Abstract
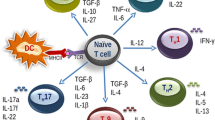
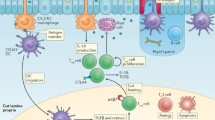
Food allergy is a major public health concern in westernized countries, estimated to affect 5 % of children and 3–4 % of adults. Allergen-specific immunotherapy for food allergy is currently being actively evaluated, but is still experimental. The optimal protocol, in terms of the route of administration of the food, target maintenance dose, and duration of maintenance therapy, and the optimal patient for these procedures are still being worked out. The mechanisms underlying successful food desensitization are also unclear, in part, because there is no standard immunotherapy protocol. The mechanisms involved, however, may include mast cell and basophil suppression, development of food-specific IgG4 antibodies, reduction in the food-specific IgE/IgG4 ratio, up-regulation and expansion of natural or inducible regulatory T cells, a skewing from a Th2 to a Th1 profile, and the development of anergy and/or deletion in antigen-specific cells. Additional studies are required to elucidate and understand these mechanisms by which desensitization and tolerance are achieved, which may reveal valuable biomarkers for evaluating and following food allergic patients on immunotherapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DBPCFC:
-
Double-blind placebo-controlled food challenge
- iTRegs :
-
Inducible regulatory T cells
- IT:
-
Immunotherapy
- mAb:
-
Monoclonal antibody
- nTRegs :
-
Natural regulatory T cells
- OFC:
-
Oral food challenge
- OIT:
-
Oral immunotherapy
- SIgA:
-
Secretory IgA
- SLIT:
-
Sublingual immunotherapy
- SPT:
-
Skin prick test
- Syk:
-
Spleen tyrosine kinase
- TRegs :
-
Regulatory T cells
References
Sicherer SH, Sampson HA (2010) Food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 125:S116–125
Branum AM, Lukacs SL (2008) Food allergy among U.S. children: trends in prevalence and hospitalizations. NCHS Data Brief: 1–8
Lee LA, Burks AW (2006) Food allergies: prevalence, molecular characterization, and treatment/prevention strategies. Annu Rev Nutr 26:539–565
Sicherer SH, Munoz-Furlong A, Sampson HA (2003) Prevalence of peanut and tree nut allergy in the United States determined by means of a random digit dial telephone survey: a 5-year follow-up study. J Allergy Clin Immunol 112:1203–1207
Grundy J, Matthews S, Bateman B, Dean T, Arshad SH (2002) Rising prevalence of allergy to peanut in children: data from 2 sequential cohorts. J Allergy Clin Immunol 110:784–789
Skripak JM, Matsui EC, Mudd K, Wood RA (2007) The natural history of IgE-mediated cow’s milk allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 120:1172–1177
Jarvinen KM, Beyer K, Vila L, Bardina L, Mishoe M, Sampson HA (2007) Specificity of IgE antibodies to sequential epitopes of hen's egg ovomucoid as a marker for persistence of egg allergy. Allergy 62:758–765
Skolnick HS, Conover-Walker MK, Koerner CB, Sampson HA, Burks W, Wood RA (2001) The natural history of peanut allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 107:367–374
Bock SA, Munoz-Furlong A, Sampson HA (2001) Fatalities due to anaphylactic reactions to foods. J Allergy Clin Immunol 107:191–193
Bock SA, Munoz-Furlong A, Sampson HA (2007) Further fatalities caused by anaphylactic reactions to food, 2001-2006. J Allergy Clin Immunol 119:1016–1018
Sicherer SH, Noone SA, Munoz-Furlong A (2001) The impact of childhood food allergy on quality of life. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 87:461–464
Cummings AJ, Knibb RC, King RM, Lucas JS (2010) The psychosocial impact of food allergy and food hypersensitivity in children, adolescents and their families: a review. Allergy 65:933–945
Sicherer SH, Furlong TJ, DeSimone J, Sampson HA (2001) The US Peanut and Tree Nut Allergy Registry: characteristics of reactions in schools and day care. J Pediatr 138:560–565
Furlong TJ, DeSimone J, Sicherer SH (2001) Peanut and tree nut allergic reactions in restaurants and other food establishments. J Allergy Clin Immunol 108:867–870
Boyano-Martinez T, Garcia-Ara C, Pedrosa M, Diaz-Pena JM, Quirce S (2009) Accidental allergic reactions in children allergic to cow's milk proteins. J Allergy Clin Immunol 123:883–888
Vander Leek TK, Liu AH, Stefanski K, Blacker B, Bock SA (2000) The natural history of peanut allergy in young children and its association with serum peanut-specific IgE. J Pediatr 137:749–755
Akdis CA, Akdis M (2011) Mechanisms of allergen-specific immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 127:18–27, quiz 8-9
Fujita H, Soyka MB, Akdis M, Akdis CA (2012) Mechanisms of allergen-specific immunotherapy. Clin Transl Allergy 2:2
Nelson HS, Lahr J, Rule R, Bock A, Leung D (1997) Treatment of anaphylactic sensitivity to peanuts by immunotherapy with injections of aqueous peanut extract. J Allergy Clin Immunol 99:744–751
Fernandez-Rivas M, Garrido Fernandez S, Nadal JA, Diaz de Durana MD, Garcia BE, Gonzalez-Mancebo E, Martin S, Barber D, Rico P, Tabar AI (2009) Randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of sublingual immunotherapy with a Pru p 3 quantified peach extract. Allergy 64:876–883
Pereira C, Bartolome B, Asturias JA, Ibarrola I, Tavares B, Loureiro G, Machado D, Chieira C (2009) Specific sublingual immunotherapy with peach LTP (Pru p 3). One year treatment: a case report. Cases J 2:6553
Garcia BE, Gonzalez-Mancebo E, Barber D, Martin S, Tabar AI, Diaz de Durana AM, Garrido-Fernandez S, Salcedo G, Rico P, Fernandez-Rivas M. Sublingual immunotherapy in peach allergy: monitoring molecular sensitizations and reactivity to apple fruit and Platanus pollen. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol 20: 514–520
Kerzl R, Simonowa A, Ring J, Ollert M, Mempel M (2007) Life-threatening anaphylaxis to kiwi fruit: protective sublingual allergen immunotherapy effect persists even after discontinuation. J Allergy Clin Immunol 119:507–8
Mempel M, Rakoski J, Ring J, Ollert M (2003) Severe anaphylaxis to kiwi fruit: immunologic changes related to successful sublingual allergen immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 111:1406–9
Enrique E, Pineda F, Malek T, Bartra J, Basagana M, Tella R, Castello JV, Alonso R, de Mateo JA, Cerda-Trias T, San Miguel-Moncin Mdel M, Monzon S, Garcia M, Palacios R, Cistero-Bahima A (2005) Sublingual immunotherapy for hazelnut food allergy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study with a standardized hazelnut extract. J Allergy Clin Immunol 116:1073–9
Kim EH, Bird JA, Kulis M, Laubach S, Pons L, Shreffler W, Steele P, Kamilaris J, Vickery B, Burks AW. Sublingual immunotherapy for peanut allergy: clinical and immunologic evidence of desensitization. J Allergy Clin Immunol 127: 640–6e1
Enrique E, Malek T, Pineda F, Palacios R, Bartra J, Tella R, Basagana M, Alonso R, Cistero-Bahima A (2008) Sublingual immunotherapy for hazelnut food allergy: a follow-up study. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 100:283–4
Keet CA, Frischmeyer-Guerrerio PA, Thyagarajan A, Schroeder JT, Hamilton RG, Boden S, Steele P, Driggers S, Burks AW, Wood RA. The safety and efficacy of sublingual and oral immunotherapy for milk allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 129: 448–55, 55 e1–5
Varshney P, Jones SM, Scurlock AM, Perry TT, Kemper A, Steele P, Hiegel A, Kamilaris J, Carlisle S, Yue X, Kulis M, Pons L, Vickery B, Burks AW. A randomized controlled study of peanut oral immunotherapy: clinical desensitization and modulation of the allergic response. J Allergy Clin Immunol 127: 654–660
Jones SM, Pons L, Roberts JL, Scurlock AM, Perry TT, Kulis M, Shreffler WG, Steele P, Henry KA, Adair M, Francis JM, Durham S, Vickery BP, Zhong X, Burks AW (2009) Clinical efficacy and immune regulation with peanut oral immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 124(292–300):e1–97
Meglio P, Bartone E, Plantamura M, Arabito E, Giampietro PG (2004) A protocol for oral desensitization in children with IgE-mediated cow's milk allergy. Allergy 59:980–7
Clark AT, Islam S, King Y, Deighton J, Anagnostou K, Ewan PW (2009) Successful oral tolerance induction in severe peanut allergy. Allergy 64:1218–20
Nadeau KC, Schneider LC, Hoyte L, Borras I, Umetsu DT. Rapid oral desensitization in combination with omalizumab therapy in patients with cow’s milk allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 127: 1622–1624
Longo G, Barbi E, Berti I, Meneghetti R, Pittalis A, Ronfani L, Ventura A (2008) Specific oral tolerance induction in children with very severe cow's milk-induced reactions. J Allergy Clin Immunol 121:343–7
Itoh N, Itagaki Y, Kurihara K. Rush specific oral tolerance induction in school-age children with severe egg allergy: one year follow up. Allergol Int 59: 43–51
Buchanan AD, Green TD, Jones SM, Scurlock AM, Christie L, Althage KA, Steele PH, Pons L, Helm RM, Lee LA, Burks AW (2007) Egg oral immunotherapy in nonanaphylactic children with egg allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 119:199–205
Staden U, Blumchen K, Blankenstein N, Dannenberg N, Ulbricht H, Dobberstein K, Ziegert M, Niggemann B, Wahn U, Beyer K (2008) Rush oral immunotherapy in children with persistent cow's milk allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 122:418–9
Blumchen K, Ulbricht H, Staden U, Dobberstein K, Beschorner J, de Oliveira LC, Shreffler WG, Sampson HA, Niggemann B, Wahn U, Beyer K. Oral peanut immunotherapy in children with peanut anaphylaxis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 126: 83–91 e1
Dupont C, Kalach N, Soulaines P, Legoue-Morillon S, Piloquet H, Benhamou PH. Cow's milk epicutaneous immunotherapy in children: a pilot trial of safety, acceptability, and impact on allergic reactivity. J Allergy Clin Immunol 125: 1165–1167
Skripak JM, Nash SD, Rowley H, Brereton NH, Oh S, Hamilton RG, Matsui EC, Burks AW, Wood RA (2008) A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of milk oral immunotherapy for cow's milk allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 122:1154–60
Vickery BP, Pons L, Kulis M, Steele P, Jones SM, Burks AW. Individualized IgE-based dosing of egg oral immunotherapy and the development of tolerance. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 105: 444–450
Staden U, Rolinck-Werninghaus C, Brewe F, Wahn U, Niggemann B, Beyer K (2007) Specific oral tolerance induction in food allergy in children: efficacy and clinical patterns of reaction. Allergy 62:1261–1269
Rolinck-Werninghaus C, Staden U, Mehl A, Hamelmann E, Beyer K, Niggemann B (2005) Specific oral tolerance induction with food in children: transient or persistent effect on food allergy? Allergy 60:1320–1322
Vickery BP, Burks W. Oral immunotherapy for food allergy. Curr Opin Pediatr 22: 765–770
Nadeau KC, Kohli A, Iyengar S, DeKruyff RH, Umetsu DT. Oral immunotherapy and anti-IgE antibody-adjunctive treatment for food allergy. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am 32: 111–133
Nowak-Wegrzyn A, Sampson HA. Future therapies for food allergies. J Allergy Clin Immunol 127: 558–573; quiz 74–75
Meglio P, Giampietro PG, Gianni S, Galli E (2008) Oral desensitization in children with immunoglobulin E-mediated cow's milk allergy—follow-up at 4 yr and 8 months. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 19:412–419
Vickery BP, Pons L, Kulis M, Steele P, Jones SM, Burks AW (2010) Individualized IgE-based dosing of egg oral immunotherapy and the development of tolerance. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 105:444–450
Blumchen K, Ulbricht H, Staden U, Dobberstein K, Beschorner J, de Oliveira LC, Shreffler WG, Sampson HA, Niggemann B, Wahn U, Beyer K (2010) Oral peanut immunotherapy in children with peanut anaphylaxis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 126(83–91):e1
Keet CA, Frischmeyer-Guerrerio PA, Thyagarajan A, Schroeder JT, Hamilton RG, Boden S, Steele P, Driggers S, Burks AW, Wood RA (2012) The safety and efficacy of sublingual and oral immunotherapy for milk allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 129:448–455, 55 e1–5
Varshney P, Steele PH, Vickery BP, Bird JA, Thyagarajan A, Scurlock AM, Perry TT, Jones SM, Burks AW (2009) Adverse reactions during peanut oral immunotherapy home dosing. J Allergy Clin Immunol 124:1351–1352
Lack G Update on risk factors for food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 129: 1187–1197
Larche M, Akdis CA, Valenta R (2006) Immunological mechanisms of allergen-specific immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol 6:761–771
Berin MC, Shreffler WG (2008) T(H)2 adjuvants: implications for food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 121:1311–1320, quiz 21-2
Chatila TA, Li N, Garcia-Lloret M, Kim HJ, Nel AE (2008) T-cell effector pathways in allergic diseases: transcriptional mechanisms and therapeutic targets. J Allergy Clin Immunol 121:812–823, quiz 24-5
Nograles KE, Zaba LC, Shemer A, Fuentes-Duculan J, Cardinale I, Kikuchi T, Ramon M, Bergman R, Krueger JG, Guttman-Yassky E (2009) IL-22-producing “T22” T cells account for upregulated IL-22 in atopic dermatitis despite reduced IL-17-producing TH17 T cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol 123:1244–1252, e2
Jutel M, Akdis M, Budak F, Aebischer-Casaulta C, Wrzyszcz M, Blaser K, Akdis CA (2003) IL-10 and TGF-beta cooperate in the regulatory T cell response to mucosal allergens in normal immunity and specific immunotherapy. Eur J Immunol 33:1205–1214
Francis JN, Till SJ, Durham SR (2003) Induction of IL-10 + CD4 + CD25+ T cells by grass pollen immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 111:1255–1261
Akdis M, Blaser K, Akdis CA (2005) T regulatory cells in allergy: novel concepts in the pathogenesis, prevention, and treatment of allergic diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol 116:961–968, quiz 9
Palomares O, Yaman G, Azkur AK, Akkoc T, Akdis M, Akdis CA (2010) Role of Treg in immune regulation of allergic diseases. Eur J Immunol 40:1232–1240
Gri G, Piconese S, Frossi B, Manfroi V, Merluzzi S, Tripodo C, Viola A, Odom S, Rivera J, Colombo MP, Pucillo CE (2008) CD4 + CD25+ regulatory T cells suppress mast cell degranulation and allergic responses through OX40-OX40L interaction. Immunity 29:771–781
Kearley J, Barker JE, Robinson DS, Lloyd CM (2005) Resolution of airway inflammation and hyperreactivity after in vivo transfer of CD4 + CD25+ regulatory T cells is interleukin 10 dependent. J Exp Med 202:1539–1547
Kearley J, Robinson DS, Lloyd CM (2008) CD4 + CD25+ regulatory T cells reverse established allergic airway inflammation and prevent airway remodeling. J Allergy Clin Immunol 122:617–624, e6
Meiler F, Klunker S, Zimmermann M, Akdis CA, Akdis M (2008) Distinct regulation of IgE, IgG4 and IgA by T regulatory cells and toll-like receptors. Allergy 63:1455–1463
Lin W, Truong N, Grossman WJ, Haribhai D, Williams CB, Wang J, Martin MG, Chatila TA (2005) Allergic dysregulation and hyperimmunoglobulinemia E in Foxp3 mutant mice. J Allergy Clin Immunol 116:1106–1115
Chatila TA, Blaeser F, Ho N, Lederman HM, Voulgaropoulos C, Helms C, Bowcock AM (2000) JM2, encoding a fork head-related protein, is mutated in X-linked autoimmunity-allergic disregulation syndrome. J Clin Invest 106:R75–81
Josefowicz SZ, Niec RE, Kim HY, Treuting P, Chinen T, Zheng Y, Umetsu DT, Rudensky AY. Extrathymically generated regulatory T cells control mucosal TH2 inflammation. Nature 482: 395–399
Duan W, So T, Mehta AK, Choi H, Croft M (2011) Inducible CD4 + LAP + Foxp3- regulatory T cells suppress allergic inflammation. J Immunol 187:6499–6507
Mucida D, Kutchukhidze N, Erazo A, Russo M, Lafaille JJ, Curotto de Lafaille MA (2005) Oral tolerance in the absence of naturally occurring Tregs. J Clin Invest 115:1923–1933
Atarashi K, Tanoue T, Shima T, Imaoka A, Kuwahara T, Momose Y, Cheng G, Yamasaki S, Saito T, Ohba Y, Taniguchi T, Takeda K, Hori S, Ivanov, II, Umesaki Y, Itoh K, Honda K. Induction of colonic regulatory T cells by indigenous Clostridium species. Science 331: 337–41
Radulovic S, Jacobson MR, Durham SR, Nouri-Aria KT (2008) Grass pollen immunotherapy induces Foxp3-expressing CD4+ CD25+ cells in the nasal mucosa. J Allergy Clin Immunol 121:1467–1472, 72 e1
Allam JP, Wurtzen PA, Reinartz M, Winter J, Vrtala S, Chen KW, Valenta R, Wenghoefer M, Appel T, Gros E, Niederhagen B, Bieber T, Lund K, Novak N (2010) Phl p 5 resorption in human oral mucosa leads to dose-dependent and time-dependent allergen binding by oral mucosal Langerhans cells, attenuates their maturation, and enhances their migratory and TGF-beta1 and IL-10-producing properties. J Allergy Clin Immunol 126:638–645, e1
Taylor A, Akdis M, Joss A, Akkoc T, Wenig R, Colonna M, Daigle I, Flory E, Blaser K, Akdis CA (2007) IL-10 inhibits CD28 and ICOS costimulations of T cells via src homology 2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase 1. J Allergy Clin Immunol 120:76–83
Marshall JS, Leal-Berumen I, Nielsen L, Glibetic M, Jordana M (1996) Interleukin (IL)-10 inhibits long-term IL-6 production but not preformed mediator release from rat peritoneal mast cells. J Clin Invest 97:1122–1128
Schandene L, Alonso-Vega C, Willems F, Gerard C, Delvaux A, Velu T, Devos R, de Boer M, Goldman M (1994) B7/CD28-dependent IL-5 production by human resting T cells is inhibited by IL-10. J Immunol 152:4368–4374
Chen W, Jin W, Hardegen N, Lei KJ, Li L, Marinos N, McGrady G, Wahl SM (2003) Conversion of peripheral CD4 + CD25- naive T cells to CD4 + CD25+ regulatory T cells by TGF-beta induction of transcription factor Foxp3. J Exp Med 198:1875–1886
Liu YJ (2006) Thymic stromal lymphopoietin: master switch for allergic inflammation. J Exp Med 203:269–273
Lee EB, Kim KW, Hong JY, Jee HM, Sohn MH, Kim KE (2010) Increased serum thymic stromal lymphopoietin in children with atopic dermatitis. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 21:e457–460
Siracusa MC, Saenz SA, Hill DA, Kim BS, Headley MB, Doering TA, Wherry EJ, Jessup HK, Siegel LA, Kambayashi T, Dudek EC, Kubo M, Cianferoni A, Spergel JM, Ziegler SF, Comeau MR, Artis D. TSLP promotes interleukin-3-independent basophil haematopoiesis and type 2 inflammation. Nature 477: 229–233
Zhu Z, Oh MH, Yu J, Liu YJ, Zheng T (2011) The role of TSLP in IL-13-induced atopic march. Sci Rep 1:23
Pushparaj PN, Tay HK, H'Ng SC, Pitman N, Xu D, McKenzie A, Liew FY, Melendez AJ (2009) The cytokine interleukin-33 mediates anaphylactic shock. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:9773–9778
Koyasu S, Moro K, Tanabe M, Takeuchi T (2010) Natural helper cells: a new player in the innate immune response against helminth infection. Adv Immunol 108:21–44
Koyasu S, Moro K (2011) Innate Th2-type immune responses and the natural helper cell, a newly identified lymphocyte population. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 11:109–114
Chang YJ, Kim HY, Albacker LA, Baumgarth N, McKenzie AN, Smith DE, Dekruyff RH, Umetsu DT. Innate lymphoid cells mediate influenza-induced airway hyper-reactivity independently of adaptive immunity. Nat Immunol 12: 631–638
Allakhverdi Z, Comeau MR, Jessup HK, Delespesse G (2009) Thymic stromal lymphopoietin as a mediator of crosstalk between bronchial smooth muscles and mast cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol 123(958–60):e2
Van Ree R, Van Leeuwen WA, Dieges PH, Van Wijk RG, De Jong N, Brewczyski PZ, Kroon AM, Schilte PP, Tan KY, Simon-Licht IF, Roberts AM, Stapel SO, Aalberse RC (1997) Measurement of IgE antibodies against purified grass pollen allergens (Lol p 1, 2, 3 and 5) during immunotherapy. Clin Exp Allergy 27:68–74
Gleich GJ, Zimmermann EM, Henderson LL, Yunginger JW (1982) Effect of immunotherapy on immunoglobulin E and immunoglobulin G antibodies to ragweed antigens: a six-year prospective study. J Allergy Clin Immunol 70:261–271
Eberlein-Konig B, Ullmann S, Thomas P, Przybilla B (1995) Tryptase and histamine release due to a sting challenge in bee venom allergic patients treated successfully or unsuccessfully with hyposensitization. Clin Exp Allergy 25:704–712
Jutel M, Muller UR, Fricker M, Rihs S, Pichler WJ, Dahinden C (1996) Influence of bee venom immunotherapy on degranulation and leukotriene generation in human blood basophils. Clin Exp Allergy 26:1112–1118
Plewako H, Wosinska K, Arvidsson M, Bjorkander J, Skov PS, Hakansson L, Rak S (2006) Basophil interleukin 4 and interleukin 13 production is suppressed during the early phase of rush immunotherapy. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 141:346–353
Varshney P, Jones SM, Scurlock AM, Perry TT, Kemper A, Steele P, Hiegel A, Kamilaris J, Carlisle S, Yue X, Kulis M, Pons L, Vickery B, Burks AW (2011) A randomized controlled study of peanut oral immunotherapy: clinical desensitization and modulation of the allergic response. J Allergy Clin Immunol 127:654–660
Bedoret D, Singh AK, Shaw V, Hoyte EG, Hamilton R, Dekruyff RH, Schneider LC, Nadeau KC, Umetsu DT. Changes in antigen-specific T-cell number and function during oral desensitization in cow's milk allergy enabled with omalizumab. Mucosal Immunol 5: 267–276
Scadding G, Durham S (2009) Mechanisms of sublingual immunotherapy. J Asthma 46:322–334
Allam JP, Peng WM, Appel T, Wenghoefer M, Niederhagen B, Bieber T, Berge S, Novak N (2008) Toll-like receptor 4 ligation enforces tolerogenic properties of oral mucosal Langerhans cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol 121:368–374, e1
Allam JP, Novak N, Fuchs C, Asen S, Berge S, Appel T, Geiger E, Kochan JP, Bieber T (2003) Characterization of dendritic cells from human oral mucosa: a new Langerhans' cell type with high constitutive FcepsilonRI expression. J Allergy Clin Immunol 112:141–148
Nouri-Aria KT, Wachholz PA, Francis JN, Jacobson MR, Walker SM, Wilcock LK, Staple SQ, Aalberse RC, Till SJ, Durham SR (2004) Grass pollen immunotherapy induces mucosal and peripheral IL-10 responses and blocking IgG activity. J Immunol 172:3252–3259
Zemann B, Schwaerzler C, Griot-Wenk M, Nefzger M, Mayer P, Schneider H, de Weck A, Carballido JM, Liehl E (2003) Oral administration of specific antigens to allergy-prone infant dogs induces IL-10 and TGF-beta expression and prevents allergy in adult life. J Allergy Clin Immunol 111:1069–1075
Wakkach A, Fournier N, Brun V, Breittmayer JP, Cottrez F, Groux H (2003) Characterization of dendritic cells that induce tolerance and T regulatory 1 cell differentiation in vivo. Immunity 18:605–617
Bottcher MF, Jenmalm MC (2002) Breastfeeding and the development of atopic disease during childhood. Clin Exp Allergy 32:159–161
Scadding GW, Shamji MH, Jacobson MR, Lee DI, Wilson D, Lima MT, Pitkin L, Pilette C, Nouri-Aria K, Durham SR. Sublingual grass pollen immunotherapy is associated with increases in sublingual Foxp3-expressing cells and elevated allergen-specific immunoglobulin G4, immunoglobulin A and serum inhibitory activity for immunoglobulin E-facilitated allergen binding to B cells. Clin Exp Allergy 40: 598–606
Kulis M, Saba K, Kim EH, Bird JA, Kamilaris N, Vickery BP, Staats H, Burks AW. Increased peanut-specific IgA levels in saliva correlate with food challenge outcomes after peanut sublingual immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 129: 1159–1162
Itoh N, Itagaki Y, Kurihara K (2010) Rush specific oral tolerance induction in school-age children with severe egg allergy: one year follow up. Allergol Int 59:43–51
Jutel M, Jaeger L, Suck R, Meyer H, Fiebig H, Cromwell O (2005) Allergen-specific immunotherapy with recombinant grass pollen allergens. J Allergy Clin Immunol 116:608–613
Reisinger J, Horak F, Pauli G, van Hage M, Cromwell O, Konig F, Valenta R, Niederberger V (2005) Allergen-specific nasal IgG antibodies induced by vaccination with genetically modified allergens are associated with reduced nasal allergen sensitivity. J Allergy Clin Immunol 116:347–354
Golden DB, Meyers DA, Kagey-Sobotka A, Valentine MD, Lichtenstein LM (1982) Clinical relevance of the venom-specific immunoglobulin G antibody level during immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 69:489–93
Muller U, Helbling A, Bischof M (1989) Predictive value of venom-specific IgE, IgG and IgG subclass antibodies in patients on immunotherapy with honey bee venom. Allergy 44:412–418
Schroeder HW Jr, Cavacini L (2010) Structure and function of immunoglobulins. J Allergy Clin Immunol 125:S41–52
Wachholz PA, Durham SR (2004) Mechanisms of immunotherapy: IgG revisited. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 4:313–318
Till SJ, Francis JN, Nouri-Aria K, Durham SR (2004) Mechanisms of immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 113:1025–1034, quiz 35
Uermosi C, Beerli RR, Bauer M, Manolova V, Dietmeier K, Buser RB, Kundig TM, Saudan P, Bachmann MF (2010) Mechanisms of allergen-specific desensitization. J Allergy Clin Immunol 126:375–383
Carballido JM, Carballido-Perrig N, Kagi MK, Meloen RH, Wuthrich B, Heusser CH, Blaser K (1993) T cell epitope specificity in human allergic and nonallergic subjects to bee venom phospholipase A2. J Immunol 150:3582–3591
Shreffler WG, Wanich N, Moloney M, Nowak-Wegrzyn A, Sampson HA (2009) Association of allergen-specific regulatory T cells with the onset of clinical tolerance to milk protein. J Allergy Clin Immunol 123:43–52, e7
Weiner HL (2000) Oral tolerance, an active immunologic process mediated by multiple mechanisms. J Clin Invest 106:935–7
Hoyne GF, Tan K, Corsin-Jimenez M, Wahl K, Stewart M, Howie SE, Lamb JR (2000) Immunological tolerance to inhaled antigen. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 162:S169–174
Nadeau KC, Schneider LC, Hoyte L, Borras I, Umetsu DT (2011) Rapid oral desensitization in combination with omalizumab therapy in patients with cow's milk allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 127:1622–1624
MacGlashan DW Jr, Bochner BS, Adelman DC, Jardieu PM, Togias A, McKenzie-White J, Sterbinsky SA, Hamilton RG, Lichtenstein LM (1997) Down-regulation of Fc(epsilon)RI expression on human basophils during in vivo treatment of atopic patients with anti-IgE antibody. J Immunol 158:1438–1445
Stone KD, Prussin C, Metcalfe DD (2010) IgE, mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils. J Allergy Clin Immunol 125:S73–80
Kitaura J, Song J, Tsai M, Asai K, Maeda-Yamamoto M, Mocsai A, Kawakami Y, Liu FT, Lowell CA, Barisas BG, Galli SJ, Kawakami T (2003) Evidence that IgE molecules mediate a spectrum of effects on mast cell survival and activation via aggregation of the FcepsilonRI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:12911–12916
Corren J, Shapiro G, Reimann J, Deniz Y, Wong D, Adelman D, Togias A (2008) Allergen skin tests and free IgE levels during reduction and cessation of omalizumab therapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 121:506–511
Noga O, Hanf G, Kunkel G (2003) Immunological and clinical changes in allergic asthmatics following treatment with omalizumab. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 131:46–52
Hill DA, Siracusa MC, Abt MC, Kim BS, Kobuley D, Kubo M, Kambayashi T, Larosa DF, Renner ED, Orange JS, Bushman FD, Artis D (2012) Commensal bacteria-derived signals regulate basophil hematopoiesis and allergic inflammation. Nat Med 18:538–546
Turcanu V, Maleki SJ, Lack G (2003) Characterization of lymphocyte responses to peanuts in normal children, peanut-allergic children, and allergic children who acquired tolerance to peanuts. J Clin Invest 111:1065–1072
Nagata S, McKenzie C, Pender SL, Bajaj-Elliott M, Fairclough PD, Walker-Smith JA, Monteleone G, MacDonald TT (2000) Human Peyer's patch T cells are sensitized to dietary antigen and display a Th cell type 1 cytokine profile. J Immunol 165:5315–5321
Faria AM, Weiner HL (2005) Oral tolerance. Immunol Rev 206:232–59
Meiler F, Zumkehr J, Klunker S, Ruckert B, Akdis CA, Akdis M (2008) In vivo switch to IL-10-secreting T regulatory cells in high dose allergen exposure. J Exp Med 205:2887–2898
Aslam A, Chan H, Warrell DA, Misbah S, Ogg GS. Tracking antigen-specific T-cells during clinical tolerance induction in humans. PLoS One 5: e11028
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is published as part of the Special Issue on Food Allergy [34:6].
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rachid, R., Umetsu, D.T. Immunological mechanisms for desensitization and tolerance in food allergy. Semin Immunopathol 34, 689–702 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-012-0333-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-012-0333-9