Abstract
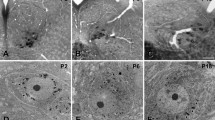
Byin situ hybridization histochemistry, expression of mRNAs for the two species of serine/threonine protein kinase Akt, Akt1 and Akt2, were examined in the mouse brain during normal development and in the hypoglossal nucleus following axotomy. On the embryonic days, the gene expression for Akt1 and Akt2 was detected at high levels throughout the entire neuroaxis, then decreased gradually to adult levels during postnatal development. In the adult brain, the gene expression for Akt1 and Akt2 was weak in almost all neurons with no difference of expression levels. The expression level of Akt1 mRNA in the affected hypoglossal nucleus increased dramatically after 48 h to 7 d following axotomy of the hypoglossal nerve, whereas no change was seen in the level of Akt2 mRNA. The present findings suggest that Akt may contribute some important roles not only in neurogenesis, but also in regeneration of injured neuron.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altomare D. A., Guo K., Cheng T. O., Makris A., Yang S. I., Kaplan D. R., Morrison D. K., Golemis E. A., and Tsichlis P. N. (1995). Cloning, chromosomal localization and expression analysis of the mouse AKT2 oncogene.Oncogene 11, 1055–1060.
Bellacosa A., Testa J. R., Staal S. P., and Tsichlis P. N. (1991) A retroviral oncogene, akt, encoding a serine-threonine kinase containing an SH2-like region.Science 254, 274–277.
Bellacosa, A., Franke, T. F., Gonzalez-Portal M. E., Datta K., Taguchi T., Gardner J., Chen J. Q., Testa J. R., and Tsichlis P. N. (1993) Structure, expression and chromosomal mapping of c-akt: relationship to v-akt and its implication.Oncogene 8, 745–754.
Burgering B. M. and Coffer P. J. (1995) Protein kinase B(c-Akt) in phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase signal transduction.Nature 376, 599–602.
Carter A. N. and Downes C. P. (1992) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase is activated by nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor in PC12 cells.J. Biol. Chem. 267, 14,563–14,567.
Carpenter C. L. and Cantley L. C. (1996) Phosphoinositide kinases.Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 8, 153–158.
Cheng J. Q., Godwin, A. K., Bellacossa A., Taguchi T., Franke T. F., Hamilton T. C., Tsichlis P. N., and Testa J. R. (1992) Akt2, a putative oncogene encoding a member of a subfamily of protein serine/threonine protein kinases, is amplified in human ovarian carcinomas.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 9267–9271.
Coffer P. J. and Woodgett J. R. (1991) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel putative protein-serine kinase related to the cAMP-dependent and protein kinase C families.Eur. J. Biochem. 201, 475–481.
Datta K., Franke T. S., Chan T. O., Makris A., Yang S., Kaplan D. R., Morrison D. K., Golemis E. A., and Tsichlis P. N. (1995) AH/PH domain-mediated interaction between Akt molecules and its potential role in Akt regulation.Mol. Cell. Biol. 15, 2304–2310.
Dudek H., Datta S. R., Franke T. F., Birnbaum M. J., Yao R., Cooper G. M., Segal R. A., Kaplan D. R., and Greenberg M. E. (1997) Regulation of neuronal survival by the serine-threonine protein kinase Akt.Science 275, 661–665.
Franke T. F., Tartof K. D., and Tsichlis P. N. (1994) The SH2-like Akt homology (AH) domain of c-akt is present in multiple copies in the genome of vertebrate and invertebrate eucaryotes. Cloning and characterization of the Drosophila melanogaster c-akt homolog Dakt1.Oncogene 9, 141–148.
Franke T. F., Yang S, Chang T. O., Datta K., Kazlauskas A., Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., and Tsichlis P. N. (1995) The protein kinase encoded by the Akt proto-oncogene is a target of the PDGF-activated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase.Cell 81, 727–736.
Franke T. F., Kaplan D. R., Cantley L. C., and Toker A. (1997) Direct regulation of the Akt proto-oncogene product by phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate.Science 275, 665–668.
Ito, Y., Goto K., and Kondo H. (1995) Localization of mRNA for phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in brain of developing and mature rats.Mol. Brain Res. 34, 149–153.
Ito, Y., Sakagami H., and Kondo H. (1996) Enhanced gene expression for phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in the hypoglossal motoneurons following axonal crush.Mol. Brain Res. 37, 329–332.
Kimura K., Hattori S., Kabuyama Y., Shizawa Y., Takayanagi J., Nakamura S., Toki S., Matsuda Y., Onodera K., and Fukui Y. (1994) Neurite outgrowth of PC12 cells is suppressed by wortmannin, a specific inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase.J. Biol. Chem. 269, 18,961–18,967.
Klippel A., Kavanaugh W. M., Pot D., and Williams L. (1997) A specific product of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase directly activates the protein kinase Akt through its pleckstrin homology domain.Mol. Cell. Biol. 17, 338–344.
Lemmon M. A., Ferguson K. M., and Schlessinger J. (1996) PH domains: diverse sequences with a common fold recruit signaling molecules to the cell surface.Cell 85, 621–624.
Li Y., Chopp M., Jiang N., and Zaloga C. (1995) In situ detection of DNA fragmentation after focal cerebral ischemia in mice.Mol. Brain Res. 28, 164–168.
Parrizas M., Saltie A. R., and Leroith D. (1997) Insulin-like growth factor I, inhibits apoptosis using the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and mitogen activating protein kinase pathways.J. Biol. Chem. 272, 154–161.
Pollard H., Cantagrel S., Charriaut-Marlangue C., Moreau J., and Ben Ari Y. (1994) Apoptosis associated DNA fragmentation in epileptic brain damage.Neuroreport 5, 1053–1055.
Soltoff S. P., Rabin S. L., Cantley L. C., and Kaplan D. R. (1992) Nerve growth factor promotes the activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and its association with the trk tyrosine kinase.J. Biol. Chem. 267, 17,472–17,477.
Staal S. P. (1987) Molecular cloning of the akt oncogene and its human homologues AKT1 and AKT2: amplification of AKT1 in a primary human gastric adenocarcinoma.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84, 5034–5037.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Owada, Y., Utsunomiya, A., Yoshimoto, T. et al. Expression of mRNA for Akt, serine-threonine protein kinase, in the brain during development and its transient enhancement following axotomy of hypoglossal nerve. J Mol Neurosci 9, 27–33 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02789392
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02789392