Abstract
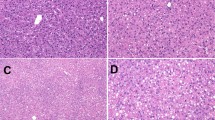
The capability of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD)2 and six congeners to induce toxic and biochemical changes in rats was investigated. In addition to TCDD, the following compounds were administered at a dose of 40 or 400 μg/kg/day for three days P.O.: 2,7-dichlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (DCDD); 1,2,4-trichlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TrCDD); 1,2,3,4-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin; l,2,3,4,6,7,8,9-octachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin; 3,3′,4,4′,5-pentachlorobiphenyl (PCB); and 2,2′,4,4′,5,5′-hexachlorobiphenyl (HCB). Six days after treatment the animals were killed. Lipid peroxidation and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-PX) activity were determined in liver and kidney. Hepatic aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase (AHH) activity was determined 48 hr following the administration of 400 μg/kg of each congener or 40 μg/kg of TCDD. With the exception of PCB and TCDD, the other congeners produced no toxic or biochemical changes at the doses given as determined by the above parameters. PCB (400 μg/kg) resulted in a 4-fold increase in lipid peroxidation and a 69% decrease in GSH-PX activity. These results were comparable to the effects of a 40 μg/kg dose of TCDD. PCB treatment resulted in a 80% decrease in thymus weight, and a 3.8-fold increase in AHH activity which were comparable to the effects of TCDD. A correlation appears to exist between the ability to induce hepatic AHH activity, enhance lipid peroxidation. inhibit GSH-PX activity, and decrease body and thymus weights.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Abbreviations
- TCDD:
-
2,7-dichlorodibenzo-p-dioxin
- DCDD:
-
1,2,4-trichlorodibenzo-p-dioxin
- TrCDD:
-
1,2,3,4,6,7,8,9-octachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin
- OCDD:
-
3,3′,4,4′,5-pentachlorobiphenyl
- PCB:
-
2,2′,4,4′,5,5′-hexachlorobiphenyl
- HCB:
-
malondialdehyde
- MDA:
-
aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase
- AHH:
-
glutathione peroxidase
- GSH-PX:
-
8-aminolevulinic acid
- ALA:
-
structure-activity relations
References
Albro PW, Corbett JT, Harris M, Lawson LD (1978) Effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin on lipid profiles in tissue of the Fisher rat. Chem Biol Interact 23:315–33
Albro PW, Corbett JT, Schroeder JL (1986) Effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin on lipid peroxidation in microsomal systemsin vitro. Chem Biol Interact 57:301–313
Dehnen W, Tomingas R, Roos J (1973) A modified method for the assay of benzo[a]pyrene hydroxylase. Anal Biochem 53:378–383
Durk H, Frank H (1984) Carbon tetrachloride metabolismin vivo and exhalation of volatile alkanes: Dependence upon oxygen partial pressure. Toxicology 30:249–257
Goldstein JA, Haas JR, Linko P, Harvan DJ (1978) 2,3,7,8-Tetrachloro-dibenzofuran in a commercially available 99% pure polychlorinated biphenyl isomer identified as the inducer of hepatic cytochrome P-448 and aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase in the rat. Drug Metab Dispos 6:258–264
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (1984) Lipid peroxidation, oxygen radicals, cell damage, and antioxidant therapy. Lancet, June 23, i:1396–1397
Hassan MQ, Stohs SJ, Murray WJ (1983) Comparative ability of TCDD to induce lipid peroxidation in rats, guinea pigs, and Syrian golden hamsters. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 31:649–657
Hochstein P, Jain SK (1981) Association of lipid peroxidation and polymerization of membrane proteins with erythrocyte aging. Fed Proc 40:183–188
Kimbrough RD (1979) The carcinogenic and other chronic effects of persistent halogenated organic compounds. Ann NY Acad Sci 320:415–418
Lee YH, Layman DK, Bell RR (1981) Glutathione peroxidase activity in iron-deficient rats. J Nutr 111:194–200
Lowry OH, Rosebrough AL, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin-phenol Reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mason RP, Chignell CF (1981) Free radicals in pharmacology and toxicology—selected topics. Pharm Rev 33:189–212
McKinney JD, Singh P (1981) Structure-activity relationships in halogenated biphenyls: Unifying hypothesis for structural specificity. Chem Biol Interact 33:271–283
Neal RA, Beatty PW, Gasiewicz TA (1979) Studies of the mechanisms of toxicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in mammalian systems. Drug Met Rev 13:1315–1325
Paglia DE, Valentine WN (1967) Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med 70:158–169
Plaa GL, Witschi H (1976) Chemicals, drugs and lipid peroxidation. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 16:125–151
Poland A, Glover E (1973a) Chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins: potent inducers of δ-aminolevulinic acid synthetase and aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase. II. A study of the structure-activity relationship. Mol Pharmacol 9:736–747
— (1973b) 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin: a potent inducer of δ-aminolevulinic acid synthetase. Science 179:476–477
Poland A, Knutson JC (1982) 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and related halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons: examination of the mechanism of toxicity. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 22:517–554
Robertson LW, Regel U, Fuser JG, Oesch F (1985) Absence of lipid peroxidation as determined by ethane exhalation in rats treated with 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). Arch Toxicol 57:13–16
Sawyer T, Safe S (1982) PCB isomers and congeners: Induction of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase and ethoxyresorufin O-deethylase activities in rat hepatoma cells. Toxicol Lett 18:87–94
Schwetz BA, Norris JM, Sparschu GL, Rowe VK, Gehring PJ, Emerson JL, Gerbig CG (1973) Toxicology of chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins. Environ Hlth Perspect 5:87–99
Slater TF (1982) Lipid peroxidation. Biochem Soc Trans 10:70–71
Stohs SJ, Hassan MQ, Murray WJ (1983) Lipid peroxidation as a possible cause of TCDD toxicity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 111:854–859
— (1984) Effects of BHA, d-α-tocopherol and retinol acetate on TCDD-induced changes in lipid peroxidation, glutathione peroxidase activity and survival. Xenobiotica 14(7):553–537
Sweeney GD, Jones KG, Cole FM, Bradford D, Krestyhski F (1979) Iron deficiency prevents liver toxicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Science 204:332–335
Tappel AL (1973) Lipid peroxidation damage to cell components. Fed Proc 33:1870–1874
Thigpen JE, Faith RE, McConnell EE, Moore JA (1975) Increased susceptibility of bacterial infection as a sequela of exposure to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Infect Immunol 12:1319–1324
Uchiyama M, Mihara M (1978) Determination of malonaidehyde precursor in tissues by thiobarbituric acid test. Analyt Biochem 86:271–278
Vos JG, Moore JA (1974) Suppression of cellular immunity in rats and mice by maternal treatment with 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 47:777–794
Vos JG, Faith RE, Luster MI (1980) Immune alterations. In: Kimbrough, RD (ed) Halogenated Biphenyls, Terphenyls, Naphthalenes, Dibenzodioxins and Related Products, pp 241–266. Elsevier, North Holland
Vos JG, Kreeftenberg JG, Engel HWB, Minderhoud A, Van Noreljansen LM (1978) Studies on 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced immune suppression and decreased resistance to infection: Endotoxin hypersensitivity, serum zinc concentrations and effect of thymosin treatment. Toxicology 9:75–86
Younes M, Siegers CP (1984) Interrelation between lipid peroxidation and other hepatotoxic events. Biochem Pharmacol 33:2001–2003
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shara, M.A., Stohs, S.J. Biochemical and toxicological effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) congeners in female rats. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 16, 599–605 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055816
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055816