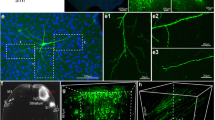
Summary
We have analyzed the development of neuronal projections inDrosophila by fusing the gene encodingDrosophila kinesin, a microtubule-associated motor protein, toEscherichia coli lacZ, and employing the resulting chimeric protein as a reporter molecule for labelling cells by the “enhancer-trap” method. Expression of kinesin-β-galactosidase in neurons has afforded a detailed view of the morphologies and projections of neurons. The images of cells provided by this method will facilitate anatomical and genetic investigations of theDrosophila nervous system as well as other cell types.
Article PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
References
Ashburner M (1989) Drosophila: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Bastiani MJ, Harrelson AL, Snow PM, Goodman CS (1987) Expression of fasciclin I and II glycoproteins on subsets of axon pathways during neuronal development in the grosshopper. Cell 48:745–755
Bellen HJ, O'Kane CJ, Wilson C, Grossniklaus U, Gehring WJ (1989) P-Element-mediated enhancer detection: a versatile method to study development inDrosophila. Genes Dev 3:1288–1300
Bier E, Vaessin H, Shepherd S, Lee K, McCall K, Barbel S, Ackerman L, Carretto R, Uemura T, Grell E, Jan LY, Jan YN (1989) Searching for pattern and mutation in theDrosophila genome with a P-lacZ vector. Genes Dev 3:1273–1287
Bodmer R, Jan YN (1987) Morphological differentiation of the embryonic peripheral neurons in Drosophila. Roux's Arch Dev Biol 196:69–77
Campos-Ortega J, Hartenstein V (1985) The embryonic development of Drosophila melanogaster. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Endow SA, Hatsumi M (1991) A multimember kinesin gene family inDrosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:4424–4427
Fehon RG, Johansen K, Rebay I, Artavanis-Tsakonis S (1991) Complex cellular and subcellular regulation ofNotch expression during embryonic and imaginal development ofDrosophila: Implications forNotch function. J Cell Biol 113:657–669
Fredieu JR, Mahowald AP (1989) Glial interactions with neurons duringDrosophila embryogenesis. Development 106:739–748
Ghysen A (1978) Sensory axons recognize defined pathways inDrosophila central nervous system. Nature 271:869–872
Ghysen A (1991) Le developpement du Système nerveux chez la drosophile. These d'agregation de l'enseignement supérieur, Université Libre de Bruxelles, Brussels
Ghysen A, Dambly-Chaudiere C, Aceves E, Jan LY, Jan YN (1986) Sensory neurons and peripheral pathways inDrosophila embryos. Roux's Arch Dev Biol 195:281–289
Greningloh G, Rehm EJ, Goodman CS (1991) Genetic analysis of growth cone guidance inDrosophila: fasciclin II functions as a neuronal recognition molecule. Cell 67:45–57
Halpern ME, Chiba A, Johansen J, Keshishian H (1991) Growth cone behavior underlying the development of stereotypic connections inDrosophila embryos. J Neurosci 11:3227–3238
Hartenstein V (1988) Development ofDrosophila larval sensory organs: spatiotemporal pattern of sensory neurones, peripheral axonal pathways and sensilla differentiation. Development 102:869–886
Hartenstein V, Jan YN (1992) StudyingDrosophila embryogenesis with P-IacZ enhancer trap lines. Roux's Arch Dev Biol 201:194–220
Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sininsky JJ, White TJ (1990) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic Press, San Diego
Jacobs JR, Goodman CS (1989) Embryonic development of axon pathways in theDrosophila CNS: I. A glial scaffold appears before the first growth cones. J Neurosci 9:2402–2411
Jacobs JR, Hiromi Y, Patel NH, Goodman CS (1989) Lineages migration and morphogenesis of longitudinal glia in theDrosophila CNS as revealed by a molecular lineage marker. Neuron 2:1625–1631
Johansen J, Halpern ME, Keshishian H (1989) Axonal guidance and the development of muscle fiber-specific innervation inDrosophila embryos. J Neurosci 9:4318–4332
Klambt C, Jacobs JR, Goodman CS (1991) The midline of theDrosophila central nervous system: a model for the genetic analysis of cell fate, cell migration and growth cone guidance. Cell 64:801–815
Lindsley DL, Grell EH (1968) Genetic variations in Drosophila melanogaster. Publication no 627 Carnegie Institution of Washington, Washington, DC
Mahowald AP, Kambysellis MP (1977) Oogenesis. In: Ashburner M, Wright TRF (eds) Biology ofDrosophila, part 2D. Academic Press, New York, pp 141–224
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Meinertzhagen IA, O'Neil SD (1991) Synaptic organization of columnar elements in the lamina of the wild type inDrosophila melanogaster. J Comp Neurol 305:232–263
Moses K, Rubin GM (1991)glass Encodes a site-specific DNA-binding protein that is regulated in response to positional signals in the devolopingDrosophila eye. Genes Dev 5:583–593
Nose A, Mahajan VB, Goodman CS (1992) Connectin: a hemophilic cell adhesion molecule expressed on a subset of muscles and the motoneurons that innervate them inDrosophila. Cell 70:553–567
O'Kane CJ, Gehring WJ (1987) Detection in situ of genomic regulatory elements inDrosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:9123–9127
Palka J, Malone MA, Ellison RL, Wigston DJ (1986) Central projections of identifiedDrosophila sensory neurons in relation to their time of development. J Neurosci 6:1822–1830
Patel NH, Snow PM, Goodman CS (1987) Characterization and cloning of fasciclin III: a glycoprotein expressed on a subset of neurons and axon pathways inDrosophila. Cell 48:975–988
Rubin GM, Spradling AC (1982) Genetic transformation ofDrosophila with transposable element vectors. Science 218:348–353
Simpson P, Carteret C (1990) Proneural clusters: equivalence groups in the epithelium ofDrosophila. Development 110:927–932
Sink H, Whitington PM (1991) Pathfinding in the central nervous system and periphery by identified embryonicDrosophila motor axons. Development 112:307–316
Spradling AC, Rubin GM (1982) Transposition of cloned P elements intoDrosophila germ line chromosomes. Science 218:341–347
Steward RJ, Pesavento PA, Woerpel DN, Goldstein LS (1991) Identification and partial characterization of six members of the kinesin superfamily inDrosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:8470–8474
Thomas JB, Bastiani MJ, Bate M, Goodman CS (1984) From grasshopper toDrosophila: a common plan for neuronal development. Nature 310:203–207
Thummel C, Boulet AM, Lipshitz HD (1988) Vectors forDrosophila P-element-mediated transformation and tissue culture transfection. Gene 74:445–456
Vale RD, Schnapp BJ, Reese TS, Sheetz MP (1985a) Organelle, bead and microtubule translocations promoted by soluble factors from the squid giant axon. Cell 40:559–569
Vale RD, Reese TS, Sheetz MP (1985b) Identification of a novel force-generating protein, kinesin, involved in microtubule-based motility. Cell 42:39–50
Vale RD, Schnapp BJ, Mitchison T, Steuer E, Reese TS, Sheetz MP (1985c) Different axoplasmic proteins generate movement in opposite directions along microtubules in vitro. Cell 43:623–632
Vallee RB, Bloom GS (1991) Mechanisms of fast and slow axonal transport. Annu Rev Neurosci 14:59–92
Wyman RJ, Thomas JB (1983) What genes are necessary to make an identified synapse? Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology 48:641–652
Yang JT, Saxton WM, Goldstein LS (1988) Isolation and characterization of the gene encoding the heavy chain ofDrosophila kinesin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:1864–1868
Yang JT, Laymon RA, Goldstein LS (1989) A three-domain structure of kinesin heavy chain revealed by DNA sequencing and microtubule binding analysis. Cell 56:879–889
Yang JT, Saxton WM, Stewart RJ, Raff EC, Goldstein LS (1990) Evidence that the head of kinesin is sufficient for force generation and motility in vitro. Science 249:42–47
Zipursky SL, Venkatesh TR, Teplow DB, Benzer S (1984) Neuronal development in theDrosophila retina: monoclonal antibodies as molecular probes. Cell 36:15–26
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: Y.N. Jan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giniger, E., Wells, W., Jan, L.Y. et al. Tracing neurons with a kinesin-β-galactosidase fusion protein. Roux's Arch Dev Biol 202, 112–122 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00636536
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00636536