Abstract
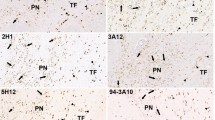
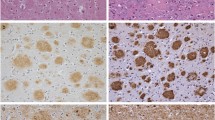
αB-crystallin is a member of the small heatshock protein family. Under pathological conditions, the expression of αB-crystallin increases in proliferating astrocytes, which suggests that this protein, in addition to glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), can be a marker for gliosis in neurodegenerative diseases. Immunoblotting and immunohistochemical methods were used for the detection of αB-crystallin in the brains of Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients and nondemented controls. An increase in αB-cyrstallin expression was found in the brains of AD patients. Immunoreaction was present in reactive astrocytes, microglia, and oligodendrocytes, indicating that all types of glia respond to the stress associated with AD pathology. Colocalization of GFAP and αB-crystallin was found in fibrous astrocytes. However, the intensity and range of αB-crystallin expression appeared to be limited as compared with the large increase in the number of GFAP-positive astrocytes. This indicates that expression of αB-crystallin is not a marker for gliosis in AD. Immunoreactivity to αB-crystallin in both astrocytes and microglia was found mainly restricted to areas with senile plaques and neurofibrillary tangles, suggesting the association of αB-crystallin with amyloid deposition in AD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe K, St George-Hyslop PH, Tanzi RE, Kogure K (1991) Induction of amyloid precursor protein mRNA after heat shock in cultured human lymphoblastoid cells. Neurosci Lett 125: 169–171
Aoyama A, Fröli E, Schäfer R, Klemenz R (1993) αB-crystallin expression in mouse NIH 3T3: fibroblasts glucocoticoid responsiveness, ras oncogene-mediated modulation and involvement in thermal protection. Mol Cell Biol 13: 1824–1835
Bhat SP, Nagineni CN (1989) αB subunit of lens-specific protein α-crystallin is present in other ocular and non-ocular tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 158: 319–325
De Jong WW, Leunissen JAM, Voorter CEM (1993) Evolution of the α-crystallin/small heat-shock protein family. Mol Biol Evol 10: 103–126
Delacourte A (1990) General and dramatic glial reaction in Alzheimer brains. Neurology 40: 33–37
Duguid JR, Rohwer RG, Seed B (1988) Isolation of cDNAs of scrapie-modulated RNAs by subtractive hybridization of a cDNA library. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 5738–5742
Frederickson RCA (1992) Astroglia in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 13: 239–253
Grundke-Iqbal I, Fleming J, Tung YC, Lassmann H, Iqbal K, Joshi JG (1990) Ferritin is a component of the neuritic (senile) plaque in Alzheimer's dementia. Acta Neuropathol 81: 105–110
Haass C, Hung AY, Selkoe DJ (1991) Processing of β-amyloid precursor protein in microglia and astroctytes favors an internal localization over constitutive secretion. J Neurosci 11: 3783–3793
Hamos JE, Oblas B, Pulaski-Salo D, Welch WJ, Bole DG, Drachman DA (1991) Expression of heat shock proteins in Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 41: 345–350
Horwitz J (1992) Alpha-Crystallin can function as a molecular chaperone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 10449–10453
Iwaki T, Wisniewski T, Iwaki A, Corbin E, Tomokane N, Tateishi J, Goldman JE (1992) Accumulation of αB-crystallin in central nervous system glia and neurons in pathological conditions. Am J Pathol 140: 345–356
Jellinger K, Paulus W, Grundke-Iqbal I, Riederer P, Youdim MBH (1990) Brain iron and ferritin in Parkinson's and Alzheimer's diseases. J Neural Transm [P-D Sect] 2: 327–340
Kato K, Shinohara H, Kurobe N, Inaguma Y, Shimizu K, Ohshima K (1991) Tissue distribution and developmental profiles of immunoreactive αB-crystallin in the rat determined with a sensitive immunoassay system. Acta Biochim Biophys 1074: 201–208
Khachaturian ZS (1985) Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol 42: 1097–1104
Klementz R, Fröhli E, Steiger RH, Schäfer R, Aoyama A (1991) αB-crystallin is a small heat-shock protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 3652–3656
Lindsay RM (1986) Reactive gliosis. In: Fedoroff S, Vernadakis A (eds) Astrocytes, vol 3. Academic Press, New York, pp 231–262
Lolova I (1991) Qualitative and quantitative glial changes in the hippocampus of aged rats. Anat Anz Jena 172: 263–271
Lowe J, McDermott H, Pike I, Spendove I, Landon M, Mayer RJ (1992) αB-crystallin expression in non-lenticular tissues and selective presence in ubiquinated inclusion bodies in human disease. J Pathol 166: 61–68
Lowe J, Errington DR, Lennox G, Pike I, Spendlove I, Landon M, Mayer RJ (1992) Ballooned neurons in several neurodegenerative diseases and stroke contain αB-crystallin. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 18: 341–350
Merck KB, Groenen PJTA, Voorter CEM, de Haard-Hoekman, Horwitz J, Bloemendal H, De Jong WW (1993) Structural and functional similarities of bovine α-crystallin and mouse small heat-shock protein. J Biol Chem 268: 1046–1052
Miller RH, Abney ER, David S, Ffrench-Constant C, Lindsay R, Patel R, Stone J, Raff MC (1986) Is reactive gliosis a property of a distinct subpopulation of astrocytes? J Neurosci 6: 22–29
Morimoto RI (1991) Heat shock: the role of transient inducible responses in cell damage, transformation, and differentiation. Cancer cells 3: 295–301
Nagineni CN, Bhat SP (1988) Maintenance of the synthesis of αB-crystallin and progressive expression of βBp-crystallin in human fetal lens epithelial cells in culture. Dev Biol 130: 402–405
Nishimura RN, Dwyer BE, Welch W, Cole R, de Vellis J, Liotta K (1988) The induction of the major heat-stress protein in purified rat glial cells. J Neurosci Res 20: 12–18
Norton WT, Aquino DA, Hozumi I, Chiu FC, Brosnan CF (1992) Quantitative aspects of reactive gliosis: a review. Neurochem Res 17: 877–885
Renkawek K, De Jong WW, Merck KB, Frenken CWGM, Van Workum FPA, Bosman GJCGM (1992) αB-crystallin is present in reactive glia in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Acta Neuropathol 83: 324–327
Renkawek K, Voorter CEM, Bosman GJCGM, van Workum FPA, de Jong WW (1993) αB-crystallin expression in reactive glia in Alzheimer disease. Adv Biosci 87: 287–288
Sawada K, Agata K, Eguchi G (1992) Crystallin gene expression in the process of lentoidogenesis in cultures of chicken lens epithelial cells. Exp Eye Res 55: 879–887
Wistow GJ, Piatigorsky J (1988) Lens crystallins: the evolution and expression of proteins for a highly specialized tissue. Annu Rev Biochem 57: 479–504
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by a grant (No. EY08202) from the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, USA
Supported by a fellowship of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Renkawek, K., Voorter, C.E.M., Bosman, G.J.C.G.M. et al. Expression of αB-crystallin in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol 87, 155–160 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00296185
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00296185