Abstract
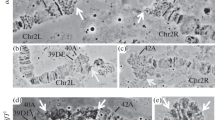
Primary spermatocyte nuclei ofDrosophila melanogaster exhibit three giant lampbrush-like loops formed by thekl-5, kl-3 andks-1 Y chromosome fertility factors. Detailed mapping of satellite DNA sequences along theY chromosome has recently shown that AAGAC satellite repeats are a significant component of thekl-5 andks-1 loop-forming regions. To determine whether these simple repeated sequences are transcribed on the loop structures we performed a series of DNARNA in situ hybridization experiments to fixed loop preparations using as a probe cloned AAGAC repeats. These experiments showed that the probe hybridizes with homologous transcripts specifically associated with thekl-5 andks-1 loops. These transcripts are detected at all stages of development of these two loops, do not appear to migrate to the cytoplasm and are degraded when loops disintegrate during the first meiotic prophase. Moreover, an examination of the testes revealed that the transcription of the AAGAC sequences is restricted to the loops of primary spermatocytes; the other cell types ofD. melanogaster spermatogenesis do not exhibit nuclear or cytoplasmic labeling. These experiments were confirmed by RNA blotting analysis which showed that transcription of the AAGAC sequences occurs in wild-type testes but not inX/O testes. The patterns of hybridization to the RNA blots indicated that the transcripts are highly heterogeneous in size, from large (migration at limiting mobility) to less than 1 kb. We discuss the possible function of the AAGAC satellite transcripts, in the light of the available information on theY chromosome loops ofD. melanogaster.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashburner M (1989)Drosophila: A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York
Bonaccorsi S, Pisano C, Puoti F, Gatti M (1988) Y chromosome loops inDrosophila melanogaster. Genetics 120:1015–1034
Brahic M, Hasse AT (1978) Detection of viral sequences of low reiteration frequency by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:6125–6129
Bromley S, Gall JG (1987) Transcription of the histone loci on lampbrush chromosomes of the newtNotophthalmus viridescens. Chromosoma 95:396–402
Brosseau GE (1960) Genetic analysis of the male fertility factors on the Y chromosome ofDrosophila melanogaster. Genetics 45:257–274
Brutlag DL (1980) Molecular arrangement and evolution of heterochromatic DNA. Annu Rev Genet 14:121–144
Diaz MO, Gall JG (1985) Giant readthrough transcription units at the histone loci on lampbrush chromosomes of the newtNotophthalmus. Chromosoma 92:243–253
Diaz MO, Barsacchi-Pilone G, Mahon KA, Gall JG (1981) Transcripts from both strands of a satellite DNA occur on lampbrush chromosome loops of the newtNotophthalmus. Cell 24:649–659
Gatti M, Pimpinelli S (1983) Cytological and genetical analysis of the Y chromosome ofDrosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma 88:349–373
Glätzer KH (1984) Preservation of nuclear RNP antigens in male germ cell development ofDrosophila hydei. Mol Gen Genet 196:236–243
Hardy RW, Tokuyasu KT, Lindsley DL (1981) Analysis of spermatogenesis inDrosophila melanogaster bearing deletions for Ychromosome fertility genes. Chromosoma 88:593–617
Hardy RW, Lindsley DL, Livak KJ, Lewis B, Siversten AL, Joslyn GL, Edwards J, Bonaccorsi S (1984) Cytogenetic analysis of a segment of the Y chromosome ofDrosophila melanogaster. Genetics 107:591–610
Hareven D, Zuckerman M, Lifschytz E (1986) Origin and evolution of the transcribed repeated sequences of the Y chromosome lampbrush loops ofDrosophila hydei. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:125–129
Hazelrigg T, Fornili P, Kaufman TC (1982) A cytogenetic analysis of X-ray induced male steriles on the Y chromosome ofDrosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma 87:535–559
Hennig W (1985) Y chromosome function and spermatogenesis inDrosophila hydei. Adv Genet 23:179–234
Huijser P, Hennig W (1987) Ribosomal DNA-related sequences in a Y chromosomal lampbrush loop ofDrosophila hydei. Mol Gen Genet 206:441–451
Hulsebos TJM, Hackstein JHP, Hennig W (1984) Lampbrush loopspecific protein ofDrosophila hydei. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:3404–3408
Kennison JA (1981) The genetical and cytological organization of the Y chromosome ofDrosophila melanogaster. Genetics 98:529–548
Lifschytz E (1979) A procedure for the cloning and identification of Y specific middle repetitive sequences inDrosophila hydei. J Mol Biol 133:267–277
Lifschytz E (1987) The developmental program of spermiogenesis inDrosophila: a genetic analysis. Int Rev Cytol 109:211–257
Lifschytz E, Hareven D, Azriel A, Brodsley H (1983) DNA clones and RNA transcripts of four lampbrush loops from the Y chromosome ofDrosophila hydei. Cell 32:191–199
Lindsley DL, Tokuyasu KT (1980) Spermatogenesis. In: Ashburner M, Wright TRF (eds) The genetics and biology ofDrosophila, vol 2d. Academic Press, New York, pp 225–294
Lohe AR, Brutlag DL (1986) Multiplicity of satellite sequences inDrosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:696–700
Lohe AR, Roberts P (1988) Evolution of satellite DNA sequences inDrosophila. In: Verma R (ed) Molecular and structural aspects of heterochromatin. Cambridge University Press, pp 148–186
Macgregor HC, Sessions SK (1986) The biological significance of variation in satellite DNA and heterochromatin in newts of the genus Triturus: an evolutionary perspective. Philos Trans R Soc Lond [Biol] 312:243–259
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York
Peacock WJ, Lohe AR, Gerlach WL, Dunsmuir P, Dennis ES, Appels R (1977) Fine structure and evolution of DNA in heterochromatin. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 42:1121–1135
Pukkila PJ (1975) Identification of the lampbrush chromosome loops which transcribe 5S ribosomal RNA inNotophthalmus (Triturus) viridescens. Chromosoma 53:71–89
Thomas PS (1980) Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:5201–5205
Trapitz P, Wlaschek M, Bunemann H (1988) Structure and function of Y chromosomal DNA. II. Analysis of lampbrush loop associated transcripts in nuclei of primary spermatocytes ofDrosophila hydei by in situ hybridization using asymmetric RNA probes of four different families of repetitive DNA. Chromosoma 96:159–170
Tullis RH, Rubin H (1980) Calcium protects DNase I from proteinase K: a new method for the removal of contaminating RNase from DNase I. Anal Biochem 107:260–264
Varley MH, Macgregor HC, Erba HP (1980a) Satellite DNA is transcribed on lampbrush chromosomes. Nature 283:686–688
Varley MH, Macgregor HC, Nardi I, Andrews C, Erba HP (1980b) Cytological evidence of transcription of highly repeated DNA sequences during the lampbrush stage inTriturus cristatus carnifex. Chromosoma 80:289–307
Vogt P, Hennig W (1986a) Molecular structure of the lampbrush loop nooses of the Y chromosome ofDrosophila hydei. I. The Y chromosome-specific repetitive DNA sequence family ay1 is dispersed in the loop DNA. Chromosoma 94:449–458
Vogt P, Hennig W (1986b) Molecular structure of the lampbrush loop nooses of the Y chromosome ofDrosophila hydei. II. Non-Y-specific DNA sequences are a major constituent of the loop. Chromosoma 94:459:467
Vogt P, Hennig W, Siegmund I (1982) Identification of cloned Y chromosomal DNA sequences from a lampbrush loop ofDrosophila hydei. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:5132–5136
Vogt P, Hennig W, ten Hacken D, Verbost P (1986) Evolution of Y chromosomal lampbrush loop DNA sequences ofDrosophila. Chromosoma 94:367–376
Wu Z, Murphy C, Gall JG (1986) A transcribed satellite DNA from the bullfrogRana catesbeiana. Chromosoma 93:291–297
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonaccorsi, S., Gatti, M., Pisano, C. et al. Transcription of a satellite DNA on twoY chromosome loops ofDrosophila melanogaster . Chromosoma 99, 260–266 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01731701
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01731701