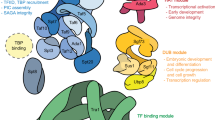
Abstract
The interactions and functions of protein inhibitors of activated STAT (PIAS) proteins are not restricted to the signal transducers and activators of transcription (STATs), but PIAS1, -2, -3 and -4 interact with and regulate a variety of distinct proteins, especially transcription factors. Although the majority of PIAS-interacting proteins are prone to modification by small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO) proteins and the PIAS proteins have the capacity to promote the modification as RING-type SUMO ligases, they do not function solely as SUMO E3 ligases. Instead, their effects are often independent of their Siz/PIAS (SP)-RING finger, but dependent on their capability to noncovalently interact with SUMOs or DNA through their SUMO-interacting motif and scaffold attachment factor-A/B, acinus and PIAS domain, respectively. Here, we present an overview of the cellular regulation by PIAS proteins and propose that many of their functions are due to their capability to mediate and facilitate SUMO-linked protein assemblies.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chung CD, Liao J, Liu B, Rao X, Jay P, Berta P, Shuai K (1997) Specific inhibition of Stat3 signal transduction by PIAS3. Science 278:1803–1805
Liu B, Liao J, Rao X, Kushner SA, Chung CD, Chang DD, Shuai K (1998) Inhibition of Stat1-mediated gene activation by PIAS1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:10626–10631
Schmidt D, Muller S (2003) PIAS/SUMO: new partners in transcriptional regulation. Cell Mol Life Sci 60:2561–2574
Hari KL, Cook KR, Karpen GH (2001) The Drosophila Su(var)2–10 locus regulates chromosome structure and function and encodes a member of the PIAS protein family. Genes Dev 15:1334–1348
Johnson ES, Gupta AA (2001) An E3-like factor that promotes SUMO conjugation to the yeast septins. Cell 106:735–744
Miura K, Rus A, Sharkhuu A, Yokoi S, Karthikeyan AS, Raghothama KG, Baek D, Koo YD, Jin JB, Bressan RA, Yun DJ, Hasegawa PM (2005) The Arabidopsis SUMO E3 ligase SIZ1 controls phosphate deficiency responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:7760–7765
Beliakoff J, Sun Z (2006) Zimp7 and Zimp10, two novel PIAS-like proteins, function as androgen receptor coregulators. Nucl Recept Signal 4:e017
Rodriguez-Magadan H, Merino E, Schnabel D, Ramirez L, Lomeli H (2008) Spatial and temporal expression of Zimp7 and Zimp10 PIAS-like proteins in the developing mouse embryo. Gene Expr Patterns 8:206–213
Potts PR, Yu H (2007) The SMC5/6 complex maintains telomere length in ALT cancer cells through SUMOylation of telomere-binding proteins. Nat Struct Mol Biol 14:581–590
Shuai K, Liu B (2005) Regulation of gene-activation pathways by PIAS proteins in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 5:593–605
Shuai K (2006) Regulation of cytokine signaling pathways by PIAS proteins. Cell Res 16:196–202
Geiss-Friedlander R, Melchior F (2007) Concepts in sumoylation: a decade on. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:947–956
Kerscher O, Felberbaum R, Hochstrasser M (2006) Modification of proteins by ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 22:159–180
Hay RT (2007) SUMO-specific proteases: a twist in the tail. Trends Cell Biol 17:370–376
Kim JH, Baek SH (2009) Emerging roles of desumoylating enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1792:155–162
Jones D, Crowe E, Stevens TA, Candido EP (2002) Functional and phylogenetic analysis of the ubiquitylation system in Caenorhabditis elegans: ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, ubiquitin-activating enzymes, and ubiquitin-like proteins. Genome Biol 3:RESEARCH0002
Broday L, Kolotuev I, Didier C, Bhoumik A, Gupta BP, Sternberg PW, Podbilewicz B, Ronai Z (2004) The small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) is required for gonadal and uterine-vulval morphogenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genes Dev 18:2380–2391
Johnson ES, Schwienhorst I, Dohmen RJ, Blobel G (1997) The ubiquitin-like protein Smt3p is activated for conjugation to other proteins by an Aos1p/Uba2p heterodimer. EMBO J 16:5509–5519
Nacerddine K, Lehembre F, Bhaumik M, Artus J, Cohen-Tannoudji M, Babinet C, Pandolfi PP, Dejean A (2005) The SUMO pathway is essential for nuclear integrity and chromosome segregation in mice. Dev Cell 9:769–779
Zhang FP, Mikkonen L, Toppari J, Palvimo JJ, Thesleff I, Janne OA (2008) Sumo-1 function is dispensable in normal mouse development. Mol Cell Biol 28:5381–5390
Yamaguchi T, Sharma P, Athanasiou M, Kumar A, Yamada S, Kuehn MR (2005) Mutation of SENP1/SuPr-2 reveals an essential role for desumoylation in mouse development. Mol Cell Biol 25:5171–5182
Huang TT, D’Andrea AD (2006) Regulation of DNA repair by ubiquitylation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7:323–334
Dennis AP, O’Malley BW (2005) Rush hour at the promoter: how the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway polices the traffic flow of nuclear receptor-dependent transcription. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 93:139–151
Weake VM, Workman JL (2008) Histone ubiquitination: triggering gene activity. Mol. Cell 29:653–663
Vertegaal AC (2007) Small ubiquitin-related modifiers in chains. Biochem Soc Trans 35:1422–1423
Vertegaal AC, Andersen JS, Ogg SC, Hay RT, Mann M, Lamond AI (2006) Distinct and overlapping sets of SUMO-1 and SUMO-2 target proteins revealed by quantitative proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 5:2298–2310
Perry JJ, Tainer JA, Boddy MN (2008) A SIM-ultaneous role for SUMO and ubiquitin. Trends Biochem Sci 33:201–208
Prudden J, Pebernard S, Raffa G, Slavin DA, Perry JJ, Tainer JA, McGowan CH, Boddy MN (2007) SUMO-targeted ubiquitin ligases in genome stability. EMBO J 26:4089–4101
Sun H, Leverson JD, Hunter T (2007) Conserved function of RNF4 family proteins in eukaryotes: targeting a ubiquitin ligase to SUMOylated proteins. EMBO J 26:4102–4112
Tatham MH, Geoffroy MC, Shen L, Plechanovova A, Hattersley N, Jaffray EG, Palvimo JJ, Hay RT (2008) RNF4 is a poly-SUMO-specific E3 ubiquitin ligase required for arsenic-induced PML degradation. Nat Cell Biol 10:538–546
Schimmel J, Larsen KM, Matic I, van Hagen M, Cox J, Mann M, Andersen JS, Vertegaal AC (2008) The ubiquitin–proteasome system is a key component of the SUMO-2/3 cycle. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 7:2107–2122
Hochstrasser M (2001) SP-RING for SUMO: new functions bloom for a ubiquitin-like protein. Cell 107:5–8
Minty A, Dumont X, Kaghad M, Caput D (2000) Covalent modification of p73alpha by SUMO-1. Two-hybrid screening with p73 identifies novel SUMO-1-interacting proteins and a SUMO-1 interaction motif. J Biol Chem 275:36316–36323
Duval D, Duval G, Kedinger C, Poch O, Boeuf H (2003) The ‘PINIT’ motif, of a newly identified conserved domain of the PIAS protein family, is essential for nuclear retention of PIAS3L. FEBS Lett 554:111–118
Tan JA, Hall SH, Hamil KG, Grossman G, Petrusz P, French FS (2002) Protein inhibitors of activated STAT resemble scaffold attachment factors and function as interacting nuclear receptor coregulators. J Biol Chem 277:16993–17001
Wong KA, Kim R, Christofk H, Gao J, Lawson G, Wu H (2004) Protein inhibitor of activated STAT Y (PIASy) and a splice variant lacking exon 6 enhance sumoylation but are not essential for embryogenesis and adult life. Mol Cell Biol 24:5577–5586
Sachdev S, Bruhn L, Sieber H, Pichler A, Melchior F, Grosschedl R (2001) PIASy, a nuclear matrix-associated SUMO E3 ligase, represses LEF1 activity by sequestration into nuclear bodies. Genes Dev 15:3088–3103
Moilanen AM, Karvonen U, Poukka H, Yan W, Toppari J, Janne OA, Palvimo JJ (1999) A testis-specific androgen receptor coregulator that belongs to a novel family of nuclear proteins. J Biol Chem 274:3700–3704
Wu L, Wu H, Ma L, Sangiorgi F, Wu N, Bell JR, Lyons GE, Maxson R (1997) Miz1, a novel zinc finger transcription factor that interacts with Msx2 and enhances its affinity for DNA. Mech Dev 65:3–17
Aravind L, Koonin EV (2000) SAP—a putative DNA-binding motif involved in chromosomal organization. Trends Biochem Sci 25:112–114
Kipp M, Gohring F, Ostendorp T, van Drunen CM, van Driel R, Przybylski M, Fackelmayer FO (2000) SAF-Box, a conserved protein domain that specifically recognizes scaffold attachment region DNA. Mol Cell Biol 20:7480–7489
Okubo S, Hara F, Tsuchida Y, Shimotakahara S, Suzuki S, Hatanaka H, Yokoyama S, Tanaka H, Yasuda H, Shindo H (2004) NMR structure of the N-terminal domain of SUMO ligase PIAS1 and its interaction with tumor suppressor p53 and A/T-rich DNA oligomers. J Biol Chem 279:31455–31461
Liu B, Gross M, ten Hoeve J, Shuai K (2001) A transcriptional corepressor of Stat1 with an essential LXXLL signature motif. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:3203–3207
Heery DM, Kalkhoven E, Hoare S, Parker MG (1997) A signature motif in transcriptional co-activators mediates binding to nuclear receptors. Nature 387:733–736
Song J, Durrin LK, Wilkinson TA, Krontiris TG, Chen Y (2004) Identification of a SUMO-binding motif that recognizes SUMO-modified proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:14373–14378
Song J, Zhang Z, Hu W, Chen Y (2005) Small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) recognition of a SUMO binding motif: a reversal of the bound orientation. J Biol Chem 280:40122–40129
Hannich JT, Lewis A, Kroetz MB, Li SJ, Heide H, Emili A, Hochstrasser M (2005) Defining the SUMO-modified proteome by multiple approaches in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 280:4102–4110
Hecker CM, Rabiller M, Haglund K, Bayer P, Dikic I (2006) Specification of SUMO1- and SUMO2-interacting motifs. J Biol Chem 281:16117–16127
Kerscher O (2007) SUMO junction-what’s your function? New insights through SUMO-interacting motifs. EMBO Rep 8:550–555
Hakli M, Karvonen U, Janne OA, Palvimo JJ (2005) SUMO-1 promotes association of SNURF (RNF4) with PML nuclear bodies. Exp Cell Res 304:224–233
Weissman AM (2001) Themes and variations on ubiquitylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:169–178
Potts PR, Yu H (2005) Human MMS21/NSE2 is a SUMO ligase required for DNA repair. Mol Cell Biol 25:7021–7032
Cheng CH, Lo YH, Liang SS, Ti SC, Lin FM, Yeh CH, Huang HY, Wang TF (2006) SUMO modifications control assembly of synaptonemal complex and polycomplex in meiosis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev 20:2067–2081
Kotaja N, Karvonen U, Janne OA, Palvimo JJ (2002) PIAS proteins modulate transcription factors by functioning as SUMO-1 ligases. Mol Cell Biol 22:5222–5234
Kahyo T, Nishida T, Yasuda H (2001) Involvement of PIAS1 in the sumoylation of tumor suppressor p53. Mol Cell 8:713–718
Takahashi Y, Toh-e A, Kikuchi Y (2001) A novel factor required for the SUMO1/Smt3 conjugation of yeast septins. Gene 275:223–231
Pichler A, Gast A, Seeler JS, Dejean A, Melchior F (2002) The nucleoporin RanBP2 has SUMO1 E3 ligase activity. Cell 108:109–120
Pichler A, Knipscheer P, Saitoh H, Sixma TK, Melchior F (2004) The RanBP2 SUMO E3 ligase is neither HECT- nor RING-type. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11:984–991
Kagey MH, Melhuish TA, Wotton D (2003) The polycomb protein Pc2 is a SUMO E3. Cell 113:127–137
Weger S, Hammer E, Heilbronn R (2005) Topors acts as a SUMO-1 E3 ligase for p53 in vitro and in vivo. FEBS Lett 579:5007–5012
Pungaliya P, Kulkarni D, Park HJ, Marshall H, Zheng H, Lackland H, Saleem A, Rubin EH (2007) TOPORS functions as a SUMO-1 E3 ligase for chromatin-modifying proteins. J Proteome Res 6:3918–3923
Zhao X, Sternsdorf T, Bolger TA, Evans RM, Yao TP (2005) Regulation of MEF2 by histone deacetylase 4- and SIRT1 deacetylase-mediated lysine modifications. Mol Cell Biol 25:8456–8464
Gregoire S, Yang XJ (2005) Association with class IIa histone deacetylases upregulates the sumoylation of MEF2 transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol 25:2273–2287
Ghisletti S, Huang W, Ogawa S, Pascual G, Lin ME, Willson TM, Rosenfeld MG, Glass CK (2007) Parallel SUMOylation-dependent pathways mediate gene- and signal-specific transrepression by LXRs and PPARgamma. Mol Cell 25:57–70
Stankovic-Valentin N, Deltour S, Seeler J, Pinte S, Vergoten G, Guerardel C, Dejean A, Leprince D (2007) An acetylation/deacetylation-SUMOylation switch through a phylogenetically conserved psiKXEP motif in the tumor suppressor HIC1 regulates transcriptional repression activity. Mol Cell Biol 27:2661–2675
Takahashi Y, Kahyo T, Toh-E A, Yasuda H, Kikuchi Y (2001) Yeast Ull1/Siz1 is a novel SUMO1/Smt3 ligase for septin components and functions as an adaptor between conjugating enzyme and substrates. J Biol Chem 276:48973–48977
Deng Z, Wan M, Sui G (2007) PIASy-mediated sumoylation of Yin Yang 1 depends on their interaction but not the RING finger. Mol Cell Biol 27:3780–3792
Reverter D, Lima CD (2005) Insights into E3 ligase activity revealed by a SUMO-RanGAP1-Ubc9-Nup358 complex. Nature 435:687–692
Tang Z, Hecker CM, Scheschonka A, Betz H (2008) Protein interactions in the sumoylation cascade: lessons from X-ray structures. FEBS J 275:3003–3015
Takahashi Y, Kikuchi Y (2005) Yeast PIAS-type Ull1/Siz1 is composed of SUMO ligase and regulatory domains. J Biol Chem 280:35822–35828
Reindle A, Belichenko I, Bylebyl GR, Chen XL, Gandhi N, Johnson ES (2006) Multiple domains in Siz SUMO ligases contribute to substrate selectivity. J Cell Sci 119:4749–4757
Knipscheer P, Flotho A, Klug H, Olsen JV, van Dijk WJ, Fish A, Johnson ES, Mann M, Sixma TK, Pichler A (2008) Ubc9 sumoylation regulates SUMO target discrimination. Mol Cell 31:371–382
Lin DY, Huang YS, Jeng JC, Kuo HY, Chang CC, Chao TT, Ho CC, Chen YC, Lin TP, Fang HI, Hung CC, Suen CS, Hwang MJ, Chang KS, Maul GG, Shih HM (2006) Role of SUMO-interacting motif in Daxx SUMO modification, subnuclear localization, and repression of sumoylated transcription factors. Mol. Cell 24:341–354
Karvonen U, Jaaskelainen T, Rytinki M, Kaikkonen S, Palvimo JJ (2008) ZNF451 is a novel PML body- and SUMO-associated transcriptional coregulator. J Mol Biol 382:585–600
Ivanov AV, Peng H, Yurchenko V, Yap KL, Negorev DG, Schultz DC, Psulkowski E, Fredericks WJ, White DE, Maul GG, Sadofsky MJ, Zhou MM, Rauscher FJ III (2007) PHD domain-mediated E3 ligase activity directs intramolecular sumoylation of an adjacent bromodomain required for gene silencing. Mol Cell 28:823–837
Zeng L, Yap KL, Ivanov AV, Wang X, Mujtaba S, Plotnikova O, Rauscher FJ 3rd, Zhou MM (2008) Structural insights into human KAP1 PHD finger-bromodomain and its role in gene silencing. Nat Struct Mol Biol 15:626–633
Hietakangas V, Anckar J, Blomster HA, Fujimoto M, Palvimo JJ, Nakai A, Sistonen L (2006) PDSM, a motif for phosphorylation-dependent SUMO modification. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:45–50
Yang SH, Galanis A, Witty J, Sharrocks AD (2006) An extended consensus motif enhances the specificity of substrate modification by SUMO. EMBO J 25:5083–5093
Anckar J, Sistonen L (2007) SUMO: getting it on. Biochem Soc Trans 35:1409–1413
Wang J, Zhang H, Iyer D, Feng XH, Schwartz RJ (2008) Regulation of cardiac specific nkx2.5 gene activity by small ubiquitin-like modifier. J Biol Chem 283:23235–23243
Wible BA, Yang Q, Kuryshev YA, Accili EA, Brown AM (1998) Cloning and expression of a novel K+ channel regulatory protein. KChAP J Biol Chem 273:11745–11751
Martin S, Nishimune A, Mellor JR, Henley JM (2007) SUMOylation regulates kainate-receptor-mediated synaptic transmission. Nature 447:321–325
Bischof O, Schwamborn K, Martin N, Werner A, Sustmann C, Grosschedl R, Dejean A (2006) The E3 SUMO ligase PIASy is a regulator of cellular senescence and apoptosis. Mol Cell 22:783–794
Onishi A, Peng GH, Hsu C, Alexis U, Chen S, Blackshaw S (2009) Pias3-dependent SUMOylation directs rod photoreceptor development. Neuron 61:234–246
Munarriz E, Barcaroli D, Stephanou A, Townsend PA, Maisse C, Terrinoni A, Neale MH, Martin SJ, Latchman DS, Knight RA, Melino G, De Laurenzi V (2004) PIAS-1 is a checkpoint regulator which affects exit from G1 and G2 by sumoylation of p73. Mol Cell Biol 24:10593–10610
Martin N, Schwamborn K, Urlaub H, Gan B, Guan JL, Dejean A (2008) Spatial interplay between PIASy and FIP200 in the regulation of signal transduction and transcriptional activity. Mol Cell Biol 28:2771–2781
Poukka H, Karvonen U, Janne OA, Palvimo JJ (2000) Covalent modification of the androgen receptor by small ubiquitin-like modifier 1 (SUMO-1). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:14145–14150
Tian S, Poukka H, Palvimo JJ, Janne OA (2002) Small ubiquitin-related modifier-1 (SUMO-1) modification of the glucocorticoid receptor. Biochem J 367:907–911
Sentis S, Le Romancer M, Bianchin C, Rostan MC, Corbo L (2005) Sumoylation of the estrogen receptor alpha hinge region regulates its transcriptional activity. Mol Endocrinol 19:2671–2684
Ohshima T, Koga H, Shimotohno K (2004) Transcriptional activity of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma is modulated by SUMO-1 modification. J Biol Chem 279:29551–29557
Tallec LP, Kirsh O, Lecomte MC, Viengchareun S, Zennaro MC, Dejean A, Lombes M (2003) Protein inhibitor of activated signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 interacts with the N-terminal domain of mineralocorticoid receptor and represses its transcriptional activity: implication of small ubiquitin-related modifier 1 modification. Mol Endocrinol 17:2529–2542
Kotaja N, Aittomaki S, Silvennoinen O, Palvimo JJ, Janne OA (2000) ARIP3 (androgen receptor-interacting protein 3) and other PIAS (protein inhibitor of activated STAT) proteins differ in their ability to modulate steroid receptor-dependent transcriptional activation. Mol Endocrinol 14:1986–2000
Kotaja N, Vihinen M, Palvimo JJ, Janne OA (2002) Androgen receptor-interacting protein 3 and other PIAS proteins cooperate with glucocorticoid receptor-interacting protein 1 in steroid receptor-dependent signaling. J Biol Chem 277:17781–17788
Yang SH, Sharrocks AD (2005) PIASx acts as an Elk-1 coactivator by facilitating derepression. EMBO J 24:2161–2171
Liu B, Yang R, Wong KA, Getman C, Stein N, Teitell MA, Cheng G, Wu H, Shuai K (2005) Negative regulation of NF-kappaB signaling by PIAS1. Mol Cell Biol 25:1113–1123
Liu B, Yang Y, Chernishof V, Loo RR, Jang H, Tahk S, Yang R, Mink S, Shultz D, Bellone CJ, Loo JA, Shuai K (2007) Proinflammatory stimuli induce IKKalpha-mediated phosphorylation of PIAS1 to restrict inflammation and immunity. Cell 129:903–914
Long J, Wang G, Matsuura I, He D, Liu F (2004) Activation of Smad transcriptional activity by protein inhibitor of activated STAT3 (PIAS3). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:99–104
Pascual G, Fong AL, Ogawa S, Gamliel A, Li AC, Perissi V, Rose DW, Willson TM, Rosenfeld MG, Glass CK (2005) A SUMOylation-dependent pathway mediates transrepression of inflammatory response genes by PPAR-gamma. Nature 437:759–763
Kim J, Sharma S, Li Y, Cobos E, Palvimo JJ, Williams SC (2005) Repression and coactivation of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein epsilon by sumoylation and protein inhibitor of activated STATx proteins. J Biol Chem 280:12246–12254
Chun TH, Itoh H, Subramanian L, Iniguez-Lluhi JA, Nakao K (2003) Modification of GATA-2 transcriptional activity in endothelial cells by the SUMO E3 ligase PIASy. Circ Res 92:1201–1208
Lee H, Quinn JC, Prasanth KV, Swiss VA, Economides KD, Camacho MM, Spector DL, Abate-Shen C (2006) PIAS1 confers DNA-binding specificity on the Msx1 homeoprotein. Genes Dev 20:784–794
van den Akker E, Ano S, Shih HM, Wang LC, Pironin M, Palvimo JJ, Kotaja N, Kirsh O, Dejean A, Ghysdael J (2005) FLI-1 functionally interacts with PIASxalpha, a member of the PIAS E3 SUMO ligase family. J Biol Chem 280:38035–38046
Zhou S, Si J, Liu T, DeWille JW (2008) PIASy represses CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein delta (C/EBPdelta) transcriptional activity by sequestering C/EBPdelta to the nuclear periphery. J Biol Chem 283:20137–20148
Tolkunova E, Malashicheva A, Parfenov VN, Sustmann C, Grosschedl R, Tomilin A (2007) PIAS proteins as repressors of Oct4 function. J Mol Biol 374:1200–1212
Yang SH, Sharrocks AD (2006) PIASxalpha differentially regulates the amplitudes of transcriptional responses following activation of the ERK and p38 MAPK pathways. Mol Cell 22:477–487
Ono K, Han J (2000) The p38 signal transduction pathway: activation and function. Cell Signal 12:1–13
Stehmeier P, Muller S (2009) Phospho-regulated SUMO interaction modules connect the SUMO system to CK2 signaling. Mol Cell 33:400–409
Weber S, Maass F, Schuemann M, Krause E, Suske G, Bauer UM (2009) PRMT1-mediated arginine methylation of PIAS1 regulates STAT1 signaling. Genes Dev 23:118–132
Depaux A, Regnier-Ricard F, Germani A, Varin-Blank N (2007) A crosstalk between hSiah2 and Pias E3-ligases modulates Pias-dependent activation. Oncogene 26:6665–6676
Albor A, El-Hizawi S, Horn EJ, Laederich M, Frosk P, Wrogemann K, Kulesz-Martin M (2006) The interaction of Piasy with Trim32, an E3-ubiquitin ligase mutated in limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2H, promotes Piasy degradation and regulates UVB-induced keratinocyte apoptosis through NFkappaB. J Biol Chem 281:25850–25866
Chen XL, Reindle A, Johnson ES (2005) Misregulation of 2 microm circle copy number in a SUMO pathway mutant. Mol Cell Biol 25:4311–4320
Chen XL, Silver HR, Xiong L, Belichenko I, Adegite C, Johnson ES (2007) Topoisomerase I-dependent viability loss in Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants defective in both SUMO conjugation and DNA repair. Genetics 177:17–30
Watts FZ, Skilton A, Ho JC, Boyd LK, Trickey MA, Gardner L, Ogi FX, Outwin EA (2007) The role of Schizosaccharomyces pombe SUMO ligases in genome stability. Biochem Soc Trans 35:1379–1384
Xhemalce B, Seeler JS, Thon G, Dejean A, Arcangioli B (2004) Role of the fission yeast SUMO E3 ligase Pli1p in centromere and telomere maintenance. EMBO J 23:3844–3853
Andrews EA, Palecek J, Sergeant J, Taylor E, Lehmann AR, Watts FZ (2005) Nse2, a component of the Smc5–6 complex, is a SUMO ligase required for the response to DNA damage. Mol Cell Biol 25:185–196
Zhao X, Blobel G (2005) A SUMO ligase is part of a nuclear multiprotein complex that affects DNA repair and chromosomal organization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:4777–4782
Mohr SE, Boswell RE (1999) Zimp encodes a homologue of mouse Miz1 and PIAS3 and is an essential gene in Drosophila melanogaster. Gene 229:109–116
Betz A, Lampen N, Martinek S, Young MW, Darnell JE Jr (2001) A Drosophila PIAS homologue negatively regulates stat92E. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:9563–9568
Roy Chowdhuri S, Crum T, Woollard A, Aslam S, Okkema PG (2006) The T-box factor TBX-2 and the SUMO conjugating enzyme UBC-9 are required for ABa-derived pharyngeal muscle in C. elegans. Dev Biol 295:664–677
Holway AH, Kim SH, La Volpe A, Michael WM (2006) Checkpoint silencing during the DNA damage response in Caenorhabditis elegans embryos. J Cell Biol 172:999–1008
Kim SH, Michael WM (2008) Regulated proteolysis of DNA polymerase eta during the DNA-damage response in C. elegans. Mol Cell 32:757–766
Catala R, Ouyang J, Abreu IA, Hu Y, Seo H, Zhang X, Chua NH (2007) The Arabidopsis E3 SUMO ligase SIZ1 regulates plant growth and drought responses. Plant Cell 19:2952–2966
Miura K, Jin JB, Hasegawa PM (2007) Sumoylation, a post-translational regulatory process in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:495–502
Roth W, Sustmann C, Kieslinger M, Gilmozzi A, Irmer D, Kremmer E, Turck C, Grosschedl R (2004) PIASy-deficient mice display modest defects in IFN and Wnt signaling. J Immunol 173:6189–6199
Bischof O, Dejean A (2007) SUMO is growing senescent. Cell Cycle 6:677–681
Liu B, Mink S, Wong KA, Stein N, Getman C, Dempsey PW, Wu H, Shuai K (2004) PIAS1 selectively inhibits interferon-inducible genes and is important in innate immunity. Nat Immunol 5:891–898
Yan W, Santti H, Janne OA, Palvimo JJ, Toppari J (2003) Expression of the E3 SUMO-1 ligases PIASx and PIAS1 during spermatogenesis in the rat. Gene Expr Patterns 3:301–308
Santti H, Mikkonen L, Anand A, Hirvonen-Santti S, Toppari J, Panhuysen M, Vauti F, Perera M, Corte G, Wurst W, Janne OA, Palvimo JJ (2005) Disruption of the murine PIASx gene results in reduced testis weight. J Mol Endocrinol 34:645–654
Tahk S, Liu B, Chernishof V, Wong KA, Wu H, Shuai K (2007) Control of specificity and magnitude of NF-kappa B and STAT1-mediated gene activation through PIASy and PIAS1 cooperation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:11643–11648
Thompson SJ, Loftus LT, Ashley MD, Meller R (2008) Ubiquitin–proteasome system as a modulator of cell fate. Curr Opin Pharmacol 8:90–95
Dorval V, Fraser PE (2007) SUMO on the road to neurodegeneration. Biochim Biophys Acta 1773:694–706
Hernandez-Toro J, Prieto C, De las Rivas J (2007) APID2NET: unified interactome graphic analyzer. Bioinformatics 23:2495–2497
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13:2498–2504
Bader GD, Betel D, Hogue CW (2003) BIND: the Biomolecular interaction network database. Nucleic Acids Res 31:248–250
Stark C, Breitkreutz BJ, Reguly T, Boucher L, Breitkreutz A, Tyers M (2006) BioGRID: a general repository for interaction datasets. Nucleic Acids Res 34:D535–D539
Salwinski L, Miller CS, Smith AJ, Pettit FK, Bowie JU, Eisenberg D (2004) The database of interacting proteins: 2004 update. Nucleic Acids Res 32:D449–D451
Keshava Prasad TS, Goel R, Kandasamy K, Keerthikumar S, Kumar S, Mathivanan S, Telikicherla D, Raju R, Shafreen B, Venugopal A, Balakrishnan L, Marimuthu A, Banerjee S, Somanathan DS, Sebastian A, Rani S, Ray S, Harrys Kishore CJ, Kanth S, Ahmed M et al (2009) Human protein reference database–2009 update. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D767–D772
Kerrien S, Alam-Faruque Y, Aranda B, Bancarz I, Bridge A, Derow C, Dimmer E, Feuermann M, Friedrichsen A, Huntley R, Kohler C, Khadake J, Leroy C, Liban A, Lieftink C, Montecchi-Palazzi L, Orchard S, Risse J, Robbe K, Roechert B et al (2007) IntAct—open source resource for molecular interaction data. Nucleic Acids Res 35:D561–D565
Chatr-aryamontri A, Ceol A, Palazzi LM, Nardelli G, Schneider MV, Castagnoli L, Cesareni G (2007) MINT: the Molecular INTeraction database. Nucleic Acids Res 35:D572–D574
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Academy of Finland, the Finnish Cancer Foundation, Kuopio Graduate School of Molecular Medicine and Sigrid Jusélius Foundation for support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rytinki, M.M., Kaikkonen, S., Pehkonen, P. et al. PIAS proteins: pleiotropic interactors associated with SUMO. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 66, 3029–3041 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-0061-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-0061-z