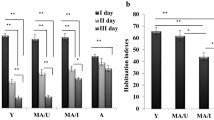
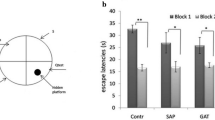
Abstract
Within the basal forebrain is a population of magnocellular neurons that provides cholinergic innervation to the hippocampus, olfactory bulb, amygdala and cortex. Extensive lesion and pharmacological studies in animals and humans support the hypothesis that these basal forebrain cholinergic neurons, in particular the medial septal nucleus (MSN) and the vertical nucleus of the diagonal band of Broca (DBv), and the nucleus basalis (NB), which project to the hippocampus and neocortex, respectively, have an important role in memory function. Memory loss associated with Alzheimer’s disease correlates highly with degeneration of NB neurons and with reduction of cortical acetylcholinesterase and choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) activities (Whitehouse et al., 1982; Bartus et al., 1985). In addition, lesions of MSN/DBv and/or NB in rodents, or selective blockade of cholinergic activity by muscarinic receptor antagonists in either animal or human subjects, elicit learning and memory deficits (Davies, 1985; Meck et al., 1987).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arimatsu, Y., and Miyamoto, M., 1989, Colocalization of NGF receptor immunoreactivity and [3h]GABA uptake activity in developing rat septum/diagonal band neurons in vitro, Neyrosci Lett., 99:39.
Ashkenazi, A., Ramachandran, J., and Capon, D.J., 1989, Acetylcholine analog stimulates DNA synthesis in brain- derived cells by a specific muscarinic receptor subtype. Nature, 340:146.
Auburger, G., Heumann, R., Heilweg, R., Korsching, S., and Thoenen, H., 1987, Developmental changes of nerve growth factor and its mRNA in the rat hippocampus: comparison with choline acetyltransferase, Dev. Biol., 120:322.
Bartus, R.T., Dean, R.L. III., Goas, J.A., and Lippa, A.S., 1980, Age-related changes in passive avoidance retention: Modulation with dietary choline, Science, 209:301.
Bartus, R.T., Dean, R.L., Pontecorvo, M.J. and Flicker, C., 1985, The cholinergic hypothesis: A historical overview, current perspective, and future directions, Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., 444:332.
Ben-Barak, J. and Dudai, Y., 1979, Cholinergic binding sites in rat hippocampal formation: properties and ontogenesis. Brain Res, 166:245.
Chandler, C.E., Parsons, L.M., Hosang, M., and Shooter, E.M., 1984, A monoclonal antibody modulates the interaction of nerve growth factor with PC 12 cells, J. Biol. Chem. 259:6882.
Daitz, H.M., and Powell, T.P.S., 1954, Studies of the connexions of the fornix system, J. Neuro. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 17:75.
Davies, P., 1985, A critical review of the role of the cholinergic system in human memory and cognition. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., 444:212.
Dreyfus, C.F., Bernd, P., Martinez, J.H., Rubin, S.J., and Black, I.B., 1989, GABAergic and cholinergic neurons exhibit high-affinity nerve growth factor binding in rat basal forebrain, Exper. Neurol., 104:181.
Fischer, W., Wictorin, K., Bjorklund, A., Williams, L.R., Varon, S., and Gage, F.H., 1987, Amelioration of cholinergic neuron atrophy and spatial memory impairment in aged rats by nerve growth factor, Nature, 329:65.
Goldschmidt, R.B., and Steward, 0., 1980, Time course of increases in retrograde labeling and increases in cell size of entorhinal cortex neurons sprouting in response to unilateral entorhinal lesions, J. Comp. Neurol., 189:359.
Gould, E., Farris, T.W., and Butcher, L.L, 1989, Basal forebrain neurons undergo somatal and dendritic remodeling during postnatal development: a single-section Golgi and choline acetyltransferase analysis, Devel. Brain Res., 46:297.
Hefti, F., 1986, Nerve growth factor promotes survival of septal cholinergic neurons after fimbrial transections, J. Neurosci., 6:2155.
Hefti, F., and Werner, W.J., 1986, Nerve growth factor and Alzheimer’s disease, Ann. Neurol., 20:275.
Hendrickson, A., and Dineen, J.T., 1982, Hypertrophy of neurons in dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus following striate cortex lesions in infant monkeys, Neurosci. Lett., 30:217.
Higgins, G.A., Koh, S., Chen, K.S., and Gage, F.H., 1989, NGF induction of NGF receptor gene expression and cholinergic neuronal hypertrophy within the basal forebrain of the adult rat. Neuron, 3:247.
Hunt, S., and Schmidt, J., 1978, Some observations on the binding patterns of a-bungarotoxin in the central nervous system of the rat. Brain Res., 157:213.
Hunt, S., and Schmidt, J., 1979, The relationship of a-bungarotoxin binding activity and cholinergic termination within the rat hippocampus. Neurosci, 4:585.
Johnson, E.M.Jr., Taniuchi, M., Clark, H.B., Springer, J.E., Koh, S., Tayrien, M.W., and Loy, R., 1987, Demonstration of the retrograde transport of nerve growth factor receptor in the peripheral and central nervous system, J. Neurosci., 7:923.
Koh, S., Chang, P., Collier, J.T., and Loy, R., 1989, Loss of NGF receptor immunoreactivity in basal forebrain neurons of aged rats: correlation with spatial memory impairment. Brain Res.. 498:397.
Koh, S., and Loy, R., 1988, Age-related loss of nerve growth factor sensitivity in rat basal forebrain neurons. Brain Res.. 440:396.
Koh, S., and Loy, R., 1989, Development of NGF-sensitive rat basal forebrain neurons and their afferent projections to hippocampus and cortex, J. Neurosci., 9:2999.
Kornack, D.R., Lu, B., and Black, I.B., 1989, Sexually dimorphic expression of the NGF receptor gene in rat brain. Soc. Neurosci, Abs., 15:954.
Kordower, J.H., Gash, D.M., Bothwell, M., Hersh, L., and Mufson, E.F., 1989, Nerve growth factor receptor and choline acetyltransferase remain colocalized in the nucleus basalis (Ch4) of Alzheimer’s patients, Neurobiol. Aging, 10:67.
Large, T.H., Bodary, S.C., Clegg, D.O., Weskamp, G., Otten, U., and Reichardt, L.F., 1986, Nerve growth factor gene expression in the developing rat brain. Sciencer 234:352.
Levi-Montalcini, R., and Booker, R., 1960, Excessive growth of the sympathetic ganglia evoked by a protein isolated from mouse salivary glands, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 46:373.
Lipton, S.A., Frosch, M.P., Phillips, M.D., Tauck, D.L., and Aizenman, E., 1988, Nicotinic antagonists enhance process outgrowth by rat retinal ganglion cells in cultures. Science, 239:1293.
Lipton, S.A., and Kater, S.B., 1988, Neurotransmitter regulation of neuronal outgrowth, plasticity and survival. Trends in Neurosci.A 12:265.
Loy, R., Heyer, D., Clagett-Dame, M., and DiStefano, P.S., 1989, Localization of NGF receptor in human basal forebrain using two new monoclonal antibodies: comparison of normal and Alzheimer brains, Soc. Neurosci. Abs. 15:1364.
Loy, R., and Sheldon, R.A., 1987, Sexually dimorphic development of cholinergic enzymes in the rat septohippocampal system. Dev, Brain Res./ 34:156.
Loy, R., Tayrien, M.W., and Springer, J., 1985, Sexual dimorphism in regional muscarinic receptor binding in rat hippocampus, Anat. Ree., 211:100A.
Mandel, R.J., Gage, F.H., and Thai, L.J., 1989, Spatial learning in rats: correlation with cortical choline acetyltransferase and improvement with NGF following NBM damage, Exp. Neurol., 104:208.
Meek, W.H., and Church, R.M., 1987, Nutrients that modify the speed of internal clock and memory storage processes, Behav. Neurosci., 101:465.
Meek, W.H., Church, R.M., Wenk, G.L., and Olton, D.S., 1987, Nucleus basalis magnocellularis and medial septal area lesions differentially impair temporal memory, J. Neurosci., 7:3505.
Meek, W.H., Smith, R.A., and Williams, C.L., 1988, Pre- and postnatal choline supplementation produces long-term facilitation of spatial memory, Devel. Psychobiol., 21:339.
Meek, W.H., Smith, R.A., and Williams, C.L., 1989, Organizational changes in cholinergic activity and enhanced spatial memory as a function of pre- and/or postnatal choline supplementation, Behav. Neurosci 103:1234.
Meek, W.H., and Williams, C.L., 1990, Choline supplementation during pre- and postnatal development eliminates proactive interference in spatial memory, Devel. Brain Res. in press.
Milner, T.A., Loy, R., and Amaral, D.G., 1983, An anatomical study of the development of the septo-hippocampal projection in the rat. Dev. Brain Res., 8:343.
Mizumori, S.J., Patterson, T.A., Sternberg, H., Rosenzweig, M.R., Bennett, E.L., and Timiras, P.S., 1985, Effects of dietary choline on memory and brain chemistry in aged mice. Ngyroliql, Aging, 6:51.
Morris, R.G.M., 1984, Development of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat, J. Neurosci. Meth., 11:47.
Mufson, E.J., Bothwell, M.A., and Kordower, J.H., 1989, Loss of nerve growth factor receptor-containing neurons in Alzheimer’s disease: a quantitative analysis across subregions of the basal forebrain, Exper. Neurol., 105:221.
Nadler, J.V., Matthews, D.A., Cotman, C.W., and Lynch, G.S., 1974, Development of cholinergic innervation in the hippocampal formation of the rat. II. Quantitative changes in choline acetyltransferase and acetylcholinesterase activities. Develop. Biol., 36:142.
Paxinos, G., and Watson, C., 1986, The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, Second Edition. Academic Press, Orlando, FL.
Pearson, R.C.A., Sofroniew, M.V., and Powell, T.P.S., 1984, Hypertrophy of immunohistochemically identified cholinergic neurons of the basal nucleus of Meynert following ablation of the contralateral cortex in the rat. Brain Res, 311:194.
Pearson, P.C.A., Sofroniew, M.V., and Powell, T.P.S., 1985, Hypertrophy of cholinergic neurones of the rat basal nucleus following section of the corpus callosum. Brain 338:337.
Rinne, J.O., Paljarvi, L., and Rinne, U.K., 1987, Neuronal size and density in the nucleus basalis of Meynert in Alzheimer’s disease, J. Neurol. Sci, 79:67.
Rotter, A., Field, P.M., and Raisman, G., 1979, Muscarinic receptors in the central nervous system of the rat. III. Postnatal development of binding of [3H]propylbenzilylcholine mustard. Brain Res., Rev., 1:185.
Shelton, D.L., Nadler, J. V., and Cotman, C.W., 1979, Development of high affinity choline uptake and associated acetylcholine synthesis in the rat fascia dentata. Brain Res, 163:263.
Sofroniew, M.V., Pearson, R.C.A., and Powell, T.P.S., 1987, The cholinergic nuclei of the basal forebrain of the rat: normal structure, development and experimentally induced degeneration. Brain Res, 411:310.
Springer, J.E., Koh, S., Tayrien, M.W., and Loy, R., 1987, Basal forebrain magnocellular neurons stain for nerve growth factor receptors: correlation with cholinergic cell bodies and effects of axotomy, J. Neurosci. Res, 17:111.
Taniuchi, M., and Johnson, E.M. Jr., 1985, Characterization of the binding properties and retrograde axonal transport of a monoclonal antibody directed against the rat nerve growth factor receptor, J. Cell Biol, 101:1100.
Toran-Allerand, D., and MacLusky, N.J., 1989, Co-localization of NGF and estrogen receptors: implications for the basal forebrain, Soc. Neurosci. Abs. 15:954.
Tucker, R.W., Meade-Cobun, K., and Ferris, D., 1990, Cell shape and increased free cytosolic calcium [Ca2+]i induced by growth factors. Cell Calcium. 11:201.
Vogels, O.J.M., Broere, C.A.J., Ter Laak, H.J., Ten Donkelaar, H.J., Nieuwenhuys, R., and Schulte, B.P.M., 1990, Cell loss and shrinkage in the nucleus basalis of Meynert complex in Alzheimer’s disease, Neurobiol. Aging, 11:3.
Whitehouse, P.J., Price, D.L., Struble, R.G., Clark, A.W.,Coyle, J.T., and DeLong, M.R., 1982, Alzheimer’s disease and senile dementia: loss of neurons in the basal forebrain. Science, 215:1237.
Whittemore, S.R., Ebendal, T., Larkfors, L., Olson, L., Sciger, A., Stromberg, I., and Persson, H., 1986, Developmental and regional expression of ß-nerve growth factor messenger RNA and protein in the rat central nervous system, Proc. Natl. Aqad. Sci.. 83:817.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1991 Plenum Press, New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Loy, R., Heyer, D., Williams, C.L., Meck, W.H. (1991). Choline-Induced Spatial Memory Facilitation Correlates with Altered Distribution and Morphology of Septal Neurons. In: Napier, T.C., Kalivas, P.W., Hanin, I. (eds) The Basal Forebrain. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 295. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-0145-6_21
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-0145-6_21
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4757-0147-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-4757-0145-6
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive