Abstract
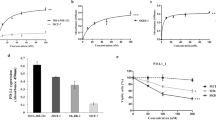
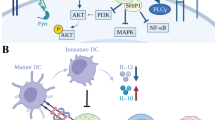
Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) are critical in regulating apoptosis resistance in cancer. Antagonists of IAPs, such as LCL161, are in clinical development and show promise as anti-cancer agents for solid and hematological cancers, with preliminary data suggesting they may act as immunomodulators. IAP antagonists hypersensitize tumor cells to TNF-α-mediated apoptosis, an effect that may work in synergy with that of cancer vaccines. This study aimed to further investigate the immunomodulatory properties of LCL161 on human immune subsets. T lymphocytes treated with LCL161 demonstrated significantly enhanced cytokine secretion upon activation, with little effect on CD4 and CD8 T-cell survival or proliferation. LCL161 treatment of peripheral blood mononuclear cells significantly enhanced priming of naïve T cells with synthetic peptides in vitro. Myeloid dendritic cells underwent phenotypic maturation upon IAP antagonism and demonstrated a reduced capacity to cross-present a tumor antigen-based vaccine. These effects are potentially mediated through an observed activation of the canonical and non-canonical NF-κB pathways, following IAP antagonism with a resulting upregulation of anti-apoptotic molecules. In conclusion, this study demonstrated the immunomodulatory properties of antagonists at physiologically relevant concentrations and indicates their combination with immunotherapy requires further investigation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hodi FS, O’Day SJ, McDermott DF et al (2010) Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med 363:711–723. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1003466
Kantoff PW, Higano CS, Shore ND et al (2010) Sipuleucel-T immunotherapy for castration-resistant prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 363:411–422. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1001294
Heine A, Held SA, Bringmann A, Holderried TA, Brossart P (2011) Immunomodulatory effects of anti-angiogenic drugs. Leukemia 25:899–905. doi:10.1038/leu.2011.24
Ott PA, Adams S (2011) Small-molecule protein kinase inhibitors and their effects on the immune system: implications for cancer treatment. Immunotherapy 3:213–227. doi:10.2217/imt.10.99
Du C, Fang M, Li Y, Li L, Wang X (2000) Smac, a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c-dependent caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition. Cell 102:33–42
Yang QH, Du C (2004) Smac/DIABLO selectively reduces the levels of c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 but not that of XIAP and livin in HeLa cells. J Biol Chem 279:16963–16970. doi:10.1074/jbc.M401253200
Varfolomeev E, Vucic D (2011) Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins: fascinating biology leads to attractive tumor therapeutic targets. Future Oncol 7:633–648. doi:10.2217/fon.11.40
Vucic D, Fairbrother WJ (2007) The inhibitor of apoptosis proteins as therapeutic targets in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13:5995–6000. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0729
Varfolomeev E, Blankenship JW, Wayson SM et al (2007) IAP antagonists induce autoubiquitination of c-IAPs, NF-κB activation, and TNFalpha-dependent apoptosis. Cell 131:669–681. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.10.030
Vince JE, Wong WW, Khan N et al (2007) IAP antagonists target cIAP1 to induce TNFalpha-dependent apoptosis. Cell 131:682–693. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.10.037
Wu H, Tschopp J, Lin SC (2007) Smac mimetics and TNFalpha: a dangerous liaison? Cell 131:655–658. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.10.042
Dai Y, Liu M, Tang W, Li Y, Lian J, Lawrence TS, Xu L (2009) A Smac-mimetic sensitizes prostate cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis via modulating both IAPs and NF-κB. BMC Cancer 9:392. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-9-392
Varfolomeev E, Alicke B, Elliott JM et al (2009) X chromosome-linked inhibitor of apoptosis regulates cell death induction by proapoptotic receptor agonists. J Biol Chem 284:34553–34560. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.040139
Fakler M, Loeder S, Vogler M, Schneider K, Jeremias I, Debatin KM, Fulda S (2009) Small molecule XIAP inhibitors cooperate with TRAIL to induce apoptosis in childhood acute leukemia cells and overcome Bcl-2-mediated resistance. Blood 113:1710–1722. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-09-114314
Loeder S, Zenz T, Schnaiter A, Mertens D, Winkler D, Dohner H, Debatin KM, Stilgenbauer S, Fulda S (2009) A novel paradigm to trigger apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Res 69:8977–8986. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2604
Matsuzawa A, Tseng PH, Vallabhapurapu S, Luo JL, Zhang W, Wang H, Vignali DA, Gallagher E, Karin M (2008) Essential cytoplasmic translocation of a cytokine receptor-assembled signaling complex. Science 321:663–668. doi:10.1126/science.1157340
Vallabhapurapu S, Matsuzawa A, Zhang W, Tseng PH, Keats JJ, Wang H, Vignali DA, Bergsagel PL, Karin M (2008) Nonredundant and complementary functions of TRAF2 and TRAF3 in a ubiquitination cascade that activates NIK-dependent alternative NF-κB signaling. Nat Immunol 9:1364–1370. doi:10.1038/ni.1678
Gardam S, Turner VM, Anderton H, Limaye S, Basten A, Koentgen F, Vaux DL, Silke J, Brink R (2011) Deletion of cIAP1 and cIAP2 in murine B lymphocytes constitutively activates cell survival pathways and inactivates the germinal center response. Blood 117:4041–4051. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-10-312793
Tseng PH, Matsuzawa A, Zhang W, Mino T, Vignali DA, Karin M (2010) Different modes of ubiquitination of the adaptor TRAF3 selectively activate the expression of type I interferons and proinflammatory cytokines. Nat Immunol 11:70–75. doi:10.1038/ni.1819
Dupoux A, Cartier J, Cathelin S, Filomenko R, Solary E, Dubrez-Daloz L (2009) cIAP1-dependent TRAF2 degradation regulates the differentiation of monocytes into macrophages and their response to CD40 ligand. Blood 113:175–185. doi:10.1182/blood-2008-02-137919
Conte D, Holcik M, Lefebvre CA, Lacasse E, Picketts DJ, Wright KE, Korneluk RG (2006) Inhibitor of apoptosis protein cIAP2 is essential for lipopolysaccharide-induced macrophage survival. Mol Cell Biol 26:699–708. doi:10.1128/MCB.26.2.699-708.2006
Waldele K, Silbermann K, Schneider G, Ruckes T, Cullen BR, Grassmann R (2006) Requirement of the human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV-1) tax-stimulated HIAP-1 gene for the survival of transformed lymphocytes. Blood 107:4491–4499. doi:10.1182/blood-2005-08-3138
Zane L, Sibon D, Legras C et al (2010) Clonal expansion of HTLV-1 positive CD8+ cells relies on cIAP-2 but not on c-FLIP expression. Virology 407:341–351. doi:10.1016/j.virol.2010.07.023
Dougan M, Dougan S, Slisz J et al (2010) IAP inhibitors enhance co-stimulation to promote tumor immunity. J Exp Med 207:2195–2206. doi:10.1084/jem.20101123
Infante JR, Dees EC, Burris HAI et al (2010) A phase I study of LCL161, an oral IAP inhibitor, in patients with advanced cancer. The 101st annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research, Washington
Houghton PJ, Kang MH, Reynolds CP et al (2011) Initial testing (Stage 1) of LCL161, a SMAC mimetic, by the pediatric preclinical testing program. Pediatr Blood Cancer. doi:10.1002/pbc.23167
Weisberg E, Ray A, Barrett R et al (2010) Smac mimetics: implications for enhancement of targeted therapies in leukemia. Leukemia 24:2100–2109. doi:10.1038/leu.2010.212
Knights AJ, Nuber N, Thomson CW et al (2009) Modified tumour antigen-encoding mRNA facilitates the analysis of naturally occurring and vaccine-induced CD4 and CD8 T cells in cancer patients. Cancer Immunol Immunother 58:325–338. doi:10.1007/s00262-008-0556-8
Robson NC, McAlpine T, Knights AJ, Schnurr M, Shin A, Chen W, Maraskovsky E, Cebon J (2010) Processing and cross-presentation of individual HLA-A, -B, or -C epitopes from NY-ESO-1 or an HLA-A epitope for Melan-A differ according to the mode of antigen delivery. Blood 116:218–225. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-10-249458
Platt CD, Ma JK, Chalouni C, Ebersold M, Bou-Reslan H, Carano RA, Mellman I, Delamarre L (2010) Mature dendritic cells use endocytic receptors to capture and present antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:4287–4292. doi:10.1073/pnas.0910609107
Chauhan D, Neri P, Velankar M et al (2007) Targeting mitochondrial factor Smac/DIABLO as therapy for multiple myeloma (MM). Blood 109:1220–1227. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-04-015149
Zippelius A, Pittet MJ, Batard P et al (2002) Thymic selection generates a large T cell pool recognizing a self-peptide in humans. J Exp Med 195:485–494
Duewell P, Kisser U, Heckelsmiller K et al (2011) ISCOMATRIX adjuvant combines immune activation with antigen delivery to dendritic cells in vivo leading to effective cross-priming of CD8+ T Cells. J Immunol 187:55–63. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1004114
Klein O, Schmidt C, Knights A, Davis ID, Chen W, Cebon J (2011) Melanoma vaccines: developments over the past 10 years. Expert Rev Vaccin 10:853–873. doi:10.1586/erv.11.74
Ouaaz F, Arron J, Zheng Y, Choi Y, Beg AA (2002) Dendritic cell development and survival require distinct NF-κB subunits. Immunity 16:257–270
Hayden MS, Ghosh S (2004) Signaling to NF-κB. Genes Dev 18:2195–2224. doi:10.1101/gad.1228704
Bonizzi G, Karin M (2004) The two NF-κB activation pathways and their role in innate and adaptive immunity. Trends Immunol 25:280–288. doi:10.1016/j.it.2004.03.008
Davis ID, Chen W, Jackson H et al (2004) Recombinant NY-ESO-1 protein with ISCOMATRIX adjuvant induces broad integrated antibody and CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cell responses in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:10697–10702. doi:10.1073/pnas.0403572101
Nicholaou T, Ebert L, Davis ID, Robson N, Klein O, Maraskovsky E, Chen W, Cebon J (2006) Directions in the immune targeting of cancer: lessons learned from the cancer-testis Ag NY-ESO-1. Immunol Cell Biol 84:303–317. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1711.2006.01446.x
Garrett WS, Chen LM, Kroschewski R, Ebersold M, Turley S, Trombetta S, Galan JE, Mellman I (2000) Developmental control of endocytosis in dendritic cells by Cdc42. Cell 102:325–334
Hickman-Miller HD, Yewdell JW (2006) Youth has its privileges: maturation inhibits DC cross-priming. Nat Immunol 7:125–126. doi:10.1038/ni0206-125
Schnurr M, Orban M, Robson NC, Shin A, Braley H, Airey D, Cebon J, Maraskovsky E, Endres S (2009) ISCOMATRIX adjuvant induces efficient cross-presentation of tumor antigen by dendritic cells via rapid cytosolic antigen delivery and processing via tripeptidyl peptidase II. J Immunol 182:1253–1259
van de Laar L, van den Bosch A, van der Kooij SW, Janssen HL, Coffer PJ, van Kooten C, Woltman AM (2010) A nonredundant role for canonical NF-κB in human myeloid dendritic cell development and function. J Immunol 185:7252–7261. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1000672
O’Sullivan BJ, Thomas R (2002) CD40 ligation conditions dendritic cell antigen-presenting function through sustained activation of NF-κB. J Immunol 168:5491–5498
Li M, Zhang X, Zheng X et al (2007) Immune modulation and tolerance induction by RelB-silenced dendritic cells through RNA interference. J Immunol 178:5480–5487
Carreno LJ, Riedel CA, Kalergis AM (2011) Induction of tolerogenic dendritic cells by NF-κB blockade and Fcgamma receptor modulation. Methods Mol Biol 677:339–353. doi:10.1007/978-1-60761-869-0_22
Hernandez A, Burger M, Blomberg BB et al (2007) Inhibition of NF-κB during human dendritic cell differentiation generates anergy and regulatory T-cell activity for one but not two human leukocyte antigen DR mismatches. Hum Immunol 68:715–729. doi:10.1016/j.humimm.2007.05.010
Gasparini C, Foxwell BM, Feldmann M (2009) RelB/p50 regulates CCL19 production, but fails to promote human DC maturation. Eur J Immunol 39:2215–2223. doi:10.1002/eji.200939209
Schnurr M, Chen Q, Shin A et al (2005) Tumor antigen processing and presentation depend critically on dendritic cell type and the mode of antigen delivery. Blood 105:2465–2472. doi:10.1182/blood-2004-08-3105
Acknowledgments
The contents of the published material are solely the responsibility of the Administering Institution, a Participating Institution or individual authors and do not reflect the views of NHMRC. LCL161 and LBW242 were provided by Dale Porter, Novartis Institutes for Biomedical Research, USA. NY-ESO-1/ISCOMATRIX was kindly provided by CSL Ltd. Melbourne. Buffy Coats were provided by the Red Cross Blood Service, Melbourne. We thank Rodica Stan for her helpful revision of the manuscript. Operational Infrastructure Support Program Funding of the Victorian Government and NHMRC Independent Research Institutes Infrastructure Support Scheme. JC is an NHMRC Practitioner Fellow. JF was supported by grant IGA NT12402-5 from the Ministry of Health, Czech Republic.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Knights, A.J., Fucikova, J., Pasam, A. et al. Inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP) antagonists demonstrate divergent immunomodulatory properties in human immune subsets with implications for combination therapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother 62, 321–335 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-012-1342-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-012-1342-1