Zinc Carbonate, commonly known as the smithsonite is a mineral ore of zinc with a molecular formula ZnCO3. Zinc carbonate is present as a secondary mineral in the oxidation or weathering zone of zinc-bearing ore deposits. In this short piece of article, learn more about the zinc carbonate formula, its chemical structure, zinc carbonate properties and its uses.
Zinc Carbonate Properties
| Properties of Zinc Carbonate | |
| Name | Zinc Carbonate |
| Also Known as | Smithsonite, Zinc Spar |
| Appearance | White crystalline Solid |
| Molecular Formula | ZnCO3 |
| Melting Point | ~1970 °C |
| Density | 4.4 g/cm3 |
| Molar Mass | 125.38 g/mol |
| Solubility in Water | Insoluble |
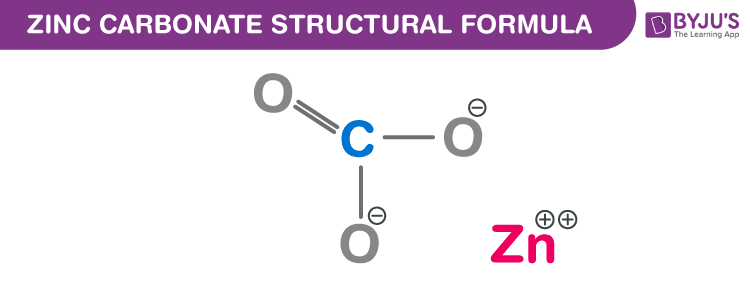
Zinc Carbonate Chemical Structure
Zinc Carbonate Uses
- Used in jewellery and accessories.
- It is present in the zinc anodes of batteries used on lightings and TV monitors
- It plays a major role in Chinese medicines
- It is important for the activity of key enzymes in humans
To learn more about such chemistry topics register to BYJU’S now!

Comments