Read the daily PIB update and stay up-to-date on current affairs for the UPSC exam
New company under Department of Space
Context:
The Union Cabinet has given its approval to the Setting up of a new company under Department of Space (DoS), to commercially exploit the research and development work carried out by Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) Centers and constituent units of DOS.
The following areas/avenues provide opportunities for commercial exploitation of ISRO programmes:
- Small satellite technology transfer to industry, wherein the new company shall take license from DoS/ISRO and sub-license to industries;
- Manufacture of small satellite launch vehicle (SLV) in collaboration with the Private Sector;
- Productionisation of Polar SLV through industry;
- Productionisation and marketing of Space-based products and services, including launch and applications;
- Transfer of Technology developed by ISRO Centers and constituent units of DoS;
- Marketing of some spin-off technologies and products, both in India and abroad; and
- Any other subject which Government of India deems fit.
First ever Diesel to Electric Converted Locomotive.
Context:
Prime ministry flagged off the first ever Diesel to Electric Converted Locomotive at Diesel Locomotive Works in Varanasi.
Details:
- In line with the Indian Railways’ Mission of 100 percent electrification, Diesel Locomotive Works, Varanasi has developed a new prototype Electric Locomotive converted from Diesel Locomotive.
- After its mandatory trials, the Prime Minister inspected the locomotive and flagged it off.
- Indian Railways has decided to convert all Diesel Locomotive to Electric Locomotive during its mid-life rehabilitation and utilise them till their codal life.
- The project is a step towards saving traction energy cost and also cut down on carbon emissions.
- Diesel Locomotive Works took just 69 days to convert two WDG3A Diesel Locos into a Twin Electric WAGC3 locomotive of 10,000 HP.
- A complete ‘Make in India’ initiative, the conversion is an Indian R&D innovation in the entire world.
National Policy on Electronics 2019
Context:
The Union Cabinet gave its approval to the National Policy on Electronics 2019 (NPE 2019), proposed by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
Salient Features of NPE 2019:
The Policy envisions positioning India as a global hub for Electronics System Design and Manufacturing – (ESDM) by encouraging and driving capabilities in the country for developing core components, including chipsets, and creating an enabling environment for the industry to compete globally.
- Create eco-system for globally competitive ESDM sector: Promoting domestic manufacturing and export in the entire value-chain of ESDM.
- Provide incentives and support for manufacturing of core electronic components.
- Provide special package of incentives for mega projects which are extremely high-tech and entail huge investments, such as semiconductor facilities display fabrication, etc.
- Formulate suitable schemes and incentive mechanisms to encourage new units and expansion of existing units.
- Promote Industry-led R&D and innovation in all sub-sectors of electronics, including grass root level innovations and early stage Start-ups in emerging technology areas such as 5G, loT/ Sensors, Artificial Intelligence (Al), Machine Learning, Virtual Reality (VR), Drones, Robotics, Additive Manufacturing, Photonics, Nano-based devices, etc.
- Provide incentives and support for significantly enhancing availability of skilled manpower, including re-skilling.
- Special thrust on Fabless Chip Design Industry, Medical Electronic Devices Industry, Automotive Electronics Industry and Power Electronics for Mobility and Strategic Electronics Industry.
- Create Sovereign Patent Fund (SPF) to promote the development and acquisition of IPs in ESDM sector.
- Promote trusted electronics value chain initiatives to improve national cyber security profile.
Major Impact
- The NPE 2019 when implemented will lead to formulation of several schemes, initiatives, projects, etc., in consultation with the concerned Ministries/ Departments, for the development of ESDM sector in the country.
- It will enable flow of investment and technology, leading to higher value addition in the domestically manufactured electronic products, increased electronics hardware manufacturing in the country and their export, while generating substantial employment opportunities.
Delhi-Ghaziabad-Meerut Corridor of RRTS.
Context:
Union Cabinet has approved the Construction of Regional Rapid Transit System (RRTS)
Salient features:
- The RRTS is a first-of-its-kind, rail-based, high-speed regional transit system to be implemented in India.
- Once operational, it will be the fastest, most comfortable and safest mode of commuter transport in the National Capital Region (NCR).
- The project involves integration with other urban transport systems in an efficient and effective manner which is possible only by adopting innovative methods of designing, technology and institutional management.
- The RRTS aims to streamline the urban transportation system, which is stressed due to intensive developments, and increase in the number of private vehicles, thus putting stress on travel infrastructure and industrial activities, and by providing the people a safe, secure, reliable, fast and comfortable public transport.
- The project is meant to ensure ‘Universal Access’ by being sensitive to the needs of women, children and vulnerable sections of the society. Safe, secure and comfortable public transport is not only critical for increasing attractiveness of public transport, but also to encourage greater mobility and participation of vulnerable and marginalized sections of the society to promote equity and inclusive development.
Benefits of RRTS:
- Implementation of the RRTS would provide much-needed additional public transport infrastructure to National Capital Region to address issues of congestion, air-pollution and catalyse balanced and sustainable regional development.
“Reforms in Exploration and Licensing Policy for enhancing domestic exploration and production of oil and gas”
Context:
The Union Cabinet has approved the Policy framework on reforms in exploration and licensing sector for enhancing domestic exploration and production of oil and gas.
Through this policy, a transparent, investor friendly and competitive policy framework is envisaged to accelerate exploration activities and provide impetus to expeditious production of oil and gas.
Objective:
The objective of the Policy is to attract new investment in Exploration and Production (E&P) Sector, intensification of exploration activities in hitherto unexplored areas and liberalizing the policy in producing basins.
Details:
The policy reforms focus on four major areas.
- Firstly, increasing exploration activities in unexpected areas. In basins where no commercial production is there, exploration blocks would be bid out exclusively on the basis of exploration work programme without any revenue or production share to Government.
- Secondly, to incentivize enhanced gas production, marketing and pricing freedom has been granted for those new gas discoveries whose Field Development Plan (FDP) is yet to be approved Fiscal incentive is also provided on additional gas production from domestic fields over and above normal production
- Thirdly, to enhance production from existing nomination fields of ONGC and OIL, enhanced production profile will be prepared by both PSUs. For production enhancement, bringing new technology, and capital, NOCs will be allowed to induct private sector partners.
- Fourthly measures will be initiated for promoting ease of doing business through setting up coordination mechanism and simplification of approval of DGH, alternate dispute resolution mechanism etc.
Proposed Participation of India in PISA.
Context:
The Union Cabinet has given ex-post facto approval to the Agreement between India and the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) for participating in the Programme for International Students Assessment (PISA), which will be conducted by the OECD in 2021.
Benefits:
- Learnings from participation in PISA will help to introduce competency-based examination reforms in the school system and help move away from rote learning.
- The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) and the National Council for Educational Research and Training (NCERT) will be part of the process and activities leading to the actual test.
Salient features:
- PISA is a competency-based assessment which unlike content-based assessment, measures the extent to which students have acquired key competencies that are essential for full participation in modern societies.
- It would lead to recognition and acceptability of Indian students and prepare them for the global economy in the 21st century.
- The CBSE and the NCERT will be part of the process and activities leading to the actual test. Schools run by the Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan (KVS), Navodaya Vidyalaya Samiti (NVS) and schools in the Union Territory of Chandigarh will participate.
- More than 80 countries, including 44 middle-income countries including Brazil, China, Thailand, Indonesia, Malaysia and Vietnam have participated in PISA.
What is PISA?
- PISA is the OECD’s (The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development ) Programme for International Student Assessment.
- Every three years it tests 15-year-old students from all over the world in reading, mathematics and science.
- The tests are designed to gauge how well the students master key subjects in order to be prepared for real-life situations in the adult world.
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development.
Context:
The Union Cabinet has approved the Implementation of an Externally Aided Project namely “National Rural Economic Transformation Project (NRETP) under the Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana – National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM) through loan assistance (IBRD Credit) from World Bank.
Benefits:
The technical assistance provided by NRETP and the higher level interventions facilitated by the project will enhance the livelihoods promotion and access to finance and scale-up initiatives on digital finance and livelihood intervention
Salient features:
- DAY-NRLM lays special emphasis on targeting the poorest of the poor and the most vulnerable communities and their financial inclusion.
- Innovative projects will be undertaken under NRETP to pilot alternate channels of financial inclusion, creating value chains around rural products, introduce innovative models in livelihoods promotion and access to finance and scale-up initiatives on digital finance and livelihoods interventions.
- DAY-NRLM provides for mutually beneficial working relationship and formal platforms for consultations between Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) and Community Based Organizations (CBOs).
- NRLM has also developed activity map to facilitate convergence in different areas of interventions where NRLM institutions and PRIs could work together which has been disseminated to all state Rural Livelihood Missions.
Khadi Gramodyog Vikas Yojana.
Context:
Cabinet approves continuation of Khadi Gramodyog Vikas Yojana from 2017-18 to 2019-20.
To bring in a new component of ‘Rozgar Yukt Gaon’ to introduce enterprise-based operation in the Khadi sector and to create employment opportunities for thousands of new artisans in the current and next financial year (2018-19 and 2019-20)
Details of Rozgar Yukta gaon:
- Rozgar Yukta Gaon (RYG) aims at introducing an ‘Enterprise-led Business Model’ in place of ‘Subsidy-led model’ through partnership among 3 stakeholders- KRDP-assisted Khadi Institution, Artisans and Business Partner.
- It will be rolled out in 50 Villages by providing 10,000 Charkhas, 2000 looms & 100 warping units to Khadi artisans, and would create direct employment for 250 Artisans per village.
- Under the Village Industry verticals, special focus shall be on Agro-based and food processing (Honey, Palmgur etc.), Handmade Paper and Leather, Pottery and Wellness and Cosmetics sectors through Product Innovation, Design Development & Product Diversification.
Kisan Urja Suraksha evam Utthaan Mahabhiyan.
Context:
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs, chaired by Prime Minister has approved launch of Kisan Urja Suraksha evam Utthaan Mahabhiyan with the objective of providing financial and water security to farmers.
The proposed scheme consists of three components:
- Component-A: 10,000 MW of Decentralized Ground Mounted Grid Connected Renewable Power Plants.
- Component-B: Installation of 17.50 lakh standalone Solar Powered Agriculture Pumps.
- Component-C: Solarisation of 10 Lakh Grid-connected Solar Powered Agriculture Pumps.
Significance of scheme:
- The Scheme will have substantial environmental impact in terms of savings of CO2 emissions. All three components of the Scheme combined together are likely to result in saving of about 27 million tonnes of CO2 emission per annum.
- Further, Component-B of the Scheme on standalone solar pumps may result in saving of 1.2 billion liters of diesel per annum and associated savings in the foreign exchange due to reduction of import of crude oil.
- The scheme has direct employment potential. Besides increasing self-employment the proposal is likely to generate employment opportunity equivalent to 6.31 lakh job years for skilled and unskilled workers.
‘SWAYATT and Start-up Runway
Context:
Union Minister of Commerce & Industry launched SWAYATT and Start-up Runway.
What is SWAYATT?
SWAYATT is an initiative to promote Start-ups, Women and Youth Advantage Through transactions on Government e Marketplace (GeM). This will bring together the key stakeholders within the Indian entrepreneurial ecosystem to Government e-Marketplace the national procurement portal.
What is Start Up Run Way?
- GeM Start-up Runway seeks to align certified Start-ups with Government procurement orders and contracts, to enable Start-ups in scaling operations from ideation to growth stage in minimal time, and spur hyper-local job-creation and wealth-generation and for achieving socially-inclusive economic growth.
- Start-up Runway will enable Start-ups to conduct market trials with government buyers, seek time-bound feedback and gain realistic product, price comparison and market valuation from potential buyers and investors.
- GeM Start-up Runway seeks to support technology development, spur research and innovation by ensuring a conducive policy environment for industrial diversification and value addition to commodities, and aligns with Government’s philosophy to turn Job-seekers into job-creators.
- GeM Start-up Runway will address goals and objectives under United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 9: Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and foster innovation.
About GeM:
Government e Marketplace, an online market place for procurement of common use goods and services by government ministries, departments and CPSEs.
International Conference and Exhibition on Energy and Environment.
Context:
CSIR-Central Institute of Mining and Fuel Research, Dhanbad is organizing an International Conference and Exhibition on Energy and Environment – Challenges and Opportunities (ENCO-2019)
Details:
- Conference aimsto deliberate and identify the R&D needs to innovate new techniques, technologies and applications for clean, safe, symbiotic sustenance of society, environment, energy and industries in post-2020 era.
- Around 1000 delegates from India and abroad will participate in the conference representing policy makers, regulators, thought leaders, managers, entrepreneurs, administrators, practicing engineers, Environmentalist, geo-environmentalists, researchers, academicians and technocrats.
- The start-ups, young researchers and students will also attend the conference. young researchers and students will also attend the conference.
Tele-Law and Nyaya Bandhu: Mobile Applications.
Context:
Department of Justice Launches Tele-Law: Mobile Application & Dashboard and Nyaya Bandhu (Pro Bono Legal Services) Mobile Application.
About Tele-law:
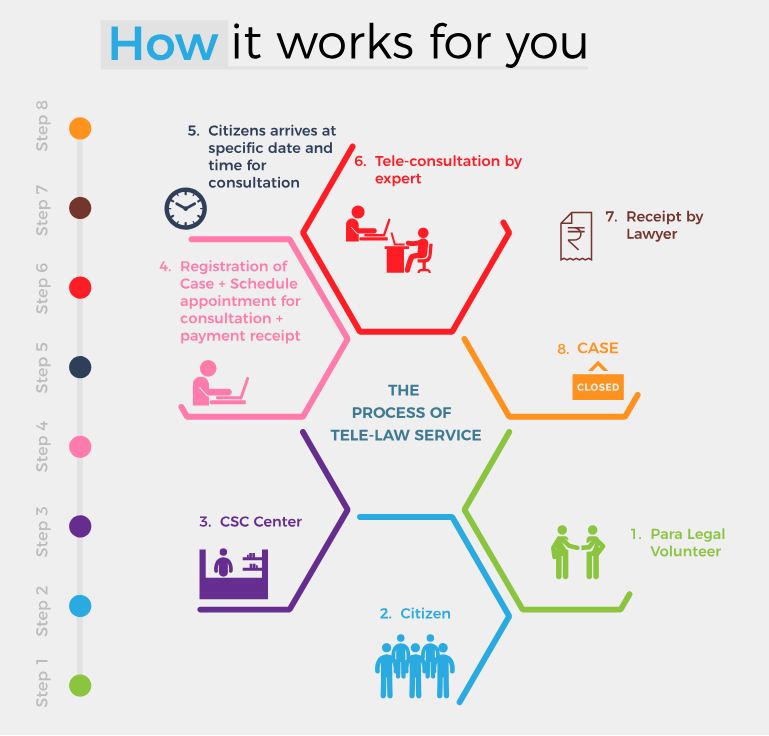
- Department of Justice has partnered with NALSA and CSC e-Governance Service India Limited for mainstreaming legal aid to the marginalised communities through Common Services Center (CSC).
- Tele-Law means the use of communications and information technology for the delivery of legal information and advice. This e-interaction between lawyers and people would be through the video-conferencing infrastructure available at the cscs.
- The concept of Tele-Law is to facilitate delivery of legal advice through a panel of lawyers stationed at the state Legal Services Authorities (SALSA) and CSC. The project initiates to connect citizens with lawyers through video conferencing facilities by the Para-Legal Volunteers stationed at identified 1800 panchayat.
About Nyaya Bandhu:
- Nyaya Bandhu (Pro Bono Legal Services) Legal services programme was launched by Minister for Law & Justice.
- An initiative of the Department of Justice, the programme is aimed at fulfilling the Department’s critical mandate of enhancing “access to justice” for marginalised sections of the society and the State’s constitutional obligation of providing “free legal aid” for all.
- The programme seeks to put in place an institutional structure which will promote pro bono culture in India.
- On one hand, the programme would facilitate delivery of quality legal assistance to the marginalised communities, on the other hand it would ensure that lawyers who volunteer their valuable time and service, towards this public service, are duly recognized for their contribution.
- Based on the premise of using technology to enhance access to justice for all, the Nyaya Bandhu app will allow marginalised individuals (referred to as “Applicants”), seeking quality legal advice and counsel, to connect via a mobile application with “Advocates” who have volunteered their time and services on this platform.
What is Pro bono?
The term pro bono, short for “pro bono publico”, is a Latin term which means “for the public good”. In practice, the term is used specifically in context of the legal profession- referring to the practice of giving voluntary legal advice to individuals and organisations that are unable to afford legal advice and/or cannot access legal aid.
Also Read:
| ISRO |
| OECD |
Comments