Abstract:
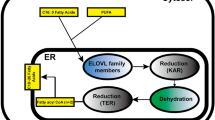
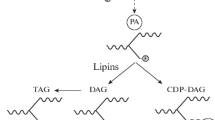
Fatty acid-binding proteins (FABPs) are members of a superfamily of lipid-binding proteins, and occur intracellularly in vertebrates and invertebrates. This review presents recent findings on the diversity of these FABPs and their proposed roles in fatty acid (FA) metabolism and other cellular processes. Special attention is paid to the structural features of the different mammalian FABP types and the physiological role of these proteins in FA transport, cell growth and differentiation, cellular signalling, gene transcription and cytoprotection. Additionally, data on FABP knockout mice and the implication of FABP in medicine are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 13 November 2001; received after revision 2 January 2002; accepted 25 January 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zimmerman, A., Veerkamp, J. New insights into the structure and function of fatty acid-binding proteins. CMLS, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 59, 1096–1116 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-002-8490-y
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-002-8490-y