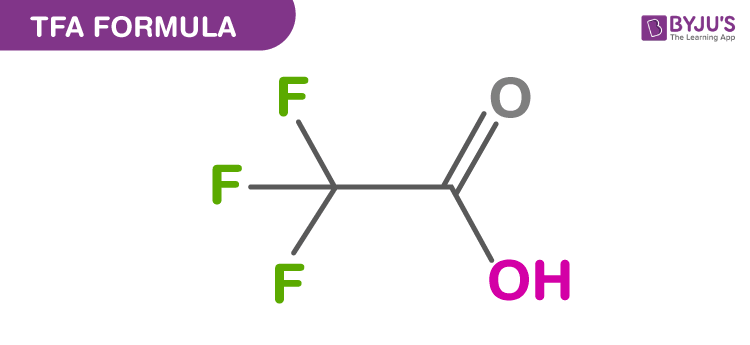
TFA stands for Trifluoroacetic acid which is also known as 2,2,2-trifluoracetic acid is an organofluorine compound. The chemical formula of TFA is CF3CO2H. It is a very strong acid finding applications in organic and inorganic chemistry as it is highly acidic. It is a colourless and odourless liquid.
The property value of hydrogen bond donor and hydrogen bond acceptor is 1 and 5 respectively. Trifluoroacetic acid is synthesised by treating the acetyl chloride in electrochemical fluorination.
Structure Of TFA Formula
Properties Of TFA Formula
| IUPAC name | 2,2,2-trifluoracetic acid |
| Chemical formula | CF3CO2H |
| Molecular weight | 114.023 g/mol |
| Density | 1.489 g.m.L-1 |
| Melting point | -15.4℃ |
| Boiling point | 72.4℃ |
| Enthalpy of vapourisation | 33 kJ/mol |
Applications Of TFA
- TFA is used as a precursor to produce fluorinate compounds like fluoroperacetic acid.
- It is used as a solvent for NMR and mass spectroscopy analysis.
- It is used as adhesives and sealant chemicals.
Safety Measures
- Extremely corrosive to eyes and skin
- Harmful when it is swallowed.
To learn more about other Chemistry related concepts, stay tuned with BYJU’S.

Comments