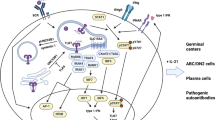
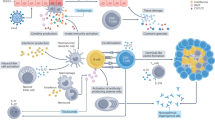
Abstract
The fact that TNF receptor family members are involved in the control of diverse gene products that effect both pro-inflammatory and homeostatic functions related to immune protection offers multiple targets for clinical intervention in a range of disease contexts. The stunning success of anti-TNF-alpha therapy in the treatment of the inflammatory disease rheumatoid arthritis perhaps best illustrates the vast potential of antagonism of TNF family members in clinical medicine [1]. The involvement of other family members, such as CD40, in many other immune regulated diseases will also no doubt lead to similar success stories. In contrast to the pro-inflammatory pathways controlled by TNF-alpha, our lab has begun to determine whether antagonism of the “homeostatic” pathways in secondary and “ectopic” or tertiary lymphoid tissues that are under the control of the TNF receptor family member lymphotoxin-beta receptor (LTBR) might represent a useful target in the treatment of certain diseases such as Sjogren’s syndrome where frank inflammation is not the primary pathogenic impetus.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feldmann M (2002) Development of anti-TNF therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Immunol 2:364–371
Drayton DL, Liao S, Mounzer HR, and Ruddle HN (2006) Lymphoid organ development: from ontogeny to neogenesis. Nat Immunol 7:344–353
Roozendaal R, Mempel RT, Pitcher AL, Gonzalez SF, Verschoor A, Mebius RE, von Andrian UH, and Carroll MC (2009) Conduits mediate transport of low-molecular-weight antigen to lymph node follicles. Immunity 30:264–276
Grabner R, Lotzer K, Dopping S, Hildner M, Radke D, Beer M, Spanbroek R, Lippert B, Reardon CA, Getz GS, Fu YX, Hehlgans T, Mebius RE, van der Wall M, Kruspe D, Englert C, Lovas A, Hu D, Randolph GJ, Weih F, Habenicht AJ (2009) Lymphotoxin beta receptor signaling promotes tertiary lymphoid organogenesis in the aorta adventitia of aged ApoE-/- mice. J Exp Med 206:233–248
Bombardieri M, Barone F, Humby F, Kelly S, McGurk M, Morgan P, Challacombe S, De Vita S, Valesini G, Spencer J, Pitzalis C (2007) Activation-induced cytidine deaminase expression in follicular dendritic cell networks and interfollicular large B cells supports functionality of ectopic lymphoid neogenesis in autoimmune sialoadenitis and MALT lymphoma in Sjogren’s syndrome. J Immunol 179:4929–4938
Manzo A, Pitzalis C (2007) Lymphoid tissue reactions in rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun Rev 7:30–34
de Boer BA, Voigt I, Kim HJ, Camacho SA, Lipp M, Forster R, Berek C (2000) Affinity maturation in ectopic germinal centers. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 251:191–195
Nasr IW, Reel M, Oberbarnscheidt MH, Mounzer RH, Baddoura FK, Ruddle NH, Lakkis FG (2007) Tertiary lymphoid tissues generate effector and memory T cells that lead to allograft rejection. Am J Transplant 7:1071–1079
Humphreys-Beher MG, Hu Y, Nakagawa Y, Wang PL, Purushotham KR (1994) Utilization of the non-obese diabetic (NOD) mouse as an animal model for the study of secondary Sjogren’s syndrome. Adv Exp Med Biol 350:631–636
Jonsson MV, Delaleu N, Jonsson R (2007) Animal models of Sjogren’s syndrome. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 32:215–224
Doyle ME, Boggs L, Attia R, Cooper LR, Saban DR, Nguyen CQ, Peck AB (2007) Autoimmune dacryoadenitis of NOD/LtJ mice and its subsequent effects on tear protein composition. Am J Pathol 171:1224–1236
Pozzilli P, Signore A, Williams AJ, Beales PE (1993) NOD mouse colonies around the world – recent facts and figures. Immunol Today 14:193–196
Gatumu MK, Skarstein K, Papandile A, Browning JL, Fava RA, Bolstad AI (2009) Blockade of lymphotoxin-beta receptor signaling reduces aspects of Sjogren’s syndrome in salivary glands of non-obese diabetic mice. Arthritis Res Ther 11:R24
Mikulowska-Mennis A, Xu B, Berberian JM, Michie SA (2001) Lymphocyte migration to inflamed lacrimal glands is mediated by vascular cell adhesion molecule-1/alpha(4)beta(1) integrin, peripheral node addressin/l-selectin, and lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 adhesion pathways. Am J Pathol 159:671–681
Browning JL, Allaire N, Ngam A-Ek, Notidis E, Hunt J, Perrin S, Fava RA (2005) Lymphotoxin-beta receptor signaling is required for the homeostatic control of HEV differentiation and function. Immunity 23:539–550
Allen CD, Cyster JG (2008) Follicular dendritic cell networks of primary follicles and germinal centers: phenotype and function. Semin Immunol 20:14–25
Carlsen HS, Baekkevold ES, Morton HC, Haraldsen G, Brandtzaeg P (2004) Monocyte-like and mature macrophages produce CXCL13 (B cell-attracting chemokine 1) in inflammatory lesions with lymphoid neogenesis. Blood 104:3021–3027
Luther SA, Ansel KM, Cyster JG (2003) Overlapping roles of CXCL13, interleukin 7 receptor alpha, and CCR7 ligands in lymph node development. J Exp Med 197:1191–1198
Kim CH, Lim HW, Kim JR, Rott L, Hillsamer P, Butcher EC (2004) Unique gene expression program of human germinal center T helper cells. Blood 104:1952–1960
Chtanova T, Tangye SG, Newton R, Frank N, Hodge MR, Rolph MS, Mackay CR (2004) T follicular helper cells express a distinctive transcriptional profile, reflecting their role as non-Th1/Th2 effector cells that provide help for B cells. J Immunol 173:68–78
Katakai T, Shimizu A (2008) Undesired meeting of lymphocytes: organ-specific infiltration and the organization of ectopic lymphoid tissue in a murine experimental autoimmune gastritis. Immunol Lett 118:103–109
Katakai T, Suto H, Sugai M, Gonda H, Togawa A, Suematsu S, Ebisuno Y, Katagiri K, Kinashi T, Shimizu A (2008) Organizer-like reticular stromal cell layer common to adult secondary lymphoid organs. J Immunol 181:6189–6200
Nagatake T, Fukuyama S, Kim DY, Goda K, Igarashi O, Sato S, Nochi T, Sagara H, Yokota Y, Jetten AM, Kaisho T, Akira S, Mimuro H, Sasakawa C, Fukui Y, Fujihashi K, Akiyama T, Inoue J, Penninger JM, Kunisawa J, Kiyono H (Oct 26, 2009) Id2-, RORgammat-, and LTbetaR-independent initiation of lymphoid organogenesis in ocular immunity. J Exp Med 206(11):2351–2364. Epub 2009 Oct 12
Vondenhoff MF, Greuter M, Goverse G, Elewaut D, Dewint P, Ware CF, Hoorweg K, Kraal G, Mebius RE (2009) LTbetaR signaling induces cytokine expression and up-regulates lymphangiogenic factors in lymph node anlagen. J Immunol 182:5439–5445
van de Pavert SA, Olivier BJ, Goverse G, Vondenhoff MF, Greuter M, Beke P, Kusser K, Höpken UE, Lipp M, Niederreither K, Blomhoff R, Sitnik K, Agace WW, Randall TD, de Jonge WJ, Mebius RE (Nov 2009) Chemokine CXCL13 is essential for lymph node initiation and is induced by retinoic acid and neuronal stimulation. Nat Immunol 10(11):1193–1199
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this paper
Cite this paper
Fava, R.A., Browning, J.L., Gatumu, M., Skarstein, K., Bolstad, AI. (2011). LTBR-Pathway in Sjogren’s Syndrome: CXCL13 Levels and B-cell-Enriched Ectopic Lymphoid Aggregates in NOD Mouse Lacrimal Glands Are Dependent on LTBR. In: Wallach, D., Kovalenko, A., Feldmann, M. (eds) Advances in TNF Family Research. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 691. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-6612-4_39
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-6612-4_39
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4419-6611-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-4419-6612-4
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)