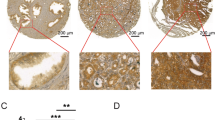
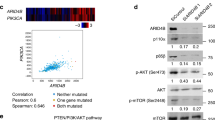
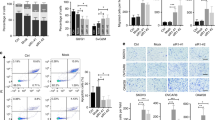
Abstract
The PI3K signaling pathway is activated in a majority of cancer types. It promotes tumorigenesis by regulating nutrient metabolism, cell proliferation, survival, migration, and angiogenesis. The underlying mechanisms of PI3K/AKT activation are mainly due to deletions or mutations in its key negative regulator gene—PTEN. However, mutations in other pathway genes, such as the tumor suppressor gene SPOP, may contribute indirectly to the activation of this pathway. Interestingly, a mutually exclusive relationship exists between genomic alterations in PTEN and mutations in SPOP in prostate cancer patients, suggesting that altered functions of these two tumor suppressors might share similar or at least partially overlapping mechanisms in tumorigenesis. Activated AKT can phosphorylate directly a number of downstream effectors and thereby inhibit or activate their functions. An important target of PI3K/AKT signaling is FOXO1 protein that can be phosphorylated directly by AKT leading to translocation of FOXO1 from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. This not only impairs FOXO1 activities on transactivation of downstream target genes, but also abolishes its transcriptional activity-independent inhibitory effect on other targets such as AR, ERG and RUNX2. Interestingly, heterozygous deletion of Pten, or mutation of Spop alone has minimal effects on tumorigenesis in the mouse prostate, suggesting that PI3K/AKT pathway interacts with other pathways to drive prostate cancer progression. Indeed, the cross talk between PI3K/AKT and other pathways, such as AR, WNT, and ERK signaling pathways is known to play essential roles in disease progression and drug resistance in prostate cancer. Therefore, co-targeting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and its cooperating pathways may be critical for improving the anti-cancer efficacy of PI3K/AKT inhibitors in the clinic.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Liu, H. Cheng, T.M. Roberts, J.J. Zhao, Targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway in cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 8, 627–644 (2009)
E. Gonzalez, T.E. McGraw, The Akt kinases: isoform specificity in metabolism and cancer. Cell Cycle 8, 2502–2508 (2009)
D.R. Alessi, S.R. James, C.P. Downes, A.B. Holmes, P.R. Gaffney, C.B. Reese, P. Cohen, Characterization of a 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase which phosphorylates and activates protein kinase Balpha. Curr. Biol. 7, 261–269 (1997)
D.D. Sarbassov, D.A. Guertin, S.M. Ali, D.M. Sabatini, Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the rictor-mTOR complex. Science 307, 1098–1101 (2005)
B.S. Carver, C. Chapinski, J. Wongvipat, H. Hieronymus, Y. Chen, S. Chandarlapaty, V.K. Arora, C. Le, J. Koutcher, H. Scher, et al., Reciprocal feedback regulation of PI3K and androgen receptor signaling in PTEN-deficient prostate cancer. Cancer Cell 19, 575–586 (2011)
B.S. Taylor, N. Schultz, H. Hieronymus, A. Gopalan, Y. Xiao, B.S. Carver, V.K. Arora, P. Kaushik, E. Cerami, B. Reva, et al., Integrative genomic profiling of human prostate cancer. Cancer Cell 18, 11–22 (2010)
V.A. Rafalski, A. Brunet, Energy metabolism in adult neural stem cell fate. Prog. Neurobiol. 93, 182–203 (2011)
L. Ojeda, J. Gao, K.G. Hooten, E. Wang, J.R. Thonhoff, T.J. Dunn, T. Gao, P. Wu, Critical role of PI3K/Akt/GSK3beta in motoneuron specification from human neural stem cells in response to FGF2 and EGF. PLoS One 6, e23414 (2011)
J. Peltier, A. O’Neill, D.V. Schaffer, PI3K/Akt and CREB regulate adult neural hippocampal progenitor proliferation and differentiation. Dev. Neurobiol. 67, 1348–1361 (2007)
B.D. Manning, A. Toker, AKT/PKB signaling: navigating the network. Cell 169, 381–405 (2017)
K. Du, M. Montminy, CREB is a regulatory target for the protein kinase Akt/PKB. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 32377–32379 (1998)
J.R. Graff, B.W. Konicek, A.M. McNulty, Z. Wang, K. Houck, S. Allen, J.D. Paul, A. Hbaiu, R.G. Goode, G.E. Sandusky, et al., Increased AKT activity contributes to prostate cancer progression by dramatically accelerating prostate tumor growth and diminishing p27Kip1 expression. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 24500–24505 (2000)
I. Shin, F.M. Yakes, F. Rojo, N.Y. Shin, A.V. Bakin, J. Baselga, C.L. Arteaga, PKB/Akt mediates cell-cycle progression by phosphorylation of p27(Kip1) at threonine 157 and modulation of its cellular localization. Nat. Med. 8, 1145–1152 (2002)
A. Brunet, A. Bonni, M.J. Zigmond, M.Z. Lin, P. Juo, L.S. Hu, M.J. Anderson, K.C. Arden, J. Blenis, M.E. Greenberg, Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96, 857–868 (1999)
X. Zhang, N. Tang, T.J. Hadden, A.K. Rishi, Akt, FoxO and regulation of apoptosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1813, 1978–1986 (2011b)
K. Hara, K. Yonezawa, M.T. Kozlowski, T. Sugimoto, K. Andrabi, Q.P. Weng, M. Kasuga, I. Nishimoto, J. Avruch, Regulation of eIF-4E BP1 phosphorylation by mTOR. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 26457–26463 (1997)
B.D. Manning, L.C. Cantley, AKT/PKB signaling: navigating downstream. Cell 129, 1261–1274 (2007)
N. Chalhoub, S.J. Baker, PTEN and the PI3-kinase pathway in cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 4, 127–150 (2009)
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network Network, The molecular taxonomy of primary prostate cancer. Cell 163, 1011–1025 (2015)
D. Robinson, E.M. Van Allen, Y.M. Wu, N. Schultz, R.J. Lonigro, J.M. Mosquera, B. Montgomery, M.E. Taplin, C.C. Pritchard, G. Attard, et al., Integrative clinical genomics of advanced prostate cancer. Cell 162, 454 (2015)
S. Wee, D. Wiederschain, S.M. Maira, A. Loo, C. Miller, R. deBeaumont, F. Stegmeier, Y.M. Yao, C. Lengauer, PTEN-deficient cancers depend on PIK3CB. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105, 13057–13062 (2008)
J. Armenia, S.A.M. Wankowicz, D. Liu, J. Gao, R. Kundra, E. Reznik, W.K. Chatila, D. Chakravarty, G.C. Han, I. Coleman, et al., The long tail of oncogenic drivers in prostate cancer. Nat. Genet. 50, 645–651 (2018)
A. Suzuki, J.L. de la Pompa, V. Stambolic, A.J. Elia, T. Sasaki, I. del Barco Barrantes, A. Ho, A. Wakeham, A. Itie, W. Khoo, et al., High cancer susceptibility and embryonic lethality associated with mutation of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in mice. Curr. Biol. 8, 1169–1178 (1998)
L.C. Trotman, M. Niki, Z.A. Dotan, J.A. Koutcher, A. Di Cristofano, A. Xiao, A.S. Khoo, P. Roy-Burman, N.M. Greenberg, T. Van Dyke, et al., Pten dose dictates cancer progression in the prostate. PLoS Biol. 1, E59 (2003)
S. Wang, J. Gao, Q. Lei, N. Rozengurt, C. Pritchard, J. Jiao, G.V. Thomas, G. Li, P. Roy-Burman, P.S. Nelson, et al., Prostate-specific deletion of the murine Pten tumor suppressor gene leads to metastatic prostate cancer. Cancer Cell 4, 209–221 (2003)
A. Di Cristofano, M. De Acetis, A. Koff, C. Cordon-Cardo, P.P. Pandolfi, Pten and p27KIP1 cooperate in prostate cancer tumor suppression in the mouse. Nat. Genet. 27, 222–224 (2001)
M.J. Kim, R.D. Cardiff, N. Desai, W.A. Banach-Petrosky, R. Parsons, M.M. Shen, C. Abate-Shen, Cooperativity of Nkx3.1 and Pten loss of function in a mouse model of prostate carcinogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 99, 2884–2889 (2002)
B.S. Carver, J. Tran, A. Gopalan, Z. Chen, S. Shaikh, A. Carracedo, A. Alimonti, C. Nardella, S. Varmeh, P.T. Scardino, et al., Aberrant ERG expression cooperates with loss of PTEN to promote cancer progression in the prostate. Nat. Genet. 41, 619–624 (2009)
J.C. King, J. Xu, J. Wongvipat, H. Hieronymus, B.S. Carver, D.H. Leung, B.S. Taylor, C. Sander, R.D. Cardiff, S.S. Couto, et al., Cooperativity of TMPRSS2-ERG with PI3-kinase pathway activation in prostate oncogenesis. Nat. Genet. 41, 524–526 (2009)
L. Ding, S. Chen, P. Liu, Y. Pan, J. Zhong, K.M. Regan, L. Wang, C. Yu, A. Rizzardi, L. Cheng, et al., CBP loss cooperates with PTEN haploinsufficiency to drive prostate cancer: implications for epigenetic therapy. Cancer Res. 74, 2050–2061 (2014)
C.E. Barbieri, S.C. Baca, M.S. Lawrence, F. Demichelis, M. Blattner, J.P. Theurillat, T.A. White, P. Stojanov, E. Van Allen, N. Stransky, et al., Exome sequencing identifies recurrent SPOP, FOXA1 and MED12 mutations in prostate cancer. Nat. Genet. 44, 685–689 (2012)
J. An, S. Ren, S.J. Murphy, S. Dalangood, C. Chang, X. Pang, Y. Cui, L. Wang, Y. Pan, X. Zhang, et al., Truncated ERG oncoproteins from TMPRSS2-ERG fusions are resistant to SPOP-mediated proteasome degradation. Mol. Cell 59, 904–916 (2015)
J. An, C. Wang, Y. Deng, L. Yu, H. Huang, Destruction of full-length androgen receptor by wild-type SPOP, but not prostate-cancer-associated mutants. Cell Rep. 6, 657–669 (2014)
M. Blattner, D.J. Lee, C. O’Reilly, K. Park, T.Y. MacDonald, F. Khani, K.R. Turner, Y.L. Chiu, P.J. Wild, I. Dolgalev, et al., SPOP mutations in prostate cancer across demographically diverse patient cohorts. Neoplasia 16, 14–20 (2014)
C. Geng, B. He, L. Xu, C.E. Barbieri, V.K. Eedunuri, S.A. Chew, M. Zimmermann, R. Bond, J. Shou, C. Li, et al., Prostate cancer-associated mutations in speckle-type POZ protein (SPOP) regulate steroid receptor coactivator 3 protein turnover. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110, 6997–7002 (2013)
C. Geng, K. Rajapakshe, S.S. Shah, J. Shou, V.K. Eedunuri, C. Foley, W. Fiskus, M. Rajendran, S.A. Chew, M. Zimmermann, et al., Androgen receptor is the key transcriptional mediator of the tumor suppressor SPOP in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 74, 5631–5643 (2014)
A.C. Groner, L. Cato, J. de Tribolet-Hardy, T. Bernasocchi, H. Janouskova, D. Melchers, R. Houtman, A.C.B. Cato, P. Tschopp, L. Gu, et al., TRIM24 is an oncogenic transcriptional activator in prostate cancer. Cancer Cell 29, 846–858 (2016)
C. Li, J. Ao, J. Fu, D.F. Lee, J. Xu, D. Lonard, B.W. O’Malley, Tumor-suppressor role for the SPOP ubiquitin ligase in signal-dependent proteolysis of the oncogenic co-activator SRC-3/AIB1. Oncogene 30, 4350–4364 (2011)
Y. Yan, J. An, Y. Yang, D. Wu, Y. Bai, W. Cao, L. Ma, J. Chen, Z. Yu, Y. He, et al., Dual inhibition of AKT-mTOR and AR signaling by targeting HDAC3 in PTEN- or SPOP-mutated prostate cancer. EMBO Mol. Med. 10, e8478 (2018)
P. Zhang, D. Wang, Y. Zhao, S. Ren, K. Gao, Z. Ye, S. Wang, C.W. Pan, Y. Zhu, Y. Yan, et al., Intrinsic BET inhibitor resistance in SPOP-mutated prostate cancer is mediated by BET protein stabilization and AKT-mTORC1 activation. Nat. Med. 23, 1055–1062 (2017)
A. Saci, L.C. Cantley, C.L. Carpenter, Rac1 regulates the activity of mTORC1 and mTORC2 and controls cellular size. Mol. Cell 42, 50–61 (2011)
R. Lasserre, X.J. Guo, F. Conchonaud, Y. Hamon, O. Hawchar, A.M. Bernard, S.M. Soudja, P.F. Lenne, H. Rigneault, D. Olive, et al., Raft nanodomains contribute to Akt/PKB plasma membrane recruitment and activation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 4, 538–547 (2008)
L. Zhuang, J. Lin, M.L. Lu, K.R. Solomon, M.R. Freeman, Cholesterol-rich lipid rafts mediate akt-regulated survival in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 62, 2227–2231 (2002)
J. Xu, L. Liao, G. Ning, H. Yoshida-Komiya, C. Deng, B.W. O’Malley, The steroid receptor coactivator SRC-3 (p/CIP/RAC3/AIB1/ACTR/TRAM-1) is required for normal growth, puberty, female reproductive function, and mammary gland development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 97, 6379–6384 (2000)
L.H. Zhang, A.A. Yin, J.X. Cheng, H.Y. Huang, X.M. Li, Y.Q. Zhang, N. Han, X. Zhang, TRIM24 promotes glioma progression and enhances chemoresistance through activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Oncogene 34, 600–610 (2015)
M. Blattner, D. Liu, B.D. Robinson, D. Huang, A. Poliakov, D. Gao, S. Nataraj, L.D. Deonarine, M.A. Augello, V. Sailer, et al., SPOP mutation drives prostate tumorigenesis in vivo through coordinate regulation of PI3K/mTOR and AR signaling. Cancer Cell 31, 436–451 (2017)
H. Huang, D.J. Tindall, Dynamic FoxO transcription factors. J. Cell Sci. 120, 2479–2487 (2007)
Y. Zhao, D.J. Tindall, H. Huang, Modulation of androgen receptor by FOXA1 and FOXO1 factors in prostate cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 10, 614–619 (2014)
X.Y. Dong, C. Chen, X. Sun, P. Guo, R.L. Vessella, R.X. Wang, L.W. Chung, W. Zhou, J.T. Dong, FOXO1A is a candidate for the 13q14 tumor suppressor gene inhibiting androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 66, 6998–7006 (2006)
B.S. Haflidadottir, O. Larne, M. Martin, M. Persson, A. Edsjo, A. Bjartell, Y. Ceder, Upregulation of miR-96 enhances cellular proliferation of prostate cancer cells through FOXO1. PLoS One 8, e72400 (2013)
V. Modur, R. Nagarajan, B.M. Evers, J. Milbrandt, FOXO proteins regulate tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand expression. Implications for PTEN mutation in prostate cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 47928–47937 (2002)
Y. Yang, H. Hou, E.M. Haller, S.V. Nicosia, W. Bai, Suppression of FOXO1 activity by FHL2 through SIRT1-mediated deacetylation. EMBO J. 24, 1021–1032 (2005)
L.R. Bohrer, P. Liu, J. Zhong, Y. Pan, J. Angstman, L.J. Brand, S.M. Dehm, H. Huang, FOXO1 binds to the TAU5 motif and inhibits constitutively active androgen receptor splice variants. Prostate 73, 1017–1027 (2013)
W. Fan, T. Yanase, H. Morinaga, T. Okabe, M. Nomura, H. Daitoku, A. Fukamizu, S. Kato, R. Takayanagi, H. Nawata, Insulin-like growth factor 1/insulin signaling activates androgen signaling through direct interactions of Foxo1 with androgen receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 7329–7338 (2007)
P. Liu, S. Li, L. Gan, T.P. Kao, H. Huang, A transcription-independent function of FOXO1 in inhibition of androgen-independent activation of the androgen receptor in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 68, 10290–10299 (2008)
S.N. Mediwala, H. Sun, A.T. Szafran, S.M. Hartig, G. Sonpavde, T.G. Hayes, P. Thiagarajan, M.A. Mancini, M. Marcelli, The activity of the androgen receptor variant AR-V7 is regulated by FOXO1 in a PTEN-PI3K-AKT-dependent way. Prostate 73, 267–277 (2013)
H.K. Lin, S. Yeh, H.Y. Kang, C. Chang, Akt suppresses androgen-induced apoptosis by phosphorylating and inhibiting androgen receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 98, 7200–7205 (2001)
P. Adamo, M.R. Ladomery, The oncogene ERG: a key factor in prostate cancer. Oncogene 35, 403–414 (2016)
S.A. Tomlins, D.R. Rhodes, S. Perner, S.M. Dhanasekaran, R. Mehra, X.W. Sun, S. Varambally, X. Cao, J. Tchinda, R. Kuefer, et al., Recurrent fusion of TMPRSS2 and ETS transcription factor genes in prostate cancer. Science 310, 644–648 (2005)
Y. Yang, A.M. Blee, D. Wang, J. An, Y. Pan, Y. Yan, T. Ma, Y. He, J. Dugdale, X. Hou, et al., Loss of FOXO1 cooperates with TMPRSS2-ERG overexpression to promote prostate tumorigenesis and cell invasion. Cancer Res. 77, 6524–6537 (2017)
I.A. San Martin, N. Varela, M. Gaete, K. Villegas, M. Osorio, J.C. Tapia, M. Antonelli, E.E. Mancilla, B.P. Pereira, S.S. Nathan, et al., Impaired cell cycle regulation of the osteoblast-related heterodimeric transcription factor Runx2-Cbfbeta in osteosarcoma cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 221, 560–571 (2009)
D. Wysokinski, E. Pawlowska, J. Blasiak, RUNX2: a master bone growth regulator that may be involved in the DNA damage response. DNA Cell Biol. 34, 305–315 (2015)
J.J. Westendorf, S.K. Zaidi, J.E. Cascino, R. Kahler, A.J. van Wijnen, J.B. Lian, M. Yoshida, G.S. Stein, X. Li, Runx2 (Cbfa1, AML-3) interacts with histone deacetylase 6 and represses the p21(CIP1/WAF1) promoter. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22, 7982–7992 (2002)
C. Ge, G. Xiao, D. Jiang, Q. Yang, N.E. Hatch, H. Roca, R.T. Franceschi, Identification and functional characterization of ERK/MAPK phosphorylation sites in the Runx2 transcription factor. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 32533–32543 (2009)
M. Qiao, P. Shapiro, M. Fosbrink, H. Rus, R. Kumar, A. Passaniti, Cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation of the RUNX2 transcription factor by cdc2 regulates endothelial cell proliferation. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 7118–7128 (2006)
C. Ge, G. Zhao, Y. Li, H. Li, X. Zhao, G. Pannone, P. Bufo, A. Santoro, F. Sanguedolce, S. Tortorella, et al., Role of Runx2 phosphorylation in prostate cancer and association with metastatic disease. Oncogene 35, 366–376 (2016)
S.K. Baniwal, O. Khalid, D. Sir, G. Buchanan, G.A. Coetzee, B. Frenkel, Repression of Runx2 by androgen receptor (AR) in osteoblasts and prostate cancer cells: AR binds Runx2 and abrogates its recruitment to DNA. Mol. Endocrinol. 23, 1203–1214 (2009)
H. Kawate, Y. Wu, K. Ohnaka, R. Takayanagi, Mutual transactivational repression of Runx2 and the androgen receptor by an impairment of their normal compartmentalization. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 105, 46–56 (2007)
H. Zhang, Y. Pan, L. Zheng, C. Choe, B. Lindgren, E.D. Jensen, J.J. Westendorf, L. Cheng, H. Huang, FOXO1 inhibits Runx2 transcriptional activity and prostate cancer cell migration and invasion. Cancer Res. 71, 3257–3267 (2011a)
S. Yang, H. Xu, S. Yu, H. Cao, J. Fan, C. Ge, R.T. Fransceschi, H.H. Dong, G. Xiao, Foxo1 mediates insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1)/insulin regulation of osteocalcin expression by antagonizing Runx2 in osteoblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 19149–19158 (2011)
Y. Yang, Y. Bai, Y. He, Y. Zhao, J. Chen, L. Ma, Y. Pan, M. Hinten, J. Zhang, R.J. Karnes, et al., PTEN loss promotes intratumoral androgen synthesis and tumor microenvironment remodeling via aberrant activation of RUNX2 in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 24, 834–846 (2018)
D.J. Mulholland, L.M. Tran, Y. Li, H. Cai, A. Morim, S. Wang, S. Plaisier, I.P. Garraway, J. Huang, T.G. Graeber, H. Wu, Cell autonomous role of PTEN in regulating castration-resistant prostate cancer growth. Cancer Cell 19, 792–804 (2011)
J. Long, W.Y. Fang, L. Chang, W.H. Gao, Y. Shen, M.Y. Jia, Y.X. Zhang, Y. Wang, H.B. Dou, W.J. Zhang, et al., Targeting HDAC3, a new partner protein of AKT in the reversal of chemoresistance in acute myeloid leukemia via DNA damage response. Leukemia 31, 2761–2770 (2017)
D.S. Welsbie, J. Xu, Y. Chen, L. Borsu, H.I. Scher, N. Rosen, C.L. Sawyers, Histone deacetylases are required for androgen receptor function in hormone-sensitive and castrate-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 69, 958–966 (2009)
V. Murillo-Garzon, R. Kypta, WNT signalling in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 14, 683–696 (2017)
D. Fang, D. Hawke, Y. Zheng, Y. Xia, J. Meisenhelder, H. Nika, G.B. Mills, R. Kobayashi, T. Hunter, Z. Lu, Phosphorylation of beta-catenin by AKT promotes beta-catenin transcriptional activity. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 11221–11229 (2007)
S.A. Tahir, G. Yang, A. Goltsov, K.D. Song, C. Ren, J. Wang, W. Chang, T.C. Thompson, Caveolin-1-LRP6 signaling module stimulates aerobic glycolysis in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 73, 1900–1911 (2013)
G. Thyssen, T.H. Li, L. Lehmann, M. Zhuo, M. Sharma, Z. Sun, LZTS2 is a novel beta-catenin-interacting protein and regulates the nuclear export of beta-catenin. Mol. Cell. Biol. 26, 8857–8867 (2006)
E.J. Yu, E. Hooker, D.T. Johnson, M.K. Kwak, K. Zou, R. Luong, Y. He, Z. Sun, LZTS2 and PTEN collaboratively regulate ss-catenin in prostatic tumorigenesis. PLoS One 12, e0174357 (2017)
H. Gao, X. Ouyang, W.A. Banach-Petrosky, W.L. Gerald, M.M. Shen, C. Abate-Shen, Combinatorial activities of Akt and B-Raf/Erk signaling in a mouse model of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 103, 14477–14482 (2006)
S. Chandarlapaty, A. Sawai, M. Scaltriti, V. Rodrik-Outmezguine, O. Grbovic-Huezo, V. Serra, P.K. Majumder, J. Baselga, N. Rosen, AKT inhibition relieves feedback suppression of receptor tyrosine kinase expression and activity. Cancer Cell 19, 58–71 (2011)
V. Serra, M. Scaltriti, L. Prudkin, P.J. Eichhorn, Y.H. Ibrahim, S. Chandarlapaty, B. Markman, O. Rodriguez, M. Guzman, S. Rodriguez, et al., PI3K inhibition results in enhanced HER signaling and acquired ERK dependency in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer. Oncogene 30, 2547–2557 (2011)
C.W. Pan, X. Jin, Y. Zhao, Y. Pan, J. Yang, R.J. Karnes, J. Zhang, L. Wang, H. Huang, AKT-phosphorylated FOXO1 suppresses ERK activation and chemoresistance by disrupting IQGAP1-MAPK interaction. EMBO J. 36, 995–1010 (2017)
M. Crumbaker, L. Khoja, A.M. Joshua, AR signaling and the PI3K pathway in prostate cancer. Cancers (Basel) 9, E34 (2017)
T. McHardy, J.J. Caldwell, K.M. Cheung, L.J. Hunter, K. Taylor, M. Rowlands, R. Ruddle, A. Henley, A. de Haven Brandon, M. Valenti, et al., Discovery of 4-amino-1-(7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)piperidine-4-carboxamides as selective, orally active inhibitors of protein kinase B (Akt). J. Med. Chem. 53, 2239–2249 (2010)
J.C. Bendell, A.M. Varghese, D.M. Hyman, T.M. Bauer, S. Pant, S. Callies, J. Lin, R. Martinez, E. Wickremsinhe, A. Fink, et al., A first-in-human phase 1 study of LY3023414, an oral PI3K/mTOR dual inhibitor, in patients with advanced cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 24, 3253–3262 (2018)
P. Toren, S. Kim, T. Cordonnier, C. Crafter, B.R. Davies, L. Fazli, M.E. Gleave, A. Zoubeidi, Combination AZD5363 with enzalutamide significantly delays enzalutamide-resistant prostate cancer in preclinical models. Eur. Urol. 67, 986–990 (2015)
A. Zoubeidi, M.E. Gleave, Co-targeting driver pathways in prostate cancer: two birds with one stone. EMBO Mol. Med. 10, e8928 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Yan, Y., Huang, H. (2019). Interplay Among PI3K/AKT, PTEN/FOXO and AR Signaling in Prostate Cancer. In: Dehm, S., Tindall, D. (eds) Prostate Cancer. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 1210. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32656-2_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32656-2_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-32655-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-32656-2
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)