A serine cluster prevents recycling of the V2 vasopressin receptor
- PMID: 9482866
- PMCID: PMC19299
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.5.2222
A serine cluster prevents recycling of the V2 vasopressin receptor
Abstract
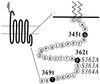
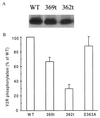
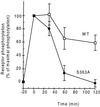
Receptor recycling plays a critical role in the regulation of cellular responsiveness to environmental stimuli. Agonist-promoted phosphorylation of G protein-coupled receptors has been related to their desensitization, internalization, and sequestration. Dephosphorylation of internalized G protein-coupled receptors by cytoplasmic phosphatases has been shown to be pH-dependent, and it has been postulated to be necessary for receptors to recycle to the cell surface. The internalized V2 vasopressin receptor (V2R) expressed in HEK 293 cells is an exception to this hypothesis because it does not recycle to the plasma membrane for hours after removal of the ligand. Because this receptor is phosphorylated only by G protein-coupled receptor kinases (GRKs), the relationship between recycling and GRK-mediated phosphorylation was examined. A nonphosphorylated V2R, truncated upstream of the GRK phosphorylation sites, rapidly returned to the cell surface after removal of vasopressin. Less-drastic truncations of V2R revealed the presence of multiple phosphorylation sites and suggested a key role for a serine cluster present at the C terminus. Replacement of any one of Ser-362, Ser-363, or Ser-364 with Ala allowed quantitative recycling of full-length V2R without affecting the extent of internalization. Examination of the stability of phosphate groups incorporated into the recycling S363A mutant V2Rs revealed that the recycling receptor was dephosphorylated after hormone withdrawal, whereas the wild-type V2R was not, providing molecular evidence for the hypothesis that GRK sites must be dephosphorylated prior to receptor recycling. These experiments uncovered a role for GRK phosphorylation in intracellular sorting and revealed a GRK-dependent anchoring domain that blocks V2R recycling.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Phosphorylation and recycling kinetics of G protein-coupled receptors.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 1999 Jan-Jul;19(1-4):315-26. doi: 10.3109/10799899909036654. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 1999. PMID: 10071767
-
The long and the short cycle. Alternative intracellular routes for trafficking of G-protein-coupled receptors.J Biol Chem. 2001 Apr 20;276(16):13096-103. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M009780200. Epub 2001 Jan 9. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11150299
-
A role for K268 in V2R folding.FEBS Lett. 2005 Sep 12;579(22):4985-90. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2005.08.003. FEBS Lett. 2005. PMID: 16115624
-
Identification of neurohypophysial hormone receptor domains involved in ligand binding and G protein coupling.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1998;449:371-85. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-4871-3_48. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1998. PMID: 10026828 Review.
-
Desensitization of G protein-coupled receptors.Recent Prog Horm Res. 1996;51:319-51; discussion 352-3. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1996. PMID: 8701085 Review.
Cited by
-
Membrane phosphoinositides regulate GPCR-β-arrestin complex assembly and dynamics.Cell. 2022 Nov 23;185(24):4560-4573.e19. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.10.018. Epub 2022 Nov 10. Cell. 2022. PMID: 36368322 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of the V2 vasopressin receptor in adaptation to limited water supply.PLoS One. 2009;4(5):e5573. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005573. Epub 2009 May 18. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19440390 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling at the endosome: cryo-EM structure of a GPCR-G protein-beta-arrestin megacomplex.FEBS J. 2021 Apr;288(8):2562-2569. doi: 10.1111/febs.15773. Epub 2021 Mar 8. FEBS J. 2021. PMID: 33605032 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor sequestration in response to β-arrestin-2 phosphorylation by ERK1/2 governs steady-state levels of GPCR cell-surface expression.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Sep 15;112(37):E5160-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1508836112. Epub 2015 Aug 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26324936 Free PMC article.
-
"ADPKD-omics": determinants of cyclic AMP levels in renal epithelial cells.Kidney Int. 2022 Jan;101(1):47-62. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2021.10.014. Epub 2021 Oct 29. Kidney Int. 2022. PMID: 34757121 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Innamorati G, Sadeghi H, Eberle A, Birnbaumer M. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:2486–2492. - PubMed
-
- Innamorati, G., Sadeghi, H. & Birnbaumer, M. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273, in press. - PubMed
-
- Goodman O B, Krupnick J G, Santini F, Gurevich V V, Penn R B, Gagnon A W, Keen J H, Benovic J L. Nature (London) 1996;383:447–450. - PubMed
-
- Goodman O B, Jr, Krupnick J G, Gurevich V V, Benovic J L, Keen J H. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:15017–15022. - PubMed
-
- von Zastrow M, Kobilka B K. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:3530–3538. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

