Regulation of cell-cell adhesion by rac and rho small G proteins in MDCK cells
- PMID: 9362522
- PMCID: PMC2139955
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.139.4.1047
Regulation of cell-cell adhesion by rac and rho small G proteins in MDCK cells
Abstract
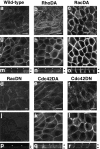
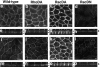
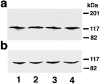
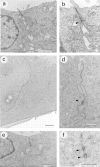
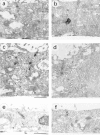
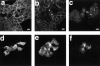
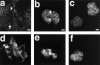
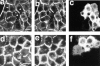
The Rho small G protein family, consisting of the Rho, Rac, and Cdc42 subfamilies, regulates various cell functions, such as cell shape change, cell motility, and cytokinesis, through reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton. We show here that the Rac and Rho subfamilies furthermore regulate cell-cell adhesion. We prepared MDCK cell lines stably expressing each of dominant active mutants of RhoA (sMDCK-RhoDA), Rac1 (sMDCK-RacDA), and Cdc42 (sMDCK-Cdc42DA) and dominant negative mutants of Rac1 (sMDCK-RacDN) and Cdc42 (sMDCK-Cdc42DN) and analyzed cell adhesion in these cell lines. The actin filaments at the cell-cell adhesion sites markedly increased in sMDCK-RacDA cells, whereas they apparently decreased in sMDCK-RacDN cells, compared with those in wild-type MDCK cells. Both E-cadherin and beta-catenin, adherens junctional proteins, at the cell-cell adhesion sites also increased in sMDCK-RacDA cells, whereas both of them decreased in sMDCK-RacDN cells. The detergent solubility assay indicated that the amount of detergent-insoluble E-cadherin increased in sMDCK-RacDA cells, whereas it slightly decreased in sMDCK-RacDN cells, compared with that in wild-type MDCK cells. In sMDCK-RhoDA, -Cdc42DA, and -Cdc42DN cells, neither of these proteins at the cell-cell adhesion sites was apparently affected. ZO-1, a tight junctional protein, was not apparently affected in any of the transformant cell lines. Electron microscopic analysis revealed that sMDCK-RacDA cells tightly made contact with each other throughout the lateral membranes, whereas wild-type MDCK and sMDCK-RacDN cells tightly and linearly made contact at the apical area of the lateral membranes. These results suggest that the Rac subfamily regulates the formation of the cadherin-based cell- cell adhesion. Microinjection of C3 into wild-type MDCK cells inhibited the formation of both the cadherin-based cell-cell adhesion and the tight junction, but microinjection of C3 into sMDCK-RacDA cells showed little effect on the localization of the actin filaments and E-cadherin at the cell-cell adhesion sites. These results suggest that the Rho subfamily is necessary for the formation of both the cadherin-based cell- cell adhesion and the tight junction, but not essential for the Rac subfamily-regulated, cadherin-based cell- cell adhesion.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Involvement of Cdc42 small G protein in cell-cell adhesion, migration and morphology of MDCK cells.Oncogene. 1999 Jul 8;18(27):3996-4006. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202773. Oncogene. 1999. PMID: 10435623
-
Constitutive activation of Rho proteins by CNF-1 influences tight junction structure and epithelial barrier function.J Cell Sci. 2003 Feb 15;116(Pt 4):725-42. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00300. J Cell Sci. 2003. PMID: 12538773
-
Different behavior of l-afadin and neurabin-II during the formation and destruction of cell-cell adherens junction.Oncogene. 1999 Feb 25;18(8):1609-17. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202451. Oncogene. 1999. PMID: 10102631
-
Cdc42, Rac1, and their effector IQGAP1 as molecular switches for cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999 Aug 19;262(1):1-6. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1999.1122. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999. PMID: 10448058 Review.
-
Regulation of cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion by the Rho family GTPases.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1999 Oct;11(5):591-6. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(99)00014-9. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10508646 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of RhoA signaling by the cAMP-dependent phosphorylation of RhoGDIα.J Biol Chem. 2012 Nov 9;287(46):38705-15. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.401547. Epub 2012 Sep 25. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23012358 Free PMC article.
-
Cdc42-dependent modulation of tight junctions and membrane protein traffic in polarized Madin-Darby canine kidney cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2001 Aug;12(8):2257-74. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.8.2257. Mol Biol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11514615 Free PMC article.
-
Localized zones of Rho and Rac activities drive initiation and expansion of epithelial cell-cell adhesion.J Cell Biol. 2007 Jul 30;178(3):517-27. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200701058. Epub 2007 Jul 23. J Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17646397 Free PMC article.
-
Rab13 regulates PKA signaling during tight junction assembly.J Cell Biol. 2004 Apr 26;165(2):175-80. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200312118. Epub 2004 Apr 19. J Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15096524 Free PMC article.
-
Localization of AtROP4 and AtROP6 and interaction with the guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor AtRhoGDI1 from Arabidopsis.Plant Mol Biol. 2000 Feb;42(3):515-30. doi: 10.1023/a:1006341210147. Plant Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10798620
References
-
- Abo A, Pick E, Hall A, Totty N, Teahan CG, Segal AW. Activation of the NADPH oxidase involves the small GTP-binding protein p21rac1 . Nature. 1991;353:668–670. - PubMed
-
- Aktories K, Rösener S, Blaschke U, Chhatwal GS. Botulinum ADP-ribosyltransferase C3: purification of the enzyme and characterization of the ADP-ribosylation reaction in platelet membranes. Eur J Biochem. 1988;172:445–450. - PubMed
-
- Ando S, Kaibuchi K, Sasaki T, Hiraoka K, Nishiyama T, Mizuno T, Asada M, Nunoi H, Matsuda I, Matsuura Y, et al. Post-translational processing of racp21s is important both for their interaction with the GDP/GTP exchange proteins and for their activation of NADPH oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:25709–25713. - PubMed
-
- Behrens J, Vakaet L, Friis R, Winterhager E, van Roy F, Mareel MM, Birchmeier W. Loss of epithelial differentiation and gain of invasiveness correlate with tyrosine phosphorylation of the E-cadherin/β-catenin complex in cells transformed with a temperature-sensitive v-src gene. J Cell Biol. 1993;120:757–766. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

