Abstract
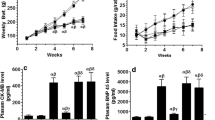
The molecular mechanisms through which ghrelin exerts its cardioprotective effects during cardiac remodeling post-myocardial infarction (MI) are poorly understood. The aim of this study was to investigate whether the cardioprotection mechanisms are mediated by modulation of JAK/STAT signaling and what triggers this modulation. Rats were divided into six groups (n = 12/group): control, sham, sham + ghrelin (100 µg/kg, s.c., daily, starting 1 day post-MI), MI, MI+ ghrelin, and MI+ ghrelin+ AG490, a potent JAK2 inhibitor (5 mg/kg, i.p., daily). All treatments were administered for 3 weeks. Administration of ghrelin to MI rats improved left ventricle (LV) architecture and restored cardiac contraction. In remote non-infarcted areas of MI rats, ghrelin reduced cardiac inflammation and lipid peroxidation and enhanced antioxidant enzymatic activity. In addition, independent of the growth factor/insulin growth factor-1 (GF/IGF-1) axis, ghrelin significantly increased the phosphorylation of JAK2 and Tyr702 and Ser727 residues of STAT3 and inhibited the phosphorylation of JAK1 and Tyr701 and Ser727 residues of STAT1, simultaneously increasing the expression of BCL-2 and decreasing in the expression of BAX, cleaved CASP3, and FAS. This effect coincided with decreased expression of SOCS3. All these beneficial effects of ghrelin, except its inhibitory action on IL-6 expression, were partially and significantly abolished by the co-administration of AG490. In conclusion, the cardioprotective effect of ghrelin against MI-induced LV injury is exerted via activation of JAK2/STAT3 signaling and inhibition of STAT1 signaling. These effects were independent of the GF/IGF-1 axis and could be partially mediated via inhibition of cardiac IL-6.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander WS, Starr R, Fenner JE, Scott CL, Handman E, Sprigg NS, Corbin JE, Cornish AL, Darwiche R, Owczarek CM, Kay TW, Nicola NA, Hertzog PJ, Metcalf D, Hilton DJ (1999) SOCS1 is a critical inhibitor of interferon gamma signaling and prevents the potentially fatal neonatal actions of this cytokine. Cell 98:597–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80047-1
Anand I, Ferrari R, Kalra G, Wahi P, Poole-Wilson P, Harris P (1989) Edema of cardiac origin: studies of body water and sodium, renal function, hemodynamic indexes and plasma hormones in untreated congestive cardiac failure. Circulation 80:299–305. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.80.2.299
Banes AK, Shaw S, Jenkins J, Redd H, Amiri F, Pollock DM, Marrero MB (2004) Angiotensin II blockade prevents hyperglycemia-induced activation of JAK and STAT proteins in diabetic rat kidney glomeruli. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 286:F653–F659. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00163.2003
Banes AK, Shaw SM, Tawfik A, Patel BP, Ogbi S, Fulton D, Marrero MB (2005) Activation of the JAK/STAT pathway in vascular smooth muscle by serotonin. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 288:C805–C812. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00385.2004
Baldanzi G, Filigheddu N, Cutrupi S, Catapano F, Bonissoni S, Fubini A, Malan D, Baj G, Granata R, Broglio F, Papotti M, Surico N, Bussolino F, Isgaard J, Deghenghi R, Sinigaglia F, Prat M, Muccioli G, Ghigo E, Graziani A (2002) Ghrelin and des-acyl ghrelin inhibit cell death in cardiomyocytes and endothelial cells through ERK1/2 and PI 3-kinase/AKT. J Cell Biol 159:1029–1037. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200207165
Barry SP, Townsend PA, Latchman DS, Stephanou A (2007) Role of the JAK-STAT pathway in myocardial injury. Trends Mol Med 13:82–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2006.12.002
Boengler K, Hilfiker-Kleiner D, Drexler H, Heusch G, Schulz R (2008) The myocardial JAK/STAT pathway: from protection to failure. Pharmacol Ther 120:172–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2008.08.002
Boengler K, Hilfiker-Kleiner D, Heusch G, Schulz R (2010) Inhibition of permeability transition pore opening by mitochondrial STAT3 and its role in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion. Basic Res Cardiol 105:771–785. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-010-0124-1
Booz GW, Day JN, Baker KM (2002) Interplay between the cardiac renin angiotensin system and JAK-STAT signaling: role in cardiac hypertrophy, ischemia/reperfusion dysfunction, and heart failure. J Mol Cell Cardiol 34:1443–1453. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmcc.2002.2076
Castellano G, Affuso F, Conza PD, Fazio S (2009) The GH/IGF-1 Axis and heart failure. Curr Cardiol Rev 5:203–215. https://doi.org/10.2174/157340309788970306
Chang YP, Tsai CC, Huang WC, Wang CY, Chen CL, Lin YS, Kai JI, Hsieh CY, Cheng YL, Choi PC, Chen SH, Chang SP, Liu HS, Lin CF (2010) Autophagy facilitates IFN-c-induced JAK2-STAT1 activation and cellular inflammation. J Biol Chem 285:28715–28722. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.133355
Chung H, Li E, Kim Y, Kim S, Park S (2013) Multiple signaling pathways mediate ghrelin-induced proliferation of hippocampal neural stem cells. J Endocrinol 218:49–59. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-13-0045
Cittadini A, Monti MG, Iaccarino G, Castiello MC, Baldi A, Bossone E, Longobardi S, Marra AM, Petrillo V, Saldamarco L, During MJ, Saccà L, Condorelli G (2012) SOCS1 gene transfer accelerates the transition to heart failure through the inhibition of the gp130/JAK/STAT pathway. Cardiovasc Res 96:381–390. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvs261
Croker BA, Kiu H (2008) Nicholson SE (2008) SOCS: regulation of the JAK/STAT signalling pathway. Semin Cell Dev Biol 19:414–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2008.07.010
Das A, Salloum FN, Filippone SM, Durrant DE, Rokosh G, Bolli R, Kukreja RC (2015) Inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin protects against reperfusion injury in diabetic heart through STAT3 signaling. Basic Res Cardiol 110:31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-015-0486-5
Dorn GW (2009) Novel pharmacotherapies to abrogate postinfarction ventricular remodeling. Nat Rev Cardiol 6:283–291. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrcardio.2009.12
El-Adawi H, Deng L, Tramontano A, Smith S, Mascareno E, Ganguly K, Castillo R, El-Sherif N (2003) The functional role of the JAK-STAT pathway in post-infarction remodeling. Cardiovasc Res 57:129–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6363(02)00614-4
Fischer P, Hilfiker-Kleiner D (2007) Survival pathways in hypertrophy and heart failure: the gp130-STAT axis. Basic Res Cardiol 102:393–4115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-007-0674-z
Frascarelli S, Ghelardoni S, Ronca-Testoni S, Zucchi R (2003) Effect of ghrelin and synthetic growth hormone secretagogues in normal and ischemic rat heart. Basic Res Cardiol 98:401–405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-003-0434-7
Friberg L, Werner S, Eggertsen G, Ahnve S (2000) Growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-1 in acute myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J 21:1547–1554. https://doi.org/10.1053/euhj.2000.2125
Fuglesteg BN, Suleman N, Tiron C, Kanhema T, Lacerda L, Andreasen TV, Sack MN, Jonassen AK, Mjøs OD, Opie LH, Lecour S (2008) Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 is involved in the cardioprotective signalling pathway activated by insulin therapy at reperfusion. Basic Res Cardiol 103:444–453. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-008-0728-x
Gedik N, Kottenberg E, Thielmann M, Frey UH, Jakob H, Peters J, Heusch G, Kleinbongard P (2017) Potential humoral mediators of remote ischemic preconditioning in patients undergoing surgical coronary revascularization. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-12833
Ghelardoni S, Carnicelli V, Frascarelli S, Ronca-Testoni S, Zucchi R (2006) Ghrelin tissue distribution: comparison between gene and protein expression. J Endocrinol Invest 29:115–121. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03344083
Harada M, Qin Y, Takano H, Minamino T, Zou Y, Toko H, Ohtsuka M, Matsuura K, Sano M, Nishi J, Iwanaga K, Akazawa H, Kunieda T, Zhu W, Hasegawa H, Kunisada K, Nagai T, Nakaya H, Yamauchi-Takihara K, Komuro I (2005) G-CSF prevents cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction by activating the JAK-STAT pathway in cardiomyocytes. Nat Med 11:305–311. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1199
Hayashidani S, Tsutsui H, Ikeuchi M, Shiomi T, Matsusaka H, Kubota T, Imanaka-Yoshida K, Itoh T, Takeshita A (2003) Targeted deletion of MMP-2 attenuates early LV rupture and late remodeling after experimental myocardial infarction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 285(3):H1229–H1235. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00207.2003
Heusch G, Musiolik J, Gedik N, Skyschally A (2011) Mitochondrial STAT3 activation and cardioprotection by ischemic postconditioning in pigs with regional myocardial ischemia/reperfusion. Circ Res 109:1302–1308. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.255604
Higuchi T, Yamauchi-Takihara K, Matsumiya G, Fukushima N, Ichikawa H, Kuratani T, Maehata Y, Sawa Y (2008) Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor prevents reperfusion injury after heart preservation. Ann Thorac Surg 85:1367–1373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2007.12.053
Hilfiker-Kleiner D, Hilfiker A, Drexler H (2005) Many good reasons to have STAT3 in the heart. Pharmacol Ther 107:131–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2005.02.003
Hilfiker-Kleiner D, Hilfiker A, Fuchs M, Kaminski K, Schaefer A, Schieffer B, Hillmer A, Schmiedl A, Ding Z, Podewski E, Podewski E, Poli V, Schneider MD, Schulz R, Park JK, Wollert KC, Drexler H (2004) Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 is required for myocardial capillary growth, control of interstitial matrix deposition, and heart protection from ischemic injury. Circ Res 95:187–195. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.RES.0000134921.50377.61
Hong F, Jaruga B, Kim WH, Radaeva S, El-Assal ON, Tian Z, Nguyen VA, Gao B (2002) Opposing roles of STAT1 and STAT3 in T cell-mediated hepatitis: regulation by SOCS. J Clin Invest 110:1503–1513. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI15841
Huang CH, Tsai MS, Chiang CY, Su YJ, Wang TD, Chang WT, Chen HW, Chen WJ (2015) Activation of mitochondrial STAT-3 and reduced mitochondria damage during hypothermia treatment for post-cardiac arrest myocardial dysfunction. Basic Res Cardiol 110:59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-015-0516-3
Isgaard J, Arcopinto M, Karason K, Cittadini A (2015) GH and the cardiovascular system: an update on a topic at heart. Endocrine 48:25–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0327-6
Izumi M, Masaki M, Hiramoto Y, Sugiyama S, Kuroda T, Terai K, Hori M, Kawase I, Hirota H (2006) Cross-talk between bone morphogenetic protein 2 and leukemia inhibitory factor through ERK 1/2 and Smad1 in protection against doxorubicin induced injury of cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 40:224–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2005.11.007
Kishore R, Verma SK (2012) Roles of STATs signaling in cardiovascular diseases. JAK-STAT 1:118–124. https://doi.org/10.4161/jkst.20115
Krishnamurthy P, Rajasingh J, Lambers E, Qin G, Losordo DW, Kishore R (2009) IL-10 inhibits inflammation and attenuates left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction via activation of STAT3 and suppression of HuR. Circ Res 104:e9–e18. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.188243
Knight RA, Scarabelli Tiziano M, Anastasis S (2012) STAT transcription in the ischemic heart. JAK-STAT 1:111–117. https://doi.org/10.4161/jkst.20078
Latchman DS, Stephanou A (2012) STAT1 deficiency in the heart protects against myocardial infarction by enhancing autophagy. J Cell Mol Med 16:386–393. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01323.x
Levy DE, Darnell JE Jr (2002) Stats: transcriptional control and biological impact. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:651–662. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm909
Ma Y, Zhang L, Edwards JN, Launikonis BS, Chen C (2012) Growth hormone secretagogues protect mouse cardiomyocytes from in vitro ischemia/reperfusion injury through regulation of intracellular calcium. PLoS ONE 7:e35265. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0035265
Mascareno E, El-Shafei M, Maulik N, Sato M, Guo Y, Das DK, Siddiqui MA (2001) JAK/STAT signaling is associated with cardiac dysfunction during ischemia and reperfusion. Circulation 104:325–329. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.104.3.325
Matsumura K, Tsuchihashi T, Fujii K, Abe I, Iida M (2002) Central ghrelin modulates sympathetic activity in conscious rabbits. Hypertension 40:694–699. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.hyp.0000035395.51441.10
McCormick J, Barry SP, Sivarajah A, Stefanutti G, Townsend PA, Lawrence KM, Eaton S, Knight RA, Thiemermann C, Latchman DS, Stephanou A (2006) Free radical scavenging inhibits STAT phosphorylation following in vivo ischemia/reperfusion injury. FASEB J 20:2115–2117. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.06-6188fje
Nagaya N, Moriya J, Yasumura Y, Uematsu M, Ono F, Shimizu W, Ueno K, Kitakaze M, Miyatake K, Kangawa K (2004) Effects of ghrelin administration on left ventricular function, exercise capacity, and muscle wasting in patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation 110:3674–3679. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000149746.62908.BB
Nagaya N, Uematsu M, Kojima M, Ikeda Y, Yoshihara F, Shimizu W, Hosoda H, Hirota Y, Ishida H, Mori H, Kangawa K (2001) Chronic administration of ghrelin improves left ventricular dysfunction and attenuates development of cardiac cachexia in rats with heart failure. Circulation 104:1430–1435. https://doi.org/10.1161/hc3601.095575
Negoro S, Kunisada K, Fujio Y, Funamoto M, Darville MI, Eizirik DL, Osugi T, Izumi M, Oshima Y, Nakaoka Y, Hirota H, Kishimoto T, Yamauchi-Takihara K (2001) Activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 protects cardiomyocytes from hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced oxidative stress through the upregulation of manganese superoxide dismutase. Circulation 104:979–981. https://doi.org/10.1161/hc3401.095947
Negoro S, Kunisada K, Tone E, Funamoto M, Oh H, Kishimoto T, Yamauchi-Takihara K (2000) Activation of JAK/STAT pathway transduces cytoprotective signal in rat acute myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res 47:797–805. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6363(00)00138-3
Oshima Y, Fujio Y, Nakanishi T, Itoh N, Yamamoto Y, Negoro S, Tanaka K, Kishimoto T, Kawase I, Azuma J (2005) STAT3 mediates cardioprotection against ischemia/reperfusion injury through metallothionein induction in the heart. Cardiovasc Res 65:428–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cardiores.2004.10.021
Omura T, Yoshiyama M, Ishikura F, Kobayashi H, Takeuchi K, Beppu S, Yoshikawa J (2001) Myocardial ischemia activates the JAK-STAT pathway through angiotensin II signaling in in vivo myocardium of rats. J Mol Cell Cardiol 33:307–316. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmcc.2000.1303
Osugi T, Oshima Y, Fujio Y, Funamoto M, Yamashita A, Negoro S, Kunisada K, Izumi M, Nakaoka Y, Hirota H, Okabe M, Yamauchi-Takihara K, Kawase I, Kishimoto T (2002) Cardiac-specific activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 promotes vascular formation in the heart. J Biol Chem 277:6676–6681. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M108246200
Pedretti S, Raddatz E (2011) STAT3a interacts with nuclear GSK3beta and cytoplasmic RISK pathway and stabilizes rhythm in the anoxic-reoxygenated embryonic heart. Basic Res Cardiol 106:355–369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-011-0152-5
Pei XM, Yung BY, Yip SP, Ying M, Benzie IF, Siu PM (2014) Desacyl ghrelin prevents doxorubicin-induced myocardial fibrosis and apoptosis via the GHSR-independent pathway. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 306:E311–E323. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00123.2013
Pemberton C, Wimalasena P, Yandle T, Soule S, Richards M (2003) C-terminal pro-ghrelin peptides are present in the human circulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 310:567–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.09.045
Pezet A, Favre H, Kelly PA, Edery M (1999) Inhibition and restoration of prolactin signal transduction by suppressors of cytokine signaling. J Biol Chem 274:24497–24502. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.35
Podewski EK, Hilfiker-Kleiner D, Hilfiker A, Morawietz H, Lichtenberg A, Wollert KC, Drexler H (2003) Alterations in Janus kinase (JAK)-signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) signaling in patients with end-stage dilated cardiomyopathy. Circulation 107:798–802. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000057545.82749
Qin F, Liang MC, Liang CS (2005) Progressive left ventricular remodeling, myocyte apoptosis, and protein signaling cascades after myocardial infarction in rabbits. Biochim Biophys Acta 1740:499–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2004.11.007
Qing Y, Stark GR (2004) Alternative activation of STAT1 and STAT3 in response to interferon-γ. J Biol Chem 279:41679–41685. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M406413200
Ram PA, Park SH, Choi HK, Waxman DJ (1996) Growth Hormone Activation of Stat 1, Stat 3, and Stat 5 in Rat Liver. Differential kinetics of hormone desensitization and growth hormone stimulation of both tyrosine phosphorylation and serine/threonine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 271:5929–5940. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.271.10.5929
Scarabelli TM, Gottlieb RA (2004) Functional and clinical repercussions of myocyte apoptosis in the multifaceted damage by ischemia/reperfusion injury: old and new concepts after 10 years of contributions. Cell Death Differ 11:S144–S152. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401544
Sivaraman V, Yellon DM (2014) Pharmacologic therapy that simulates conditioning for cardiac ischemic/reperfusion injury. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther 19:83–96. https://doi.org/10.1177/1074248413499973
Smith CC, Dixon RA, Wynne AM, Theodorou L, Ong SG, Subrayan S, Davidson SM, Hausenloy DJ, Yellon DM (2010) Leptin-induced cardioprotection involves JAK/STAT signaling that may be linked to the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 299:H1265–H1270. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00092.2010
Soeki T, Kishimoto I, Schwenke DO, Tokudome T, Horio T, Yoshida M, Hosoda H, Kangawa K (2008) Ghrelin suppresses cardiac sympathetic activity and prevents early left ventricular remodeling in rats with myocardial infarction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 294:H426–H432. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00643.2007
Stephanou A, Scarabelli TM, Brar BK, Nakanishi Y, Matsumura M, Knight RA, Latchman DS (2001) Induction of apoptosis and Fas receptor/Fas ligand expression by ischemia/reperfusion in cardiac myocytes requires serine 727 of the STAT-1 transcription factor but not tyrosine 701. J Biol Chem 276:28340–28347. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M101177200
Stephanou A, Brar BK, Knight RA, Latchman DS (2000) Opposing actions of STAT-1 and STAT-3 on the Bcl-2 and Bcl-x promoters. Cell Death Differ 7:329–330. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4400656
Stephanou A, Brar BK, Scarabelli TM, Jonassen AK, Yellon DM, Marber MS, Knight RA, Latchman DS (2000) Ischemia-induced STAT-1 expression and activation play a critical role in cardiomyocyte apoptosis. J Biol Chem 275:10002–10008. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.275.14.10002
Szczepanek K, Chen Q, Larner AC, Lesnefsky EJ (2012) Cytoprotection by the modulation of mitochondrial electron transport chain: the emerging role of mitochondrial STAT3. Mitochondrion 12:180–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2011.08.011
Takahashi T, Fukuda K, Pan J, Kodama H, Sano M, Makino S, Kato T, Manabe T, Ogawa S (1999) Characterization of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1–Induced Activation of the JAK/STAT Pathway in Rat Cardiomyocytes. Circ Res 85:884–891. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.RES.85.10884
Tesauro M, Schinzari F, Caramanti M, Lauro R, Cardillo C (2010) Metabolic and cardiovascular effects of ghrelin. Curr Diabetes Rev 6:228–253. https://doi.org/10.2174/157339910791658871
Townsend PA, Scarabelli TM, Davidson SM, Knight RA, Latchman DS, Stephanou A (2004) STAT-1 interacts with p53 to enhance DNA damage-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 279:5811–5820. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M302637200
Townsend PA, Scarabelli TM, Pasini E, Gitti G, Menegazzi M, Suzuki H, Knight RA, Latchman DS, Stephanou A (2004) Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits STAT- 1 activation and protects cardiac myocytes from ischemia/reperfusion-induced apoptosis. FASEB J 18:1621–1623. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.04-1716fje
Wakabayashi H, Taki J, Inaki A, Shiba K, Matsunari I, Kinuya S (2015) Correlation between apoptosis and left ventricular remodeling in subacute phase of myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. EJNMMI Res 5–11:72. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13550-015-0152-9
Wang Q, Lin P, Li P, Feng L, Ren Q, Xie X, Xu J (2017) Ghrelin protects the heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury via inhibition of TLR4/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Life Sci 1(186):50–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2017.08.004
Wegrzyn J, Potla R, Chwae YJ, Sepuri NB, Zhang Q, Koeck T, Derecka M, Szczepanek K, Szelag M, Gornicka A, Moh A, Moghaddas S, Chen Q, Bobbili S, Cichy J, Dulak J, Baker DP, Wolfman A, Stuehr D, Hassan MO, Fu XY, Avadhani N, Drake JI, Fawcett P, Lesnefsky EJ, Larner AC (2009) Function of mitochondrial Stat3 in cellular respiration. Science 323:793–797. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1164551
Wiley KE, Davenport AP (2002) Comparison of vasodilators in human internal mammary artery: ghrelin is a potent physiological antagonist of endothelin-1. Br J Pharmacol 136:1146–1152. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0704815
Xuan YT, Guo Y, Han H, Zhu Y, Bolli R (2001) An essential role of the JAK-STAT pathway in ischemic preconditioning. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:9050–9055. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.161283798
Yang C, Liu Z, Liu K, Yang P (2014) Mechanisms of ghrelin anti-heart failure: inhibition of Ang II induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis by down-regulating AT1R expression. PLoS ONE 9:e85785. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0085785
Yang N, Luo M, Li R, Huang Y, Zhang R, Wu Q, Wang F, Li Y, Yu X (2008) Blockage of JAK/STAT signalling attenuates renal ischaemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23:91–100. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfm509
Yasukawa H, Nagata T, Oba T, Imaizumi T (2012) SOCS3: a novel therapeutic target for cardioprotection. JAK-STAT 1:234–240. https://doi.org/10.4161/jkst.22435
Zhang G, Yin X, Qi Y, Pendyala L, Chen J, Hou H, Tang C (2010) Ghrelin and cardiovascular diseases. Curr Cardiol Rev 6:62–70. https://doi.org/10.2174/157340310790231662
Zgheib C, Zouein FA, Kurdi M, Booz GW (2012) Differential STAT3 signaling in the heart impact of concurrent signals and oxidative stress. JAK-STAT 1:101–110. https://doi.org/10.4161/jkst.19776
Zong CS, Chan J, Levy DE, Horvath C, Sadowski HB, Wang LH (2000) Mechanism of STAT3 activation by insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. J Biol Chem 275:15099–15105. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M000089200
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the deanship of the scientific research at King Khalid University for financially supporting this study and the technical staff of the animal house facility at the College pharmacy at King Saud University for their help in the study. They also would like to thank others who provided technical support.
Funding
This research was fully funded by the scientific research at King Khalid University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eid, R.A., Alkhateeb, M.A., Eleawa, S. et al. Cardioprotective effect of ghrelin against myocardial infarction-induced left ventricular injury via inhibition of SOCS3 and activation of JAK2/STAT3 signaling. Basic Res Cardiol 113, 13 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-018-0671-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-018-0671-4