Abstract
Objective
Luteolin, a common dietary flavonoid, induces apoptosis of many types of cancer cells. However, its role in glioblastoma and the potential mechanisms remain unknown. In this research, we studied the molecular mechanisms of the anti-cancer effect of luteolin in glioblastoma cancer cell lines.
Methods
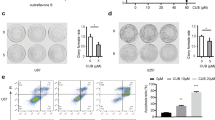
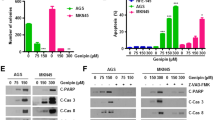
Both U251MG and U87MG human glioblastoma cell lines were tested. Cell growth was assessed by the cell counting kit-8. Cell apoptosis was detected with flow cytometry and caspase-3 immunofluorescence staining. The protein levels of caspase-3/Bax/Bcl-2 and p-PERK/p-eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP/caspase-12 pathway were analyzed using western blots. Reactive oxygen species generation was measured with DCFH-DA staining using flow cytometry. Mitochondrial membrane potential was tested with JC-1 staining. Anti-cancer effect in vivo was measured using tumor xenograft mode in nude mice.
Results
Luteolin induced a lethal endoplasmic reticulum stress response and mitochondrial dysfunction in glioblastoma cells by increasing intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels. Luteolin induced expression of ER stress-associated proteins, including phosphorylation of PERK, eIF2α, ATF4, CHOP and cleaved-caspase 12. Inhibition of ROS production by anti-oxidant N-acetylcysteine could reverse luteolin-induced ER stress and mitochondrial pathways activation as well as apoptosis. What’s more, we also showed the anticancer effect of luteolin in vivo.
Conclusions
Our results suggest that luteolin induces apoptosis through activating ER stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in glioblastoma cell lines and in vivo, which provides the anti-cancer candidate to treat glioblstoma.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wen PY, Kesari S (2008) Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med 359:492–507
Trachootham D, Alexandre J, Huang P (2009) Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: a radical therapeutic approach? Nat Rev Drug Discov 8:579–591
Yang J, Lu M, Lee C, Chen G, Lin Y, Chang F et al (2011) Selective targeting of breast cancer cells through ROS-mediated mechanisms potentiates the lethality of paclitaxel by a novel diterpene, gelomulide K. Free Radic Biol Med 51:641–657
Nogueira V, Hay N (2013) Molecular pathways: reactive oxygen species homeostasis in cancer cells and implications for cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res 19:4309–4314
Ghobrial IM, Witzig TE, Adjei AA (2005) Targeting apoptosis pathways in cancer therapy. CA Cancer J Clin 55:178–194
Tabas I, Ron D (2011) Integrating the mechanisms of apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Nat Cell Biol 13:184–190
Choi AY, Choi JH, Yoon H, Hwang K, Noh MH, Choe W et al (2011) Luteolin induces apoptosis through endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in Neuro-2a mouse neuroblastoma cells. Eur J Pharmacol 668:115–126
Neuhouser ML (2004) Dietary flavonoids and cancer risk: evidence from human population studies. Nutr Cancer 50:1–7
Mencherini T, Picerno P, Scesa C, Aquino R (2007) Triterpene, antioxidant, and antimicrobial compounds from Melissaofficinalis. J Nat Prod 70:1889–1894
Lin Y, Shi R, Wang X, Shen HM (2008) Luteolin, a flavonoid with potential for cancer prevention and therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 8:634–646
Cai X, Ye T, Liu C, Lu W, Lu M, Zhang J et al (2011) Luteolin induced G2 phase cell cycle arrest and apoptosis on non-small cell lung cancer cells. Toxicol In Vitro 25:1385–1391
Wu B, Zhang Q, Shen W, Zhu J (2008) Anti-proliferative and chemosensitizing effects of luteolin on human gastric cancer AGS cell line. Mol Cell Biochem 313:125–132
Chian S, Thapa R, Chi Z, Wang XJ, Tang X (2014) Luteolin inhibits the Nrf2 signaling pathway and tumor growth in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Co 447:602–608
Nakagawa S, Deli MA, Kawaguchi H, Shimizudani T, Shimono T, Kittel A et al (2009) A new blood-brain barrier model using primary rat brain endothelial cells, pericytes and astrocytes. Neurochem Int 54:253–263
Zou P, Zhang J, Xia Y, Kanchana K, Guo G, Chen W et al (2015) ROS generation mediates the anti-cancer effects of WZ35 via activating JNK and ER stress apoptotic pathways in gastric cancer. Oncotarget 6:5860–5876
Zhang L, Wang H, Ding K, Xu J (2015) FTY720 induces autophagy-related apoptosis and necroptosis in human glioblastoma cells. Toxicol Lett 236:43–59
Zhang K, Kaufman RJ (2008) From endoplasmic-reticulum stress to the inflammatory response. Nature 454:455–462
Hotamisligil GKS (2010) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the inflammatory basis of metabolic disease. Cell 140:900–917
Walter P, Ron D (2011) The unfolded protein response: from stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science 334:1081–1086
Desagher S, Martinou J (2000) Mitochondria as the central control point of apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol 10:369–377
Olichon A, Baricault L, Gas N, Guillou E, Valette A, Belenguer P et al (2003) Loss of OPA1 perturbates the mitochondrial inner membrane structure and integrity, leading to cytochrome c release and apoptosis. J Biol Chem 278:7743–7746
Das A, Banik NL, Ray SK (2010) Flavonoids activated caspases for apoptosis in human glioblastoma T98G and U87MG cells but not in human normal astrocytes. Cancer Am Cancer Soc 116:164–176
Selvendiran K (2006) Luteolin promotes degradation in signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 in human hepatoma cells: an implication for the antitumor potential of flavonoids. Cancer Res 66:4826–4834
Shi RX, Ong CN, Shen HM (2004) Luteolin sensitizes tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced apoptosis in human tumor cells. Oncogene 23:7712–7721
Szatrowski TP, Nathan CF (1991) Production of large amounts of hydrogen peroxide by human tumor cells. Cancer Res 51:794–798
Gorrini C, Harris IS, Mak TW (2013) Modulation of oxidative stress as an anticancer strategy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 12:931–947
Bragado P, Armesilla A, Silva A, Porras A (2007) Apoptosis by cisplatin requires p53 mediated p38α MAPK activation through ROS generation. Apoptosis 12:1733–1742
Alexandre J, Hu Y, Lu W, Pelicano H, Huang P(2007) Novel action of paclitaxel against cancer cells: bystander effect mediated by reactive oxygen species. Cancer Res 67:3512–3517
Rao R, Nalluri S, Fiskus W, Savoie A, Buckley KM, Ha K, et al (2010) Role of CAAT/enhancer binding protein homologous protein in Panobinostat-mediated potentiation of Bortezomib-induced lethal endoplasmic reticulum stress in mantle cell lymphoma cells. Clin Cancer Res 16:4742–4754
Oakes SA (2017) Endoplasmic reticulum proteostasis: a key checkpoint in cancer. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 312:C93–C102
Kim AD, Madduma HS, Piao MJ, Kang KA, Cho SJ, Hyun JW (2015) Esculetin induces apoptosis in human colon cancer cells by inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Biochem Funct 33:487–494
Boyce M, Yuan J (2006) Cellular response to endoplasmic reticulum stress: a matter of life or death. Cell Death Differ 13:363–373
Ge W, Yin Q, Xian H (2015) Wogonin induced mitochondrial dysfunction and endoplasmic reticulum stress in human malignant neuroblastoma cells via IRE1alpha-dependent pathway. J Mol Neurosci 56:652–662
Wu CT, Weng TI, Chen LP, Chiang CK, Liu SH (2013) Involvement of caspase-12-dependent apoptotic pathway in ionic radiocontrast urografin-induced renal tubular cell injury. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 266:167–175
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr Han Yanling for the technical assistance. This work was supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81371357) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation funded project under Grant (No. 2014M562665).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors disclose no potential conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Wang, H., Jia, Y. et al. Luteolin induces apoptosis by ROS/ER stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in gliomablastoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 79, 1031–1041 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-017-3299-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-017-3299-4