Flashcards for NEET Biology are designed to boost your NEET preparation. Find below flashcards for Locomotion and Movement. These flashcards on Locomotion and Movement are prepared as per the NEET syllabus. This is helpful for aspirants of NEET and other exams during last-minute revision. Flashcards For NEET Biology – Locomotion and Movement, covers all the important points that are frequently asked in the exam. Check BYJU’S for the full set of Flashcards and Study material for NEET Biology. Solve NEET Biology MCQs to check your understanding and outperform in the exam.
Recommended Videos:


Download PDF of NEET Biology Flashcards for Locomotion and Movement
| Name of the NEET sub-section | Topic | Flashcards helpful for |
| Biology | Locomotion and Movement | NEET exams |
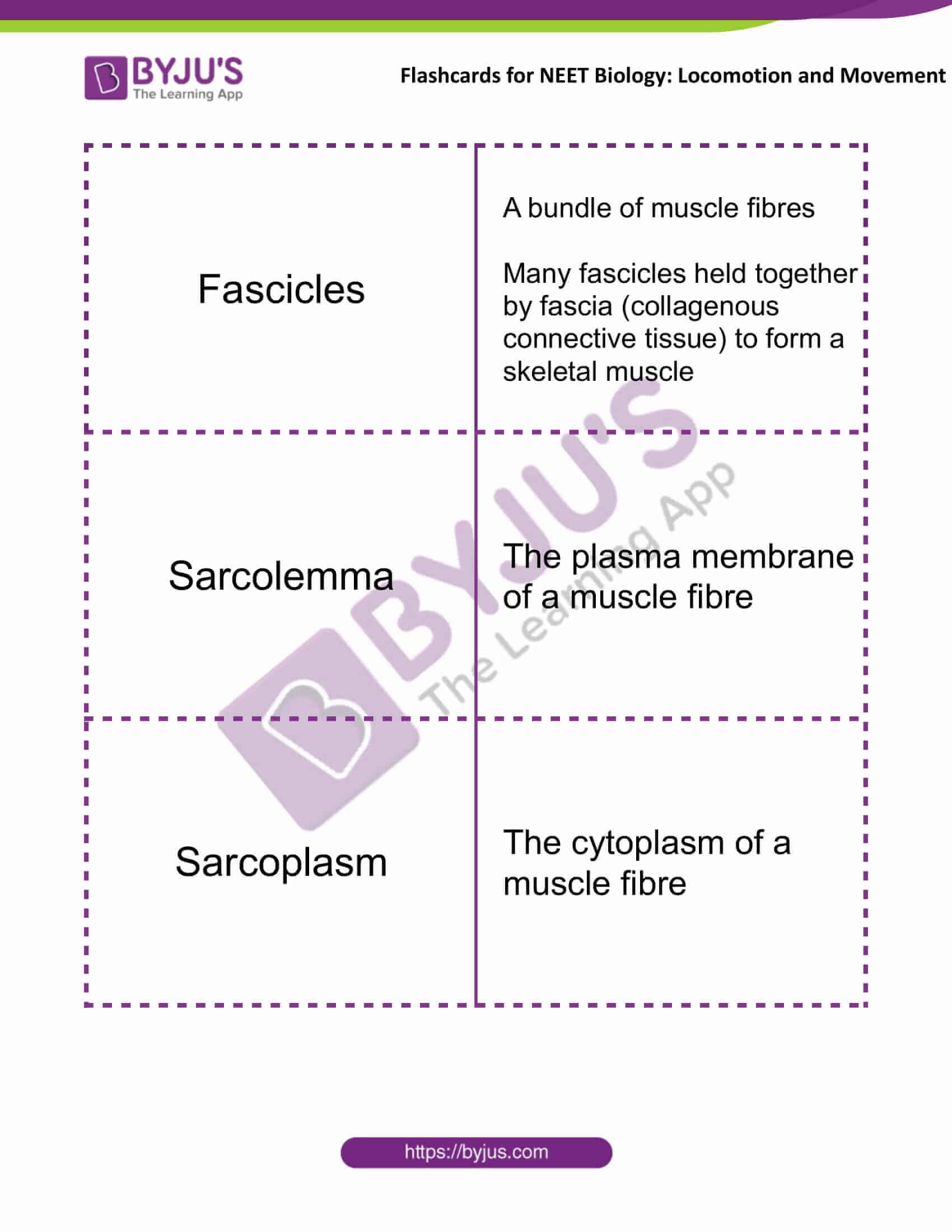
| Fascicles | A bundle of muscle fibres
Many fascicles held together by fascia (collagenous connective tissue) to form a skeletal muscle |
| Sarcolemma | The plasma membrane of a muscle fibre |
| Sarcoplasm | The cytoplasm of a muscle fibre |
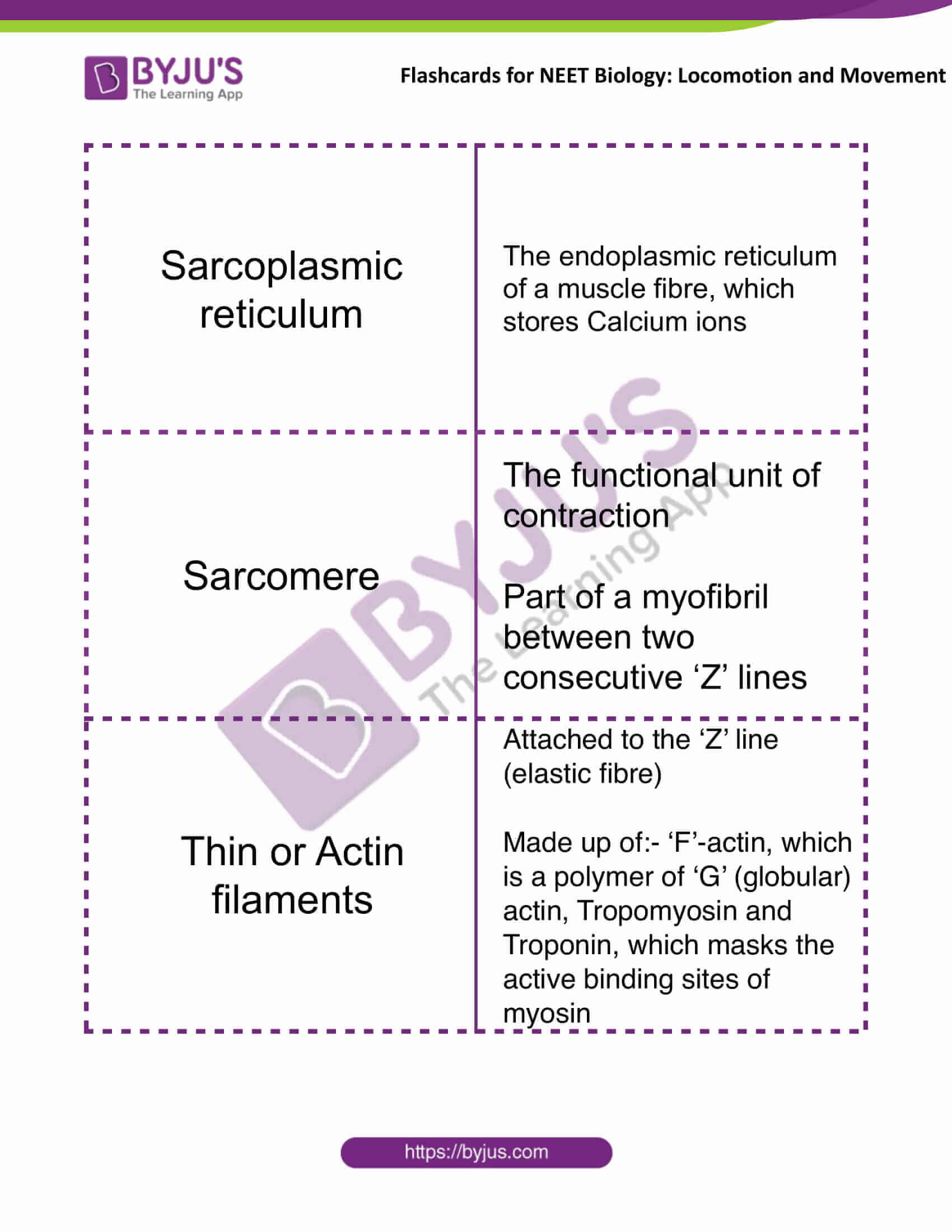
| Sarcoplasmic reticulum | The endoplasmic reticulum of a muscle fibre, which stores Calcium ions |
| Sarcomere | The functional unit of contraction
Part of a myofibril between two consecutive ‘Z’ lines |
| Thin or Actin filaments | Attached to the ‘Z’ line (elastic fibre)
Made up of:- ‘F’-actin, which is a polymer of ‘G’ (globular) actin, Tropomyosin and Troponin, which masks the active binding sites of myosin |
| Thick or Myosin filaments | Attached to the ‘M’ line in the middle (thin fibrous membrane)
Monomeric unit- Meromyosins Heavy meromyosin (HMM)- globular head and short arm Light meromyosin (LMM)- tail |
| Globular myosin head | ATPase activity
The binding site for calcium ions and actin filament |
| Anisotropic (‘A’) or dark band | Formed by overlapping actin and myosin filaments
The length remains the same during contraction |
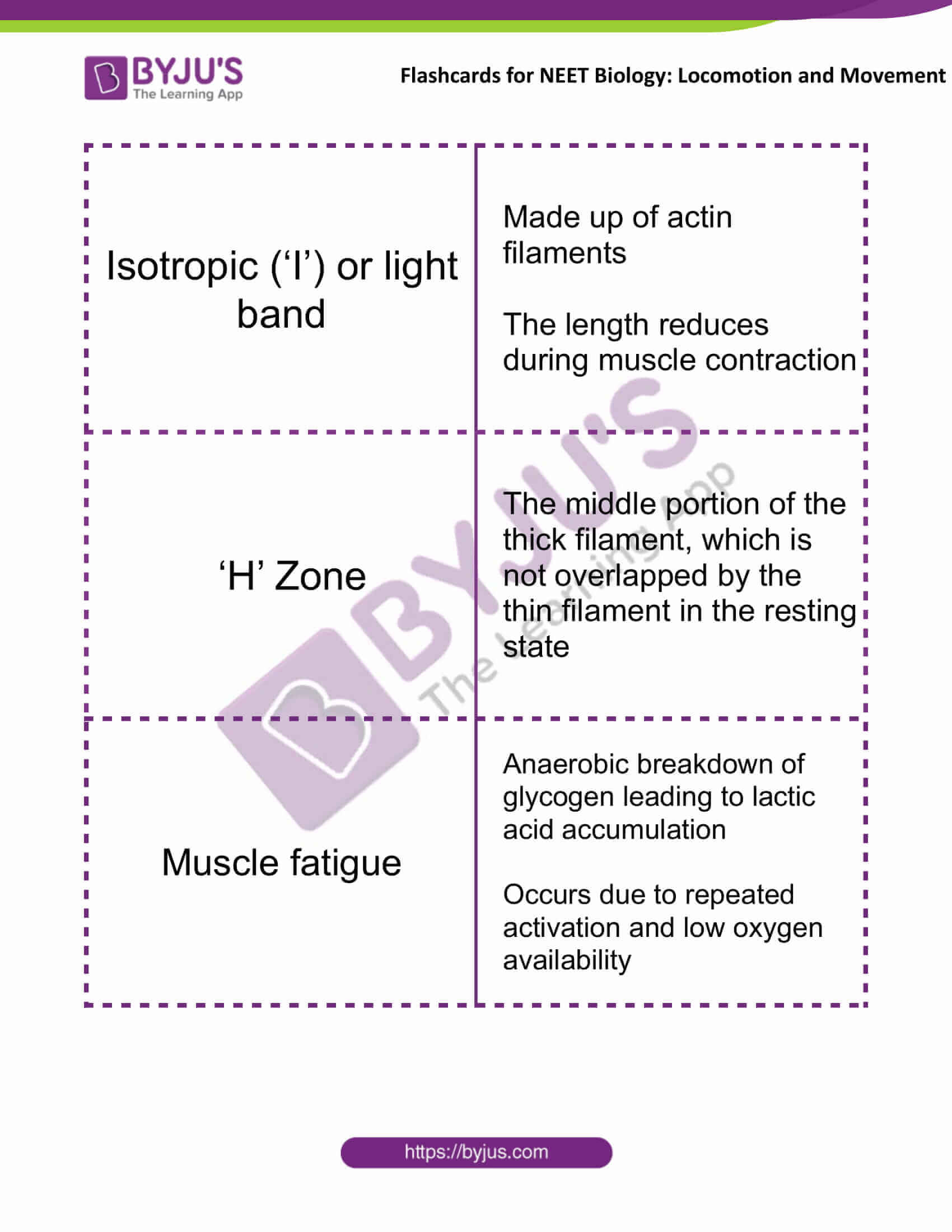
| Isotropic (‘I’) or light band | Made up of actin filaments
The length reduces during muscle contraction |
| ‘H’ Zone | The middle portion of the thick filament, which is not overlapped by the thin filament in the resting state |
| Muscle fatigue | Anaerobic breakdown of glycogen leading to lactic acid accumulation
Occurs due to repeated activation and low oxygen availability |
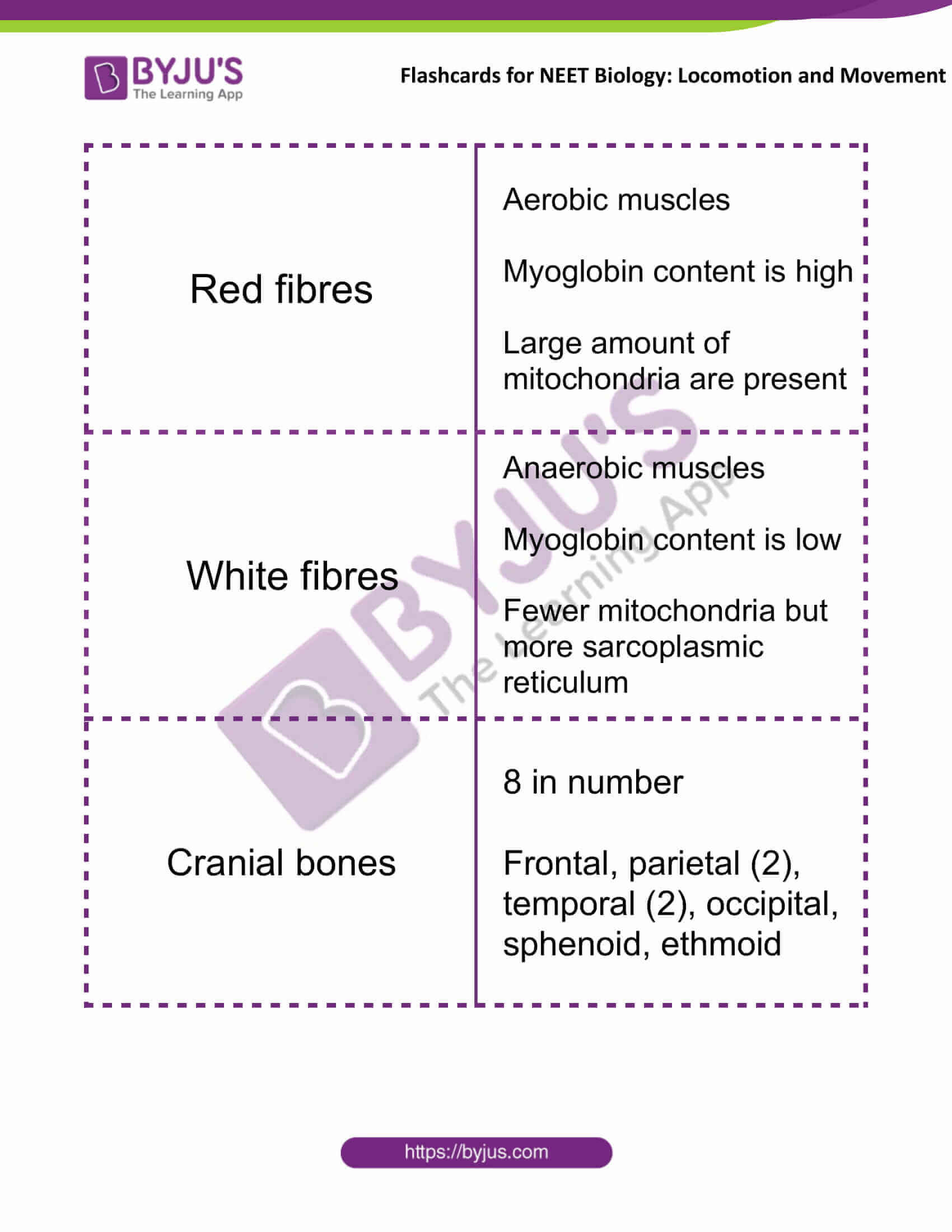
| Red fibres | Aerobic muscles
Myoglobin content is high Large amount of mitochondria are present |
| White fibres | Anaerobic muscles
Myoglobin content is low Fewer mitochondria but more sarcoplasmic reticulum |
| Cranial bones | 8 in number
Frontal, parietal (2), temporal (2), occipital, sphenoid, ethmoid |
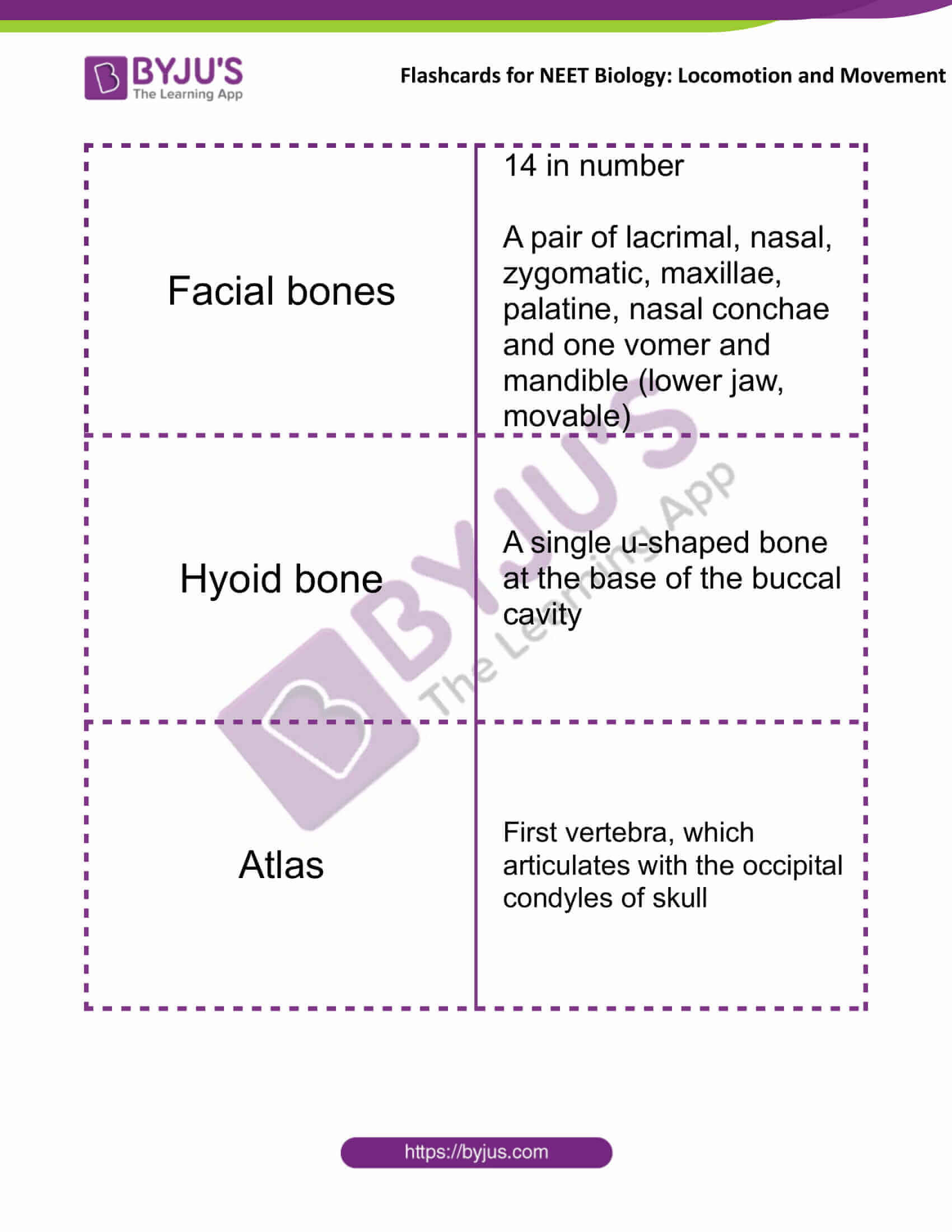
| Facial bones | 14 in number
A pair of lacrimal, nasal, zygomatic, maxillae, palatine, nasal conchae and one vomer and mandible (lower jaw, movable) |
| Hyoid bone | A single u-shaped bone at the base of the buccal cavity |
| Atlas | First vertebra, which articulates with the occipital condyles of the skull |
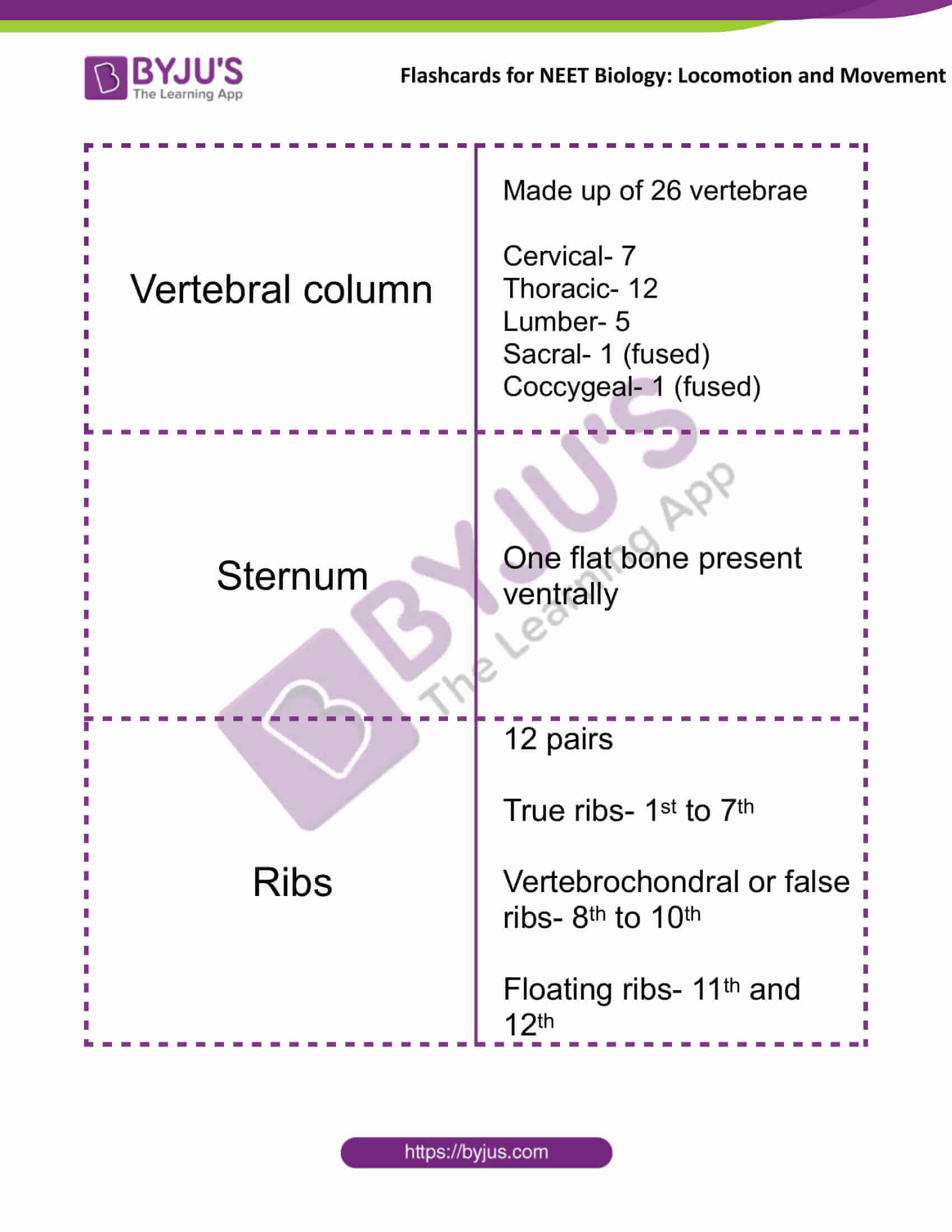
| Vertebral column | Made up of 26 vertebrae
Cervical- 7 Thoracic- 12 Lumber- 5 Sacral- 1 (fused) Coccygeal- 1 (fused) |
| Sternum | One flat bone present ventrally |
| Ribs | 12 pairs
True ribs- 1st to 7th Vertebrochondral or false ribs- 8th to 10th Floating ribs- 11th and 12th |
| Rib cage | Thoracic vertebrae, ribs and sternum |
| Forelimb | 30 bones each
Humerus, radius, ulna, carpals (8, wrist bones), metacarpals (5, palm), phalanges (14, digits) |
| Hindlimb | 30 bones each
Femur (longest bone), tibia, fibula, patella (knee cap), tarsals (7, ankle bones), metatarsals (5, sole), phalanges (14, digits) |
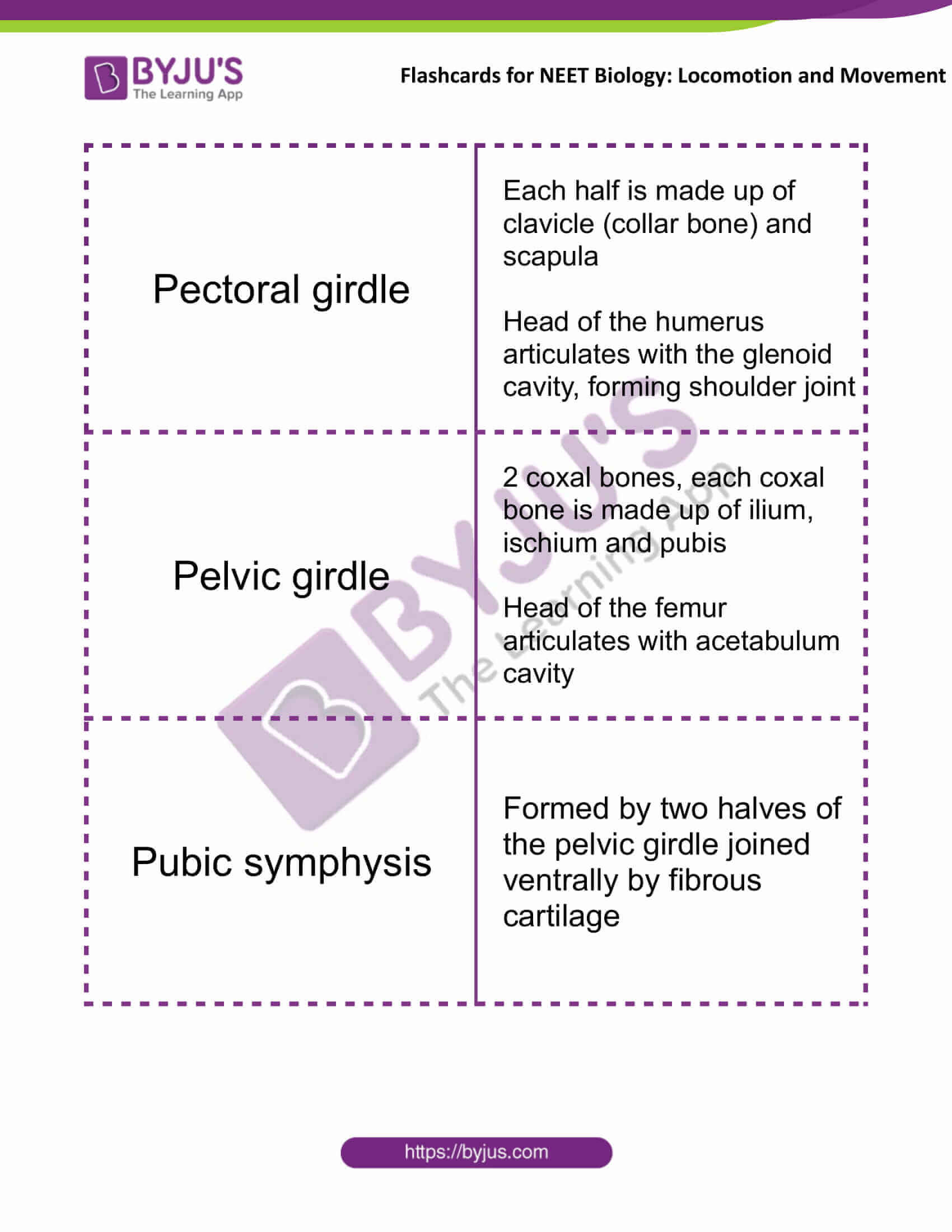
| Pectoral girdle | Each half is made up of clavicle (collar bone) and scapula
Head of the humerus articulates with the glenoid cavity, forming shoulder joint |
| Pelvic girdle | 2 coxal bones, each coxal bone is made up of ilium, ischium and pubis
Head of the femur articulates with acetabulum cavity |
| Pubic symphysis | Formed by two halves of the pelvic girdle joined ventrally by fibrous cartilage |
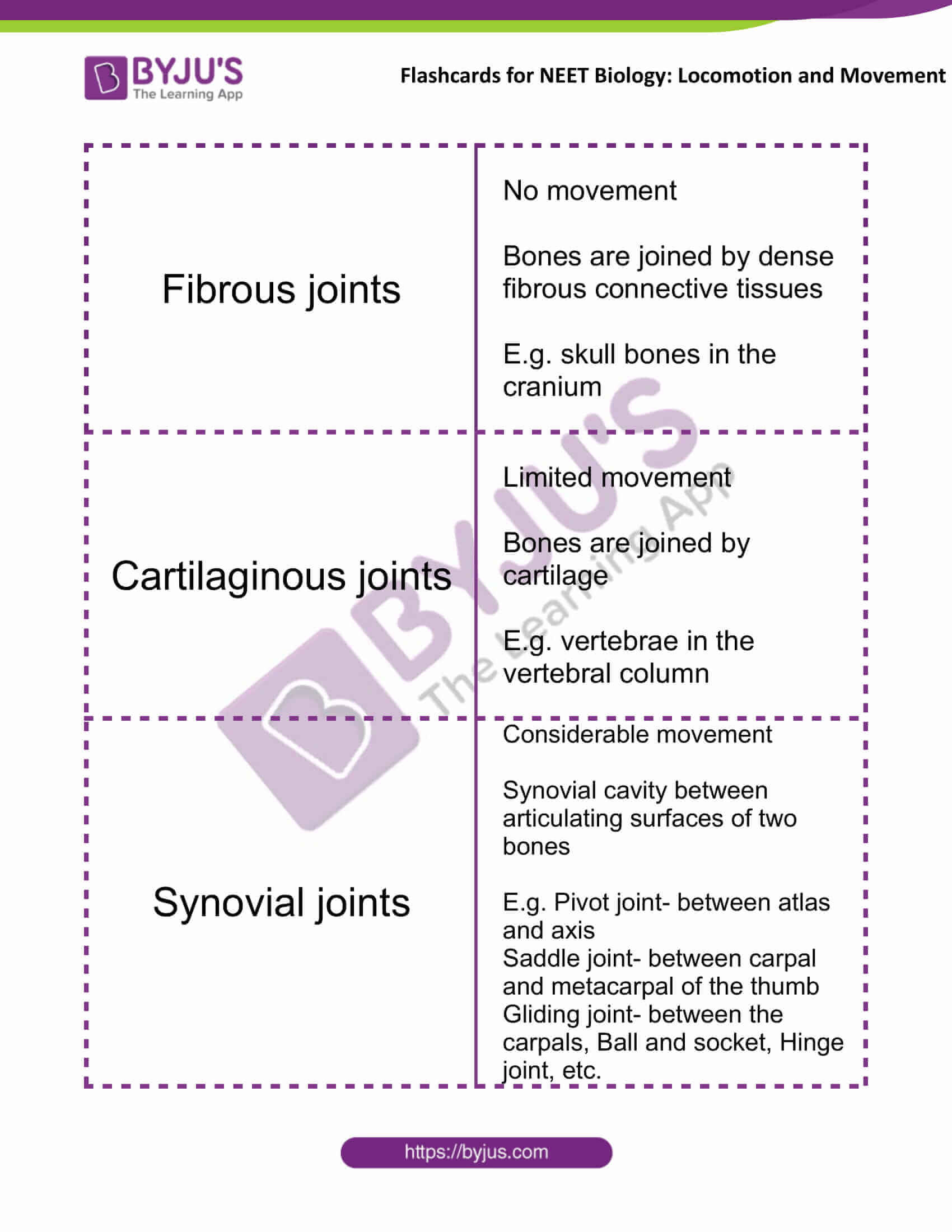
| Fibrous joints | No movement
Bones are joined by dense fibrous connective tissues E.g. skull bones in the cranium |
| Cartilaginous joints | Limited movement
Bones are joined by cartilage E.g. vertebrae in the vertebral column |
| Synovial joints | Considerable movement
Synovial cavity between articulating surfaces of two bones E.g. Pivot joint- between atlas and axis Saddle joint- between carpal and metacarpal of the thumb Gliding joint- between the carpals, Ball and socket, Hinge joint, etc. |
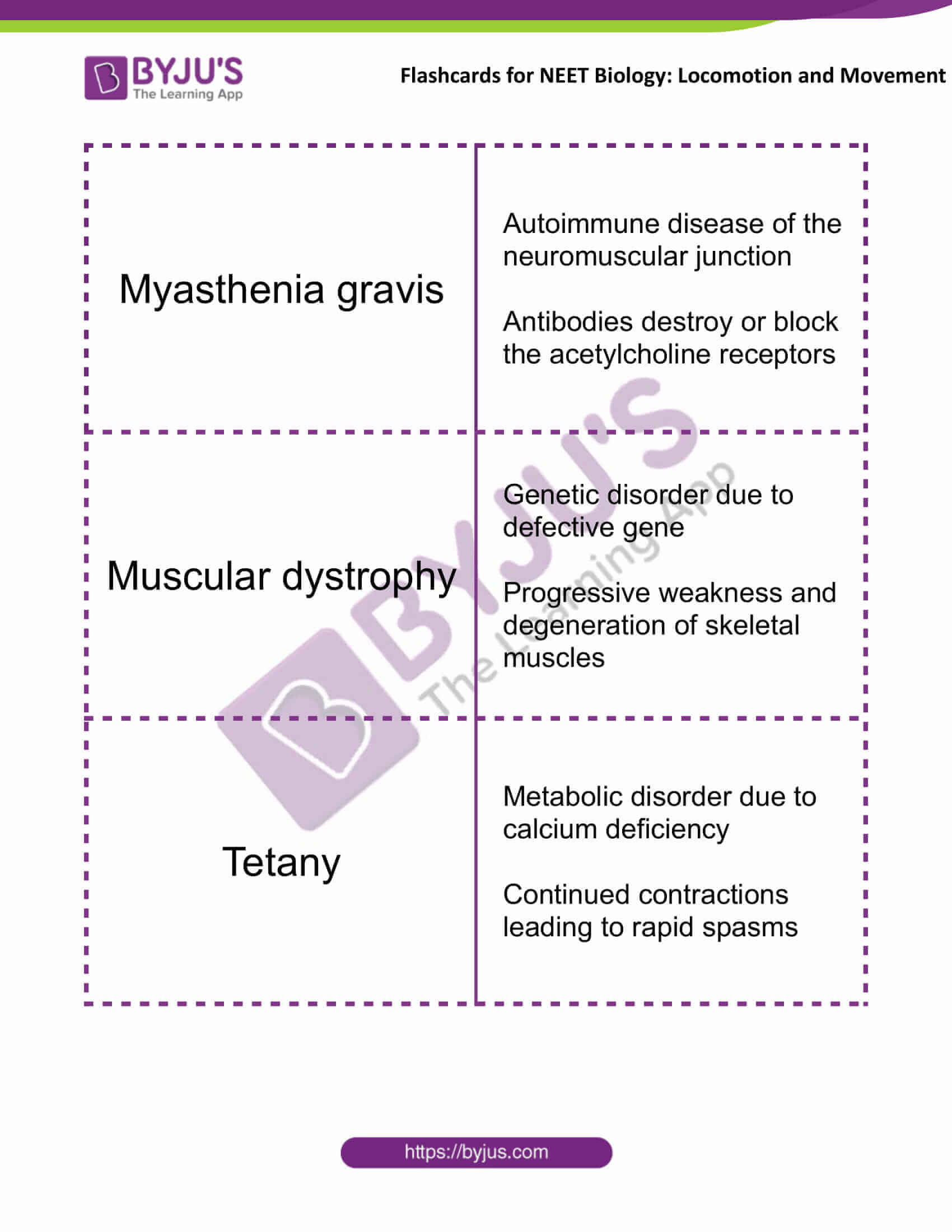
| Myasthenia gravis | Autoimmune disease of the neuromuscular junction
Antibodies destroy or block the acetylcholine receptors |
| Muscular dystrophy | Genetic disorder due to defective gene
Progressive weakness and degeneration of skeletal muscles |
| Tetany | Metabolic disorder due to calcium deficiency
Continued contractions leading to rapid spasms |
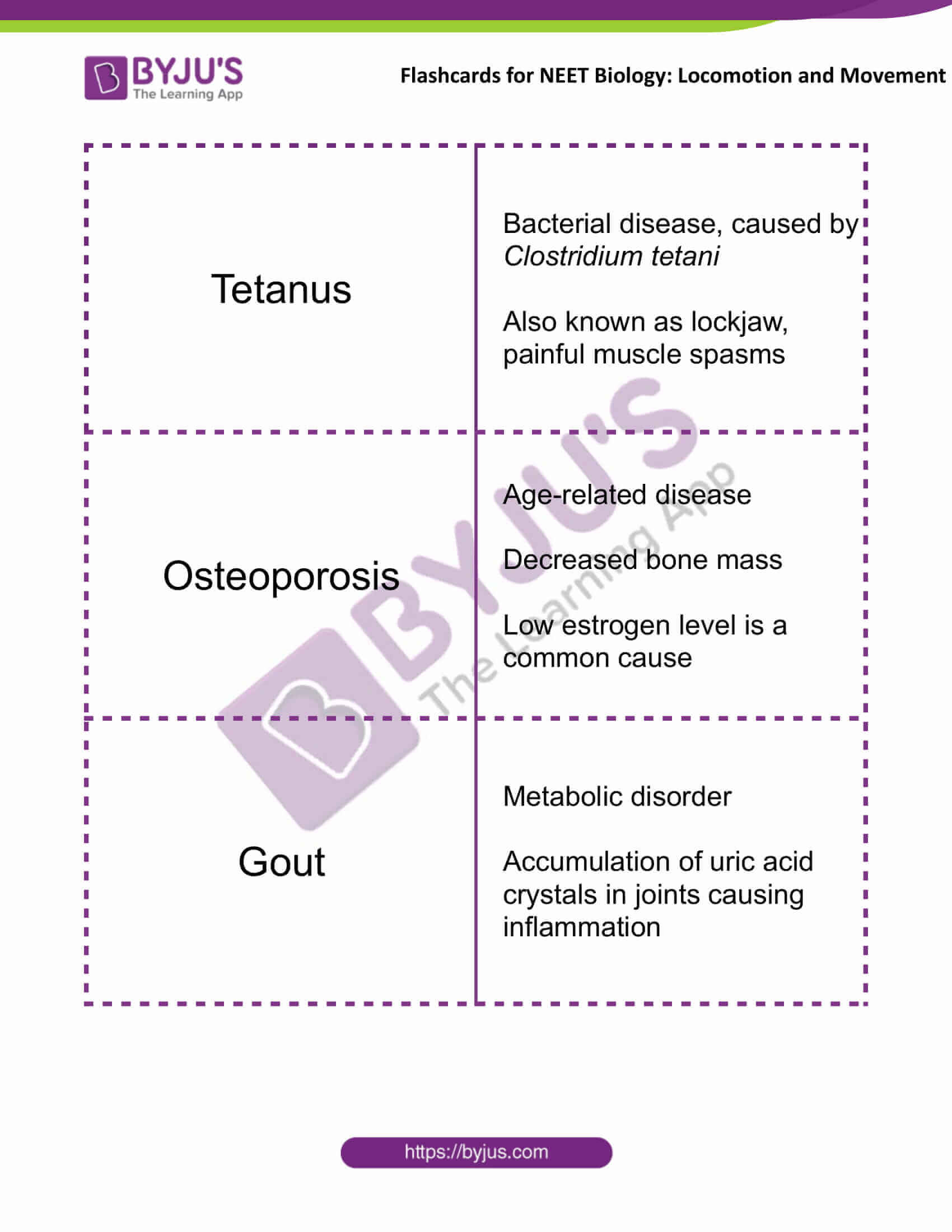
| Tetanus | A bacterial disease, caused by Clostridium tetani
Also known as lockjaw, painful muscle spasms |
| Osteoporosis | Age-related disease
Decreased bone mass Low estrogen level is a common cause |
| Gout | Metabolic disorder
Accumulation of uric acid crystals in joints causing inflammation |
Get access to the full set of flashcards for NEET Biology, only at BYJU’S.

Also Check:
NEET Flashcards: Digestion And Absorption
NEET Flashcards: Breathing And Exchange Of Gases
NEET Flashcards: Body Fluids And Circulation


Comments