Abrogation of the G2 cell cycle checkpoint associated with overexpression of HSIX1: a possible mechanism of breast carcinogenesis
- PMID: 9770533
- PMCID: PMC22878
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.21.12608
Abrogation of the G2 cell cycle checkpoint associated with overexpression of HSIX1: a possible mechanism of breast carcinogenesis
Abstract
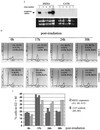
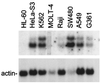
While conducting a search for cell cycle-regulated genes in human mammary carcinoma cells, we identified HSIX1, a recently discovered member of a new homeobox gene subfamily. HSIX1 expression was absent at the onset of and increased toward the end of S phase. Since its expression pattern is suggestive of a role after S phase, we investigated the effect of HSIX1 in the G2 cell cycle checkpoint. Overexpression of HSIX1 in MCF7 cells abrogated the G2 cell cycle checkpoint in response to x-ray irradiation. HSIX1 expression was absent or very low in normal mammary tissue, but was high in 44% of primary breast cancers and 90% of metastatic lesions. In addition, HSIX1 was expressed in a variety of cancer cell lines, suggesting an important function in multiple tumor types. These data support the role for homeobox genes in tumorigenesis/tumor progression, possibly through a cell cycle function.
Figures

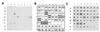
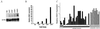
Similar articles
-
Cell cycle-regulated phosphorylation of the human SIX1 homeodomain protein.J Biol Chem. 2000 Jul 21;275(29):22245-54. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M002446200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10801845
-
Study of the G2/M cell cycle checkpoint in irradiated mammary epithelial cells overexpressing Cul-4A gene.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002 Mar 1;52(3):822-30. doi: 10.1016/s0360-3016(01)02739-0. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002. PMID: 11849807
-
Ionizing radiation inhibits the PLK cell cycle gene in a G2 checkpoint-dependent manner.Anticancer Res. 2004 Mar-Apr;24(2B):555-62. Anticancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15160994
-
Role of homeobox genes in normal mammary gland development and breast tumorigenesis.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2003 Apr;8(2):159-75. doi: 10.1023/a:1025996707117. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2003. PMID: 14635792 Review.
-
Cell cycle checkpoints and their impact on anticancer therapeutic strategies.J Cell Biochem. 2004 Feb 1;91(2):223-31. doi: 10.1002/jcb.10699. J Cell Biochem. 2004. PMID: 14743382 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting sine oculis homeoprotein 1 (SIX1): A review of oncogenic roles and potential natural product therapeutics.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 17;10(12):e33204. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33204. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39022099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biochemical characterization of the Eya and PP2A-B55α interaction.J Biol Chem. 2024 Jul;300(7):107408. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107408. Epub 2024 May 23. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38796066 Free PMC article.
-
All eyes on Eya: A unique transcriptional co-activator and phosphatase in cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2024 May;1879(3):189098. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2024.189098. Epub 2024 Mar 28. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38555001 Review.
-
In Vitro Phosphatase Assays for the Eya2 Tyrosine Phosphatase.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2743:285-300. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3569-8_18. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38147222 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of the oestrogen target gene SIX1 is associated with higher growth speed and decreased survival in HCV-positive women with hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2022 Sep 21;24(5):395. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13515. eCollection 2022 Nov. Oncol Lett. 2022. PMID: 36276500 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lewis E B. Nature (London) 1978;276:565–570. - PubMed
-
- McGinnis W, Krumlauff R. Cell. 1992;68:283–302. - PubMed
-
- Lawrence H J, Sauvageau G, Humphries R K, Largman C. Stem Cells. 1996;14:281–291. - PubMed
-
- Cillo C. Invasion Metastasis. 1994;14:38–49. - PubMed
-
- Band V, Zajchowski D, Swisshelm K, Trask D, Kulesa V, Cohen C, Connolly J, Sager R. Cancer Res. 1990;50:7351–7357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

