Lead acetate is a white crystalline compound with a chemical formula Pb(C2H3O2)2. It possesses a sweetish taste. Lead acetate can be made by boiling lead in hydrogen peroxide and acetic acid. Like other lead compounds, it is toxic too. In this short piece of article, learn more about the lead acetate formula, its chemical structure, properties and uses.
Lead Acetate Properties
| Properties of Lead Acetate | |
| Name | Lead Acetate |
| Also Known as | Plumbous Acetate, Salt Of Saturn, Goulard’s Powder,
lead (II) ethanoate |
| Appearance | Colourless Efflorescent Crystals or white powder |
| Chemical Formula | Pb(C2H3O2)2 |
| Melting Point | 280 °C (anhydrous)
75 °C (trihydrate) 22 °C (decahydrate) |
| Boiling Point | Decomposes |
| Density | 3.25 g/cm³ (anhydrous)
2..55 g/cm3 (trihydrate) 1.69 g/cm3 (decahydrate) |
| Molar Mass | 325.29 g/mol (anhydrous)
379.33g/mol (trihydrate) |
| Solubility in Water | Soluble in water |
Lead acetate Chemical Structure
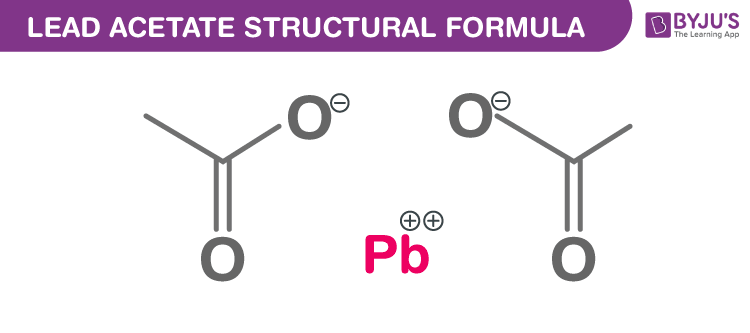
Lead Acetate Uses
- Used as a laboratory reagent and chemical
- Used in cosmetics
- Finds application in gold mining
- Used as a mordant in dyeing and textile printing.
- Used as a drier in varnishes and paints.
To learn more about such chemistry topics register to BYJU’S now!

Comments