Summary
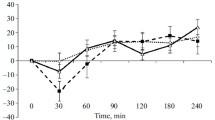
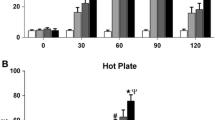
The effects of intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) administration of d-Phe-Cys-Tyr-d-Try-Orn-Thr-Pen-Thr-NH2 (CTOP), a selective mu-opioid receptor antagonist, (Allyl)2-Tyr-Aib-Aib-Phe-Leu-OH (ICI 174864) and (N,N-Bisallyl-Tyr-Gly-Gly-ψ-(CH2S)-Phe-Leu-OH (ICI 154129), selective delta-opioid receptor antagonists on blocking analgesia induced by β-endorphin, morphine, d-Ala2-NMePhe4-Gly-ol-enkephalin (DAMGO), d-Ala2-d-Leu5-enkephalin (DADLE) and d-Pen2-enkephalin (DPDPE) administered i.c.v. were studied in male ICR mice. The analgesia was assessed by the tail-flick and paw-licking (hot-plate) tests. The potencies of opioid agonists injected i.c.v. for producing analgesia were DAMGO > DADLE > β-endorphin > morphine > DPDPE. Intracerebroventricular administration of CTOP (0.05 μg) selectively antagonized inhibition of the tail-flick and paw-licking response induced by morphine, DAMGO or DADLE but not β-endorphin or DPDPE. ICI 174864 (5 μg) and ICI 154129 (5 μg) injected i.c.v. selectively antagonized analgesia induced by DPDPE or DADLE but not β-endorphin, morphine or DAMGO injected i.c.v. These results indicate that analgesia induced by morphine and DAMGO is mediated by the stimulation of mu-opioid receptors while analgesia induced by DPDPE is mediated by the stimulation of delta-opioid receptors. DADLE-induced analgesia is mediated by the stimulation of both mu- and delta-opioid receptors. Analgesia induced by β-endorphin is mediated by neither munor delta-opioid receptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- i.c.v.:
-
intracerebroventricular
- i.t.:
-
intrathecal
- CTOP:
-
d-Phe-Cys-Tyr-d-Try-Orn-Thr-Pen-Thr-NHZ
- DAMGO:
-
d-Ala2-NMePhe2-Gly-ol-enkephalin
- DADLE:
-
d-Ala2-d-Leus-enke-phalin
- DPDPE:
-
dd-Pen2-dd-Pen5-enkephalin
- ICI 174864:
-
(Allyl)2Tyr-Aib-Aib-Phe-Leu-OH
- ICI 154129:
-
(N,N-Bisallyl-Tyr-Gly-Glyψ-(CH2S)-Phe-Leu-OH
References
Barret RW, Vaught JL (1983) Evaluation of the interactions of mu and delta selective ligands with [3H]d-Ala2-d-Leu5-enkephalin binding to mouse brain membranes. Life Sci 33:2439–2448
Corbett AD, Gillan MGC, Kosterlitz HW, McKnight AT, Paterson SJ (1983) Tyr-d-Pen-Gly-Phe-L-Pen and Tyr-d-Pen-Gly-Phe-d-Pen are selective ligands for the delta-binding site. Br J Pharmacol 80:669–678
Corbett AD, Gillan MGC, Kosterlitz HW, McKnight AT, Paterson SJ, Robson LE (1984) Selectivities of opioid peptide analogues as agonists and antagonists at the delta-receptor. Br J Pharmacol 83:271–279
Cowan A, Gmerek, DE (1982) In vivo studies with ICI 154129, a putative delta receptor antagonist. Life Sci 31:2213–2216
D'Amour FE, Smith DL (1984) A method for determining loss of pain sensation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 72:74–79
Eddy NB, Leimbach D (1953) Synthesit analgesics. II. Dithienylbutenyl and dithienylbutylamides. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 107:385–393
Gormley JJ, Morley JS, Priestly T, Shaw JS, Turnbul MJ, Wheeler H (1982) In vivo evaluation of the opiate receptor antagonist ICI 154,129. Life Sci 31:1263–1266
Gulya K, Pelton IT, Hruby VJ, Yamamura HI (1986) Cyclic somatostatin octapeptide analogues with high affinity and selectivity toward mu opioid receptors. Life Sci 38:2221–2229
Gulya K, Krivan M, Nyolczas N, Sarnyai Z, Kovacs G (1988) Central effects of the potent and highly selective μ opioid antagonist d-Phe-Cys-Tyr-d-Trp-Orn-Thr-Pen-Thr-NH2 (CTOP) in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 150:355–360
Haley TJ, McCormick WG (1957) Pharmacological effects produced by intracerebral injections of drugs in the conscious mouse. Br J Pharmacol 12:12–15
Hawkins KN, Knapp RJ, Lui GK, Guyla K, Kazmierski W, Wan Y-P, Pelton JT, Hruby VJ, Yamamura HI (1989) [3H]-[H-d-Phe-Cys-Tyr-d-Trp-Orn-Thr-Pen-Thr-NH2] ([3H]CTOP), a potent and highly selective peptide for mu opioid receptors in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 248:73–80
Heyman IS, Mulvaney SA, Mosberg HI, Porreca F (1987) Opioid delta-receptor involvement in supraspinal and spinal antinociception in mice. Brain Res 420:100–108
Kosterlitz HW, Lord JAH, Paterson SJ, Waterfield AA (1980) Effects of changes in the structure of enkephalin and of narcotic analgesic drugs on their interactions with mu- and delta-receptors. Br J Pharmacol 68:333–342
Litchfield JT, Wilcoxon F (1949) A simplified method of evaluating dose effect experiments. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 96:99–113
Lord JAH, Waterfield AA, Hughes J, Kosterlitz AW (1977) Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature 267:495–499
Martin WR, Eades CG, Thompson JA, Huppler RE, Gilbert PE (1976) The effects of morphine- and nalorphine-like drugs in the non-dependent and morphine-dependent chronic spinal dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 198:66–82
Mosberg HI, Hurst R, Hruby VJ, Gee K, Yamamura HI, Galligan JJ, Burks TF (1983) Bis-Penicillamine enkephalins possess highly improved specificity toward delta opioid receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:5871–5874
Pfeiffer A, Herz A (1982) Discrimination of three opiate receptor binding sites with the use of a computerized curve-fitting technique. Mol Pharamcol 21:266–271
Porreca F, Mosberg HI, Hurst R, Hruby VJ, Burks TF (1984) Roles of mu, delta and kappa receptors in spinal and supraspinal mediation of gastrointestinal transit effects and hot-plate analgesia in the mouse. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 230:341–348
Porreca F, Heyman JS, Mosberg HI, Omnaas JR, Vaught JL (1987) Role of mu and delta receptors in the supraspinal and spinal analgesic effects of [d-Pen2,d-Pen5]enkephalin in the mouse. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 241:393–400
Priestly T, Turnbull MJ, Wei E (1985) In vivo evidence for the selectivity of ICI 154129 for the delta-opioid receptor. Neuropbarmacology 24:107–110
Schulz R, Wuster M, Herz A (1981) Pharmacological characterization of the epsilon-opioid receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 216:604–606
Shaw JS, Miller L, Turnbull MJ, Gormley JJ, Morley JS (1982) Selective antagonists at the opiate delta-receptor. Life Sci 31:1259–1262
Shook JE, Kazmierski W, Wire WS, Lemcke PK, Hruby VJ, Burks TF (1988) Opioid receptor selectivity of β-endorphin in vitro and in vivo: mu, delta and epsilon receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 246:1018–1025
Suh HH, Tseng LF (1988) Intrathecal β-funaltrexamine antagonizes intracerebroventricular β-endorphin- but not morphine-induced analgesia in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 245:587–593
Suh HH, Tseng LF (1989) β-EP, morphine and DPDPE stimulate different opioid receptors for analgesia. Pharmacologist 31:126
Suh HH, Tseng LF, Li CH (1988) β-Endorphin-(1–27) antagonizes β-endorphin- but not morphine-, d-Pen2-d-Pen5-enkephalin-and U50,488H-induced analgesia in mice. Neuropharmacology 27:957–963
Suh HH, Fujimoto JM, Tseng LF (1989) Differential mechanisms mediating β-endorphin- and morphine-induced analgesia in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 168:61–70
Takemori AE, Larsen DL, Portoghese PS (1981) The irreversible narcotic antagonistic and reversible agonistic properties of the fumaramate methyl ester derivative of naltrexone. Eur J Pharmacol 70:445–451
Tallarida RI, Murray RB (1981) Manual of pharmacologic calculations with computer programs. Springer, New York Berlin Heidelberg
Tseng LF (1982) Tolerance and cross tolerance to morphine after chronic spinal d-Ala2-d-Leu5-enkephalin infusion. Life Sci 31:987–992
Tseng LF (1983) Partial cross tolerance to d-Ala2-d-Leu5-enkephalin after chronic spinal morphine infusion. Life Sci 32:2545–2550
Ward SJ, Portoghese PS, Takemori AE (1982a) Pharmacological profiles of β-funaltrexamine (β-FNA) and β-chlornaltrexamine (β-CNA) on the mouse vas deferens preparation. Eur J Pharmacol 80:377–384
Ward SJ, Portoghese PS, Takemori AE (1982b) Pharmacological characterization in vivo of the novel opiate β-funaltrexamine (β-FNA). J Pharmacol Exp Ther 220:494–498
Wuster M, Schulz R, Herz A (1980) The direction of opioid agonists toward mu- delta- and epsilon-receptors in the vas deferens of the mouse and the rat. Life Sci 27:163–170
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suh, H.H., Tseng, L.F. Different types of opioid receptors mediating analgesia induced by morphine, DAMGO, DPDPE, DADLE and β-endorphin in mice. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 342, 67–71 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00178974
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00178974