E-Cadherin-dependent growth suppression is mediated by the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27(KIP1)
- PMID: 9679152
- PMCID: PMC2133056
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.142.2.557
E-Cadherin-dependent growth suppression is mediated by the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27(KIP1)
Abstract
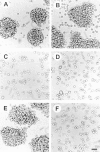
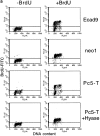
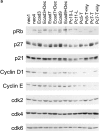
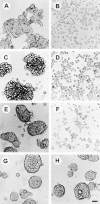
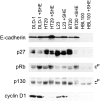
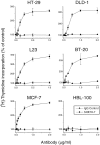
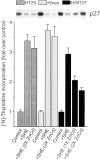
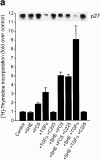
Recent studies have demonstrated the importance of E-cadherin, a homophilic cell-cell adhesion molecule, in contact inhibition of growth of normal epithelial cells. Many tumor cells also maintain strong intercellular adhesion, and are growth-inhibited by cell- cell contact, especially when grown in three-dimensional culture. To determine if E-cadherin could mediate contact-dependent growth inhibition of nonadherent EMT/6 mouse mammary carcinoma cells that lack E-cadherin, we transfected these cells with an exogenous E-cadherin expression vector. E-cadherin expression in EMT/6 cells resulted in tighter adhesion of multicellular spheroids and a reduced proliferative fraction in three-dimensional culture. In addition to increased cell-cell adhesion, E-cadherin expression also resulted in dephosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein, an increase in the level of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27(kip1) and a late reduction in cyclin D1 protein. Tightly adherent spheroids also showed increased levels of p27 bound to the cyclin E-cdk2 complex, and a reduction in cyclin E-cdk2 activity. Exposure to E-cadherin-neutralizing antibodies in three-dimensional culture simultaneously prevented adhesion and stimulated proliferation of E-cadherin transfectants as well as a panel of human colon, breast, and lung carcinoma cell lines that express functional E-cadherin. To test the importance of p27 in E-cadherin-dependent growth inhibition, we engineered E-cadherin-positive cells to express inducible p27. By forcing expression of p27 levels similar to those observed in aggregated cells, the stimulatory effect of E-cadherin-neutralizing antibodies on proliferation could be inhibited. This study demonstrates that E-cadherin, classically described as an invasion suppressor, is also a major growth suppressor, and its ability to inhibit proliferation involves upregulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27.
Figures



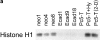

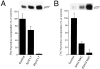
Similar articles
-
Reduced E-cadherin expression contributes to the loss of p27kip1-mediated mechanism of contact inhibition in thyroid anaplastic carcinomas.Carcinogenesis. 2005 Jun;26(6):1021-34. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgi050. Epub 2005 Feb 17. Carcinogenesis. 2005. PMID: 15718252
-
The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27(Kip1) is involved in thyroid hormone-mediated neuronal differentiation.J Biol Chem. 1999 Feb 19;274(8):5026-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.8.5026. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 9988748
-
The role of p27Kip1 in gamma interferon-mediated growth arrest of mammary epithelial cells and related defects in mammary carcinoma cells.Oncogene. 1997 May 1;14(17):2111-22. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201055. Oncogene. 1997. PMID: 9160891
-
Induction and reversal of cell adhesion-dependent multicellular drug resistance in solid breast tumors.Hum Cell. 1996 Dec;9(4):257-64. Hum Cell. 1996. PMID: 9183656 Review.
-
Modulation of p27/Cdk2 complex formation through 4D5-mediated inhibition of HER2 receptor signaling.Ann Oncol. 2001;12 Suppl 1:S21-2. doi: 10.1093/annonc/12.suppl_1.s21. Ann Oncol. 2001. PMID: 11521716 Review.
Cited by
-
Spherical bullet formation via E-cadherin promotes therapeutic potency of mesenchymal stem cells derived from human umbilical cord blood for myocardial infarction.Mol Ther. 2012 Jul;20(7):1424-33. doi: 10.1038/mt.2012.58. Epub 2012 Mar 27. Mol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22453767 Free PMC article.
-
Biofunctionalization of electrospun PCL-based scaffolds with perlecan domain IV peptide to create a 3-D pharmacokinetic cancer model.Biomaterials. 2010 Jul;31(21):5700-18. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.03.017. Epub 2010 Apr 24. Biomaterials. 2010. PMID: 20417554 Free PMC article.
-
E-cadherin homophilic ligation inhibits cell growth and epidermal growth factor receptor signaling independently of other cell interactions.Mol Biol Cell. 2007 Jun;18(6):2013-25. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e06-04-0348. Epub 2007 Mar 28. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17392517 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular endothelial cadherin controls VEGFR-2 internalization and signaling from intracellular compartments.J Cell Biol. 2006 Aug 14;174(4):593-604. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200602080. Epub 2006 Aug 7. J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16893970 Free PMC article.
-
T-cadherin-mediated cell growth regulation involves G2 phase arrest and requires p21(CIP1/WAF1) expression.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Jan;23(2):566-78. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.2.566-578.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12509455 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aberle H, Schwartz H, Kemler R. Cadherin-catenin complex: protein interactions and their implications for cadherin function. J Cell Biochem. 1996;61:514–523. - PubMed
-
- Alessandrini A, Chiaur DS, Pagano M. Regulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 by degradation and phosphorylation. Leukemia. 1997;11:342–345. - PubMed
-
- Allison DC, Yuhas JM, Ridolpho PF, Anderson SL, Johnson TS. Cytophotometric measurement of the cellular DNA content of [3H]thymidine-labeled spheroids. Demonstration that some non-labeled cells have S and G2 DNA content. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1983;16:237–246. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

