used the conformation specific antibody B8H10 which recognizes a misfolded state of SOD1 (misfSOD1) to longitudinally identify its interactome during early disease stage in SOD1G93A mice. This strategy identified a direct isozyme-specific association of misfSOD1 with Na+/K+ATPase-α3 leading to the premature impairment of its ATPase activity. Pharmacological inhibition of Na+/K+ATPase-α3 altered glutamate receptor 2 expression, modified cholinergic inputs and accelerated disease pathology. After mapping the site of direct association of misfSOD1 with Na+/K+ATPase-α3 onto a 10 amino acid stretch that is unique to Na+/K+ATPase-α3 but not found in the closely related Na+/K+ATPase-α1 isozyme, we generated a misfSOD1 binding deficient, but fully functional Na+/K+ATPase-α3 pump. Adeno associated virus (AAV)-mediated expression of this chimeric Na+/K+ATPase-α3 restored Na+/K+ATPase-α3 activity in the spinal cord, delayed pathological alterations and prolonged survival of SOD1G93A mice. Additionally, altered Na+/K+ATPase-α3 expression was observed in the spinal cord of individuals with sporadic and familial ALS. A fraction of sporadic ALS cases also presented B8H10 positive misfSOD1 immunoreactivity, suggesting that similar mechanism might contribute to the pathology.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Kaabi A, Traupe T, Stutz M, Buchs N, Heller M (2012) Cause or effect of arteriogenesis: compositional alterations of microparticles from CAD patients undergoing external counterpulsation therapy. PLoS One 7:e46822
Andersen PM, Nilsson P, Ala-Hurula V, Keranen ML, Tarvainen I, Haltia T, Nilsson L, Binzer M, Forsgren L, Marklund SL (1995) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis associated with homozygosity for an Asp90Ala mutation in CuZn-superoxide dismutase. Nat Genet 10:61–66
Atkin JD, Farg MA, Walker AK, McLean C, Tomas D, Horne MK (2008) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and induction of the unfolded protein response in human sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurobiol Dis 30:400–407
Azarias G, Kruusmagi M, Connor S, Akkuratov EE, Liu XL, Lyons D, Brismar H, Broberger C, Aperia A (2013) A specific and essential role for Na, K-ATPase alpha3 in neurons co-expressing alpha1 and alpha3. J Biol Chem 288:2734–2743
Bergh J, Zetterstrom P, Andersen PM, Brannstrom T, Graffmo KS, Jonsson PA, Lang L, Danielsson J, Oliveberg M, Marklund SL (2015) Structural and kinetic analysis of protein-aggregate strains in vivo using binary epitope mapping. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:4489–4494. doi:10.1073/pnas.1419228112
Berrow NS, Alderton D, Owens RJ (2009) The precise engineering of expression vectors using high-throughput In-Fusion PCR cloning. Methods Mol Biol 498:75–90. doi:10.1007/978-1-59745-196-3_5
Blanco G, Sanchez G, Mercer RW (1995) Comparison of the enzymatic properties of the Na, K-ATPase alpha 3 beta 1 and alpha 3 beta 2 isozymes. Biochemistry 34:9897–9903
Bories C, Amendola J, Lamotte d’Incamps B, Durand J (2007) Early electrophysiological abnormalities in lumbar motoneurons in a transgenic mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Eur J Neurosci 25:451–459
Bosco DA, Morfini G, Karabacak NM, Song Y, Gros-Louis F, Pasinelli P, Goolsby H, Fontaine BA, Lemay N, McKenna-Yasek D, Frosch MP, Agar JN, Julien JP, Brady ST, Brown RH Jr (2010) Wild-type and mutant SOD1 share an aberrant conformation and a common pathogenic pathway in ALS. Nat Neurosci 13:1396–1403. doi:10.1038/nn.2660
Chang Q, Martin LJ (2009) Glycinergic innervation of motoneurons is deficient in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis mice: a quantitative confocal analysis. Am J Pathol 174:574–585. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2009.080557
Costes SV, Daelemans D, Cho EH, Dobbin Z, Pavlakis G, Lockett S (2004) Automatic and quantitative measurement of protein-protein colocalization in live cells. Biophys J 86:3993–4003
de Carvalho Aguiar P, Sweadner KJ, Penniston JT, Zaremba J, Liu L, Caton M, Linazasoro G, Borg M, Tijssen MA, Bressman SB, Dobyns WB, Brashear A, Ozelius LJ (2004) Mutations in the Na+/K+-ATPase alpha3 gene ATP1A3 are associated with rapid-onset dystonia parkinsonism. Neuron 43:169–175
Devlin AC, Burr K, Borooah S, Foster JD, Cleary EM, Geti I, Vallier L, Shaw CE, Chandran S, Miles GB (2015) Human iPSC-derived motoneurons harbouring TARDBP or C9ORF72 ALS mutations are dysfunctional despite maintaining viability. Nat Commun 6:5999. doi:10.1038/ncomms6999
Dirren E, Towne CL, Setola V, Redmond DE Jr., Schneider BL, Aebischer P (2014) Intracerebroventricular injection of adeno-associated virus 6 and 9 vectors for cell type-specific transgene expression in the spinal cord. Hum Gene Ther 25:109–120
Dobretsov M, Stimers JR (2005) Neuronal function and alpha3 isoform of the Na/K-ATPase. Front Biosci 10:2373–2396
Ellis DZ, Rabe J, Sweadner KJ (2003) Global loss of Na, K-ATPase and its nitric oxide-mediated regulation in a transgenic mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 23:43–51
Enjin A, Rabe N, Nakanishi ST, Vallstedt A, Gezelius H, Memic F, Lind M, Hjalt T, Tourtellotte WG, Bruder C, Eichele G, Whelan PJ, Kullander K (2010) Identification of novel spinal cholinergic genetic subtypes disclose Chodl and Pitx2 as markers for fast motor neurons and partition cells. J Comp Neurol 518:2284–2304
Ezzi SA, Urushitani M, Julien JP (2007) Wild-type superoxide dismutase acquires binding and toxic properties of ALS-linked mutant forms through oxidation. J Neurochem 102:170–178. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04531.x
Filezac de L’Etang A, Maharjan N, Cordeiro Brana M, Ruegsegger C, Rehmann R, Goswami A, Roos A, Troost D, Schneider BL, Weis J, Saxena S (2015) Marinesco-Sjogren syndrome protein SIL1 regulates motor neuron subtype-selective ER stress in ALS. Nat Neurosci. doi:10.1038/nn.3903
Fraser CL, Arieff AI (2001) Na-K-ATPase activity decreases with aging in female rat brain synaptosomes. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 281:F674–F678
Fritz E, Izaurieta P, Weiss A, Mir FR, Rojas P, Gonzalez D, Rojas F, Brown RH Jr, Madrid R, van Zundert B (2013) Mutant SOD1-expressing astrocytes release toxic factors that trigger motoneuron death by inducing hyperexcitability. J Neurophysiol 109:2803–2814. doi:10.1152/jn.00500.2012
Gaudette M, Hirano M, Siddique T (2000) Current status of SOD1 mutations in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 1:83–89
Genet S, Kado RT (1997) Hyperpolarizing current of the Na/K ATPase contributes to the membrane polarization of the Purkinje cell in rat cerebellum. Pflugers Arch 434:559–567
Gros-Louis F, Soucy G, Lariviere R, Julien JP (2010) Intracerebroventricular infusion of monoclonal antibody or its derived Fab fragment against misfolded forms of SOD1 mutant delays mortality in a mouse model of ALS. J Neurochem 113:1188–1199
Guareschi S, Cova E, Cereda C, Ceroni M, Donetti E, Bosco DA, Trotti D, Pasinelli P (2012) An over-oxidized form of superoxide dismutase found in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with bulbar onset shares a toxic mechanism with mutant SOD1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:5074–5079. doi:10.1073/pnas.1115402109
Gunasekera K, Wuthrich D, Braga-Lagache S, Heller M, Ochsenreiter T (2012) Proteome remodelling during development from blood to insect-form Trypanosoma brucei quantified by SILAC and mass spectrometry. BMC Genom 13:556
Gurney ME (1994) Transgenic-mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. N Engl J Med 331:1721–1722
Gurney ME, Pu H, Chiu AY, Dal Canto MC, Polchow CY, Alexander DD, Caliendo J, Hentati A, Kwon YW, Deng HX et al (1994) Motor neuron degeneration in mice that express a human Cu, Zn superoxide dismutase mutation. Science 264:1772–1775
Hegedus J, Putman CT, Tyreman N, Gordon T (2008) Preferential motor unit loss in the SOD1 G93A transgenic mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Physiol 586:3337–3351
Hieber V, Siegel GJ, Fink DJ, Beaty MW, Mata M (1991) Differential distribution of (Na, K)-ATPase alpha isoforms in the central nervous system. Cell Mol Neurobiol 11:253–262
Ilieva EV, Ayala V, Jove M, Dalfo E, Cacabelos D, Povedano M, Bellmunt MJ, Ferrer I, Pamplona R, Portero-Otin M (2007) Oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress interplay in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain 130:3111–3123
Inquimbert P, Moll M, Kohno T, Scholz J (2013) Stereotaxic injection of a viral vector for conditional gene manipulation in the mouse spinal cord. J Vis Exp 73:e50313. doi:10.3791/50313
Kreutz F, Scherer EB, Ferreira AG, Petry Fdos S, Pereira CL, Santana F, de Souza Wyse AT, Salbego CG, Trindade VM (2013) Alterations on Na(+), K(+)-ATPase and acetylcholinesterase activities induced by amyloid-beta peptide in rat brain and GM1 ganglioside neuroprotective action. Neurochem Res 38:2342–2350. doi:10.1007/s11064-013-1145-6
Le Masson G, Przedborski S, Abbott LF (2014) A computational model of motor neuron degeneration. Neuron 83:975–988. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2014.07.001
Leroy F, Lamotte d’Incamps B, Imhoff-Manuel RD, Zytnicki D (2014) Early intrinsic hyperexcitability does not contribute to motoneuron degeneration in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. ELife 3. doi:10.7554/eLife.04046
Liguri G, Taddei N, Nassi P, Latorraca S, Nediani C, Sorbi S (1990) Changes in Na+, K(+)-ATPase, Ca2(+)-ATPase and some soluble enzymes related to energy metabolism in brains of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 112:338–342
Lingrel JB (2010) The physiological significance of the cardiotonic steroid/ouabain-binding site of the Na, K-ATPase. Annu Rev Physiol 72:395–412
Liu HN, Tjostheim S, Dasilva K, Taylor D, Zhao B, Rakhit R, Brown M, Chakrabartty A, McLaurin J, Robertson J (2012) Targeting of monomer/misfolded SOD1 as a therapeutic strategy for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 32:8791–8799
Liu J, Lillo C, Jonsson PA, Vande Velde C, Ward CM, Miller TM, Subramaniam JR, Rothstein JD, Marklund S, Andersen PM, Brannstrom T, Gredal O, Wong PC, Williams DS, Cleveland DW (2004) Toxicity of familial ALS-linked SOD1 mutants from selective recruitment to spinal mitochondria. Neuron 43:5–17
Logroscino G, Traynor BJ, Hardiman O, Chio A, Mitchell D, Swingler RJ, Millul A, Benn E, Beghi E (2010) Incidence of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in Europe. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 81:385–390
Mark RJ, Hensley K, Butterfield DA, Mattson MP (1995) Amyloid beta-peptide impairs ion-motive ATPase activities: evidence for a role in loss of neuronal Ca2+ homeostasis and cell death. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 15:6239–6249
McGrail KM, Phillips JM, Sweadner KJ (1991) Immunofluorescent localization of three Na, K-ATPase isozymes in the rat central nervous system: both neurons and glia can express more than one Na, K-ATPase. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 11:381–391
Millul A, Beghi E, Logroscino G, Micheli A, Vitelli E, Zardi A (2005) Survival of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in a population-based registry. Neuroepidemiology 25:114–119
Munzer JS, Daly SE, Jewell-Motz EA, Lingrel JB, Blostein R (1994) Tissue- and isoform-specific kinetic behavior of the Na, K-ATPase. J Biol Chem 269:16668–16676
Nishitoh H, Kadowaki H, Nagai A, Maruyama T, Yokota T, Fukutomi H, Noguchi T, Matsuzawa A, Takeda K, Ichijo H (2008) ALS-linked mutant SOD1 induces ER stress- and ASK1-dependent motor neuron death by targeting Derlin-1. Genes Dev 22:1451–1464
Pambo-Pambo A, Durand J, Gueritaud JP (2009) Early excitability changes in lumbar motoneurons of transgenic SOD1G85R and SOD1G(93A-Low) mice. J Neurophysiol 102:3627–3642
Piotrkiewicz M, Hausmanowa-Petrusewicz I (2011) Motoneuron afterhyperpolarisation duration in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Physiol 589:2745–2754
Pisani A, Martella G, Tscherter A, Costa C, Mercuri NB, Bernardi G, Shen J, Calabresi P (2006) Enhanced sensitivity of DJ-1-deficient dopaminergic neurons to energy metabolism impairment: role of Na+/K+ ATPase. Neurobiol Dis 23:54–60
Pullen AH, Athanasiou D (2009) Increase in presynaptic territory of C-terminals on lumbar motoneurons of G93A SOD1 mice during disease progression. Eur J Neurosci 29:551–561
Pun S, Santos AF, Saxena S, Xu L, Caroni P (2006) Selective vulnerability and pruning of phasic motoneuron axons in motoneuron disease alleviated by CNTF. Nat Neurosci 9:408–419
Puttaparthi K, Wojcik C, Rajendran B, DeMartino GN, Elliott JL (2003) Aggregate formation in the spinal cord of mutant SOD1 transgenic mice is reversible and mediated by proteasomes. J Neurochem 87:851–860
Rakhit R, Crow JP, Lepock JR, Kondejewski LH, Cashman NR, Chakrabartty A (2004) Monomeric Cu, Zn-superoxide dismutase is a common misfolding intermediate in the oxidation models of sporadic and familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Biol Chem 279:15499–15504
Rakhit R, Robertson J, Vande Velde C, Horne P, Ruth DM, Griffin J, Cleveland DW, Cashman NR, Chakrabartty A (2007) An immunological epitope selective for pathological monomer-misfolded SOD1 in ALS. Nat Med 13:754–759
Raoul C, Abbas-Terki T, Bensadoun JC, Guillot S, Haase G, Szulc J, Henderson CE, Aebischer P (2005) Lentiviral-mediated silencing of SOD1 through RNA interference retards disease onset and progression in a mouse model of ALS. Nat Med 11:423–428
Rotunno MS, Bosco DA (2013) An emerging role for misfolded wild-type SOD1 in sporadic ALS pathogenesis. Front Cell Neurosci 7:253. doi:10.3389/fncel.2013.00253
Saxena S, Cabuy E, Caroni P (2009) A role for motoneuron subtype-selective ER stress in disease manifestations of FALS mice. Nat Neurosci 12:627–636
Saxena S, Caroni P (2011) Selective neuronal vulnerability in neurodegenerative diseases: from stressor thresholds to degeneration. Neuron 71:35–48
Saxena S, Roselli F, Singh K, Leptien K, Julien JP, Gros-Louis F, Caroni P (2013) Neuroprotection through excitability and mTOR required in ALS motoneurons to delay disease and extend survival. Neuron 80:80–96
Schutz B (2005) Imbalanced excitatory to inhibitory synaptic input precedes motor neuron degeneration in an animal model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurobiol Dis 20:131–140. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2005.02.006
Shinoda T, Ogawa H, Cornelius F, Toyoshima C (2009) Crystal structure of the sodium-potassium pump at 2.4 A resolution. Nature 459:446–450
Tortarolo M, Grignaschi G, Calvaresi N, Zennaro E, Spaltro G, Colovic M, Fracasso C, Guiso G, Elger B, Schneider H, Seilheimer B, Caccia S, Bendotti C (2006) Glutamate AMPA receptors change in motor neurons of SOD1G93A transgenic mice and their inhibition by a noncompetitive antagonist ameliorates the progression of amytrophic lateral sclerosis-like disease. J Neurosci Res 83:134–146. doi:10.1002/jnr.20715
Urayama O, Sweadner KJ (1988) Ouabain sensitivity of the alpha 3 isozyme of rat Na, K-ATPase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 156:796–800
Urushitani M, Ezzi SA, Julien JP (2007) Therapeutic effects of immunization with mutant superoxide dismutase in mice models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:2495–2500
Urushitani M, Ezzi SA, Matsuo A, Tooyama I, Julien JP (2008) The endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi pathway is a target for translocation and aggregation of mutant superoxide dismutase linked to ALS. FASEB J Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol 22:2476–2487
Venugopal S, Hsiao CF, Sonoda T, Wiedau-Pazos M, Chandler SH (2015) Homeostatic dysregulation in membrane properties of masticatory motoneurons compared with oculomotor neurons in a mouse model for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 35:707–720. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1682-14.2015
Vucic S, Kiernan MC (2010) Upregulation of persistent sodium conductances in familial ALS. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 81:222–227
Vucic S, Nicholson GA, Kiernan MC (2008) Cortical hyperexcitability may precede the onset of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain 131:1540–1550
Wainger BJ, Kiskinis E, Mellin C, Wiskow O, Han SS, Sandoe J, Perez NP, Williams LA, Lee S, Boulting G, Berry JD, Brown RH Jr, Cudkowicz ME, Bean BP, Eggan K, Woolf CJ (2014) Intrinsic membrane hyperexcitability of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patient-derived motor neurons. Cell Rep 7:1–11. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2014.03.019
Wroe R, Wai-Ling Butler A, Andersen PM, Powell JF, Al-Chalabi A (2008) ALSOD: the amyotrophic lateral sclerosis online database. Amyotroph Lateral Scler 9:249–250
Zhang D, Hou Q, Wang M, Lin A, Jarzylo L, Navis A, Raissi A, Liu F, Man HY (2009) Na, K-ATPase activity regulates AMPA receptor turnover through proteasome-mediated proteolysis. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 29:4498–4511. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6094-08.2009
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Swiss National Science Foundation Professorship grants (PP00P3_128460, PP00P3_150756) and Frick foundation for ALS research to S.S., C.R., N.M. and A.FdLE. A.G. and J.W. were supported by a START program grant, Medical Faculty, RWTH Aachen University, by the Interdisciplinary Center for Clinical Research, IZKF Aachen (N5–3), and by the German Research Foundation, DFG (WE 1406/13–1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that no conflict of interests exists.
Additional information
C. Ruegsegger and N. Maharjan contributed equally to this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruegsegger, C., Maharjan, N., Goswami, A. et al. Aberrant association of misfolded SOD1 with Na+/K+ATPase-α3 impairs its activity and contributes to motor neuron vulnerability in ALS. Acta Neuropathol 131, 427–451 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-015-1510-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-015-1510-4