Abstract
Purpose
Osteosarcoma is a common primary malignant bone tumour, and its cure rate has stagnated over the past 25–30 years. Brazilin, a purified natural product from sappan wood (Caesalpinia sappan L.), has been proved to possess potent anti-cancer effects. In this study, we investigated the anti-cancer effect of brazilin on human osteosarcoma and elucidated the underlying mechanisms.
Methods
We exposed MG-63 cells to different concentrations of brazilin (5, 10 and 20 µM) for 24 h. Western blotting, immunocytofluorescence, luciferase reporter assays, and RT-PCR were used to evaluate whether brazilin activates FOXO family-dependent autophagy.
Results
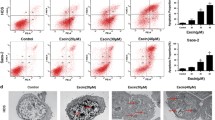
Brazilin increased autophagic flux in the human osteosarcoma cell line MG-63, as evidenced by the upregulation of LC3-II and the downregulation of P62/SQSTM1. Moreover, the pharmacological or genetic blockade of autophagy decreased brazilin-induced cell death, indicating that brazilin triggered autophagic cell death in MG-63 cells. Specifically, brazilin induced FOXO3A(Ser7) phosphorylation, activated FOXO3A nuclear translocation and increased FOXO3A reporter activity, which contributed to the expression of autophagy-related genes and subsequently initiated autophagic cell death in MG-63 cells. Importantly, the increased expression and nuclear translocation of FOXO3A were tightly related to the disturbance of calcium homeostasis, which could be prevented by chelating intracellular calcium.
Conclusions
Taken together, these data demonstrate that brazilin induces osteosarcoma cell death by inducing excessive autophagy, which is mediated through the Ca2+-FOXO3A pathway. Our study provides a new anti-tumour mechanism for brazilin treatment in osteosarcoma patients.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reed DR, Hayashi M, Wagner L, Binitie O, Steppan DA, Brohl AS, Shinohara ET, Bridge JA, Loeb DM, Borinstein SC, Isakoff MS (2017) Treatment pathway of bone sarcoma in children, adolescents, and young adults. Cancer 123(12):2206–2218. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.30589
Harrison DJ, Geller DS, Gill JD, Lewis VO, Gorlick R (2018) Current and future therapeutic approaches for osteosarcoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 18(1):39–50. https://doi.org/10.1080/14737140.2018.1413939
Onorati AV, Dyczynski M, Ojha R, Amaravadi RK (2018) Targeting autophagy in cancer. Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.31335
Duffy A, Le J, Sausville E, Emadi A (2015) Autophagy modulation: a target for cancer treatment development. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 75(3):439–447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-014-2637-z
Xu Y, Wang Q, Zhang L, Zheng M (2018) 2-Deoxy-d-glucose enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human gastric cancer cells through downregulating JNK-mediated cytoprotective autophagy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 81(3):555–564. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-018-3526-7
Tan Q, Joshua AM, Wang M, Bristow RG, Wouters BG, Allen CJ, Tannock IF (2017) Up-regulation of autophagy is a mechanism of resistance to chemotherapy and can be inhibited by pantoprazole to increase drug sensitivity. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 79(5):959–969. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-017-3298-5
Rybstein MD, Bravo-San Pedro JM, Kroemer G, Galluzzi L (2018) The autophagic network and cancer. Nat Cell Biol 20(3):243–251. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0042-2
Yang X, Zhu J, Wu J, Huang N, Cui Z, Luo Y, Sun F, Pan Q, Li Y, Yang Q (2018) (−)-Guaiol regulates autophagic cell death depending on mTOR signaling in NSCLC. Cancer Biol Ther. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2018.1451277
Xiang Y, Zhao J, Zhao M, Wang K (2018) Allicin activates autophagic cell death to alleviate the malignant development of thyroid cancer. Exp Ther Med 15(4):3537–3543. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2018.5828
Wu B, Tan M, Cai W, Wang B, He P, Zhang X (2018) Arsenic trioxide induces autophagic cell death in osteosarcoma cells via the ROS-TFEB signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 496(1):167–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.01.018
Huang K, Chen Y, Zhang R, Wu Y, Ma Y, Fang X, Shen S (2018) Honokiol induces apoptosis and autophagy via the ROS/ERK1/2 signaling pathway in human osteosarcoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Cell Death Dis 9(2):157. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-017-0166-5
Monsalve M, Olmos Y (2011) The complex biology of FOXO. Curr Drug Targets 12(9):1322–1350
Furukawa-Hibi Y, Kobayashi Y, Chen C, Motoyama N (2005) FOXO transcription factors in cell-cycle regulation and the response to oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal 7(5–6):752–760. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2005.7.752
Coomans de Brachene A, Demoulin JB (2016) FOXO transcription factors in cancer development and therapy. CMLS 73(6):1159–1172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-015-2112-y
van der Vos KE, Coffer PJ (2011) The extending network of FOXO transcriptional target genes. Antioxid Redox Signal 14(4):579–592. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2010.3419
Nirmal NP, Panichayupakaranant P (2015) Antioxidant, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory activities of standardized brazilin-rich Caesalpinia sappan extract. Pharmaceut Biol 53(9):1339–1343. https://doi.org/10.3109/13880209.2014.982295
Nirmal NP, Rajput MS, Prasad RG, Ahmad M (2015) Brazilin from Caesalpinia sappan heartwood and its pharmacological activities: a review. Asian Pac J Trop Med 8(6):421–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apjtm.2015.05.014
Young CN, Sinadinos A, Lefebvre A, Chan P, Arkle S, Vaudry D, Gorecki DC (2015) A novel mechanism of autophagic cell death in dystrophic muscle regulated by P2RX7 receptor large-pore formation and HSP90. Autophagy 11(1):113–130. https://doi.org/10.4161/15548627.2014.994402
Wang X, Wang XL, Chen HL, Wu D, Chen JX, Wang XX, Li RL, He JH, Mo L, Cen X, Wei YQ, Jiang W (2014) Ghrelin inhibits doxorubicin cardiotoxicity by inhibiting excessive autophagy through AMPK and p38-MAPK. Biochem Pharmacol 88(3):334–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2014.01.040
Sandri M (2012) FOXOphagy path to inducing stress resistance and cell survival. Nat Cell Biol 14(8):786–788. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2550
Tzivion G, Dobson M, Ramakrishnan G (2011) FoxO transcription factors; regulation by AKT and 14-3-3 proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 1813(11):1938–1945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.06.002
Lin Y, Sheng M, Weng Y, Xu R, Lu N, Du H, Yu W (2017) Berberine protects against ischemia/reperfusion injury after orthotopic liver transplantation via activating Sirt1/FoxO3alpha induced autophagy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 483(2):885–891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.01.028
Ho KK, McGuire VA, Koo CY, Muir KW, de Olano N, Maifoshie E, Kelly DJ, McGovern UB, Monteiro LJ, Gomes AR, Nebreda AR, Campbell DG, Arthur JS, Lam EW (2012) Phosphorylation of FOXO3a on Ser-7 by p38 promotes its nuclear localization in response to doxorubicin. J Biol Chem 287(2):1545–1555. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.284224
Dick O, Bading H (2010) Synaptic activity and nuclear calcium signaling protect hippocampal neurons from death signal-associated nuclear translocation of FoxO3a induced by extrasynaptic N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors. J Biol Chem 285(25):19354–19361. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.127654
Liu R, Li J, Zhang T, Zou L, Chen Y, Wang K, Lei Y, Yuan K, Li Y, Lan J, Cheng L, Xie N, Xiang R, Nice EC, Huang C, Wei Y (2014) Itraconazole suppresses the growth of glioblastoma through induction of autophagy: involvement of abnormal cholesterol trafficking. Autophagy 10(7):1241–1255. https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.28912
Fulda S, Kogel D (2015) Cell death by autophagy: emerging molecular mechanisms and implications for cancer therapy. Oncogene 34(40):5105–5113. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.458
Eijkelenboom A, Burgering BM (2013) FOXOs: signalling integrators for homeostasis maintenance. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 14(2):83–97. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3507
Ni HM, Du K, You M, Ding WX (2013) Critical role of FoxO3a in alcohol-induced autophagy and hepatotoxicity. Am J Pathol 183(6):1815–1825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.08.011
Yang M, Pi H, Li M, Xu S, Zhang L, Xie J, Tian L, Tu M, He M, Lu Y, Yu Z, Zhou Z (2016) From the cover: autophagy induction contributes to cadmium toxicity in mesenchymal stem cells via AMPK/FOXO3a/BECN1 signaling. Toxicol Sci 154(1):101–114. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfw144
Wang X, Hu S, Liu L (2017) Phosphorylation and acetylation modifications of FOXO3a: Independently or synergistically? Oncol Lett 13(5):2867–2872. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.5851
Funding
This study was funded by a grant from the Guangdong Science and Technology Project (No. 2017A020215162).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, Y., He, P., Wang, H. et al. Brazilin induces FOXO3A-dependent autophagic cell death by disturbing calcium homeostasis in osteosarcoma cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 82, 479–491 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-018-3633-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-018-3633-5