Molecular characterization and chromosomal localization of a third alpha-class hypoxia inducible factor subunit, HIF3alpha
- PMID: 9840812
- PMCID: PMC6151950
Molecular characterization and chromosomal localization of a third alpha-class hypoxia inducible factor subunit, HIF3alpha
Abstract
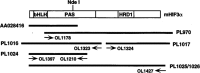
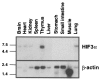
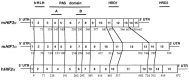
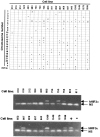
Hypoxia inducible factors (HIFs) are heterodimeric transcription factors that regulate a number of adaptive responses to low oxygen tension. They are composed of alpha- and beta-subunits that belong to the basic helix-loop-helix-PAS (bHLH-PAS) superfamily. In our efforts to identify new bHLH-PAS proteins, we cloned a cDNA encoding a novel alpha-class hypoxia inducible factor, HIF3alpha. The HIF3alpha open reading frame encodes a 662-amino acid protein with a predicted molecular weight of 73 kDa and is expressed in adult thymus, lung, brain, heart, and kidney. The N-terminal bHLH-PAS domain of this protein shares amino acid sequence identity with that of HIF1alpha and HIF2alpha (57% and 53% identity, respectively). The C-terminus of HIF3alpha contains a 36-amino acid sequence that shares 61% identity with the hypoxia responsive domain-1 (HRD1) of HIF1alpha. In transient transfections, this domain confers hypoxia responsiveness when linked to a heterologous transactivation domain. In vitro studies reveal that HIF3alpha dimerizes with a prototype beta-class subunit, ARNT, and that the resultant heterodimer recognizes the hypoxia responsive element (HRE) core sequence, TACGTG. Transient transfection experiments demonstrate that the HIF3alpha-ARNT interaction can occur in vivo, and that the activity of HIF3alpha is upregulated in response to cobalt chloride or low oxygen tension.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Molecular characterization of the murine Hif-1 alpha locus.Gene Expr. 1997;6(5):287-99. Gene Expr. 1997. PMID: 9368100 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of a subset of the basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS superfamily that interacts with components of the dioxin signaling pathway.J Biol Chem. 1997 Mar 28;272(13):8581-93. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.13.8581. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9079689
-
Structural and functional analysis of hypoxia-inducible factor 1.Kidney Int. 1997 Feb;51(2):553-5. doi: 10.1038/ki.1997.77. Kidney Int. 1997. PMID: 9027737 Review.
-
A novel bHLH-PAS factor with close sequence similarity to hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha regulates the VEGF expression and is potentially involved in lung and vascular development.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Apr 29;94(9):4273-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.9.4273. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997. PMID: 9113979 Free PMC article.
-
Oxygen(es) and the hypoxia-inducible factor-1.Biol Chem. 1997 Jul;378(7):609-16. Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9278140 Review.
Cited by
-
PACAP Modulates Expression of Hypoxia-Inducible Factors in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rat Retina.J Mol Neurosci. 2015 Dec;57(4):501-9. doi: 10.1007/s12031-015-0621-7. Epub 2015 Jul 23. J Mol Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26202258
-
Cancer/Testis Antigen PASD1 Silences the Circadian Clock.Mol Cell. 2015 Jun 4;58(5):743-54. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.03.031. Epub 2015 Apr 30. Mol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25936801 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 3α in hepatocellular carcinoma and its association with other hypoxia-inducible factors.Exp Ther Med. 2016 Jun;11(6):2470-2476. doi: 10.3892/etm.2016.3193. Epub 2016 Mar 24. Exp Ther Med. 2016. PMID: 27284334 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of MicroRNA-101 on Angiogenesis of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells during Hypoxia and in Mice with Myocardial Infarction.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Sep 3;2020:5426971. doi: 10.1155/2020/5426971. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32953883 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanceosomes as integrators of hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) and other transcription factors in the hypoxic transcriptional response.Cell Signal. 2013 Sep;25(9):1895-903. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.05.018. Epub 2013 May 21. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23707522 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams M. D.; Kelley J. M.; Gocayne J. D.; Dubnick M.; Polymeropoulos M. H.; Xiao H.; Merril C. R.; Wu A.; Olde B.; Moreno R. F.; Kerlavage A. R.; McCombie W. R.; Venter J. C. Complementary DNA sequencing: Expressed sequence tags and human genome project. Science 252:1651–1656; 1991. - PubMed
-
- Barik S.; Galinski M. S. “Megaprimer” method of PCR: Increased template concentration improves yield. Biotechniques 10:489–490; 1991. - PubMed
-
- Dolwick K. M.; Schmidt J. V.; Carver L. A.; Swanson H. I.; Bradfield C. A. Cloning and expression of a human Ah receptor cDNA. Mol. Pharmacol. 44:911–917; 1993. - PubMed
-
- Feinberg A. P.; Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal. Biochem. 132:6–13; 1983. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
