The Epstein-Barr virus oncogene product latent membrane protein 1 engages the tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated death domain protein to mediate B lymphocyte growth transformation and activate NF-kappaB
- PMID: 9356494
- PMCID: PMC25049
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.23.12592
The Epstein-Barr virus oncogene product latent membrane protein 1 engages the tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated death domain protein to mediate B lymphocyte growth transformation and activate NF-kappaB
Abstract
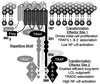
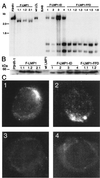
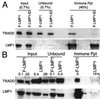
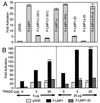
The Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) is essential for the transformation of B lymphocytes into lymphoblastoid cell lines. Previous data are consistent with a model that LMP1 is a constitutively activated receptor that transduces signals for transformation through its carboxyl-terminal cytoplasmic tail. One transformation effector site (TES1), located within the membrane proximal 45 residues of the cytoplasmic tail, constitutively engages tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors. Signals from TES1 are sufficient to drive initial proliferation of infected resting B lymphocytes, but most lymphoblastoid cells infected with a virus that does not express the 155 residues beyond TES1 fail to grow as long-term cell lines. We now find that mutating two tyrosines to an isoleucine at the carboxyl end of the cytoplasmic tail cripples the ability of EBV to cause lymphoblastoid cell outgrowth, thereby marking a second transformation effector site, TES2. A yeast two-hybrid screen identified TES2 interacting proteins, including the tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated death domain protein (TRADD). TRADD was the only protein that interacted with wild-type TES2 and not with isoleucine-mutated TES2. TRADD associated with wild-type LMP1 but not with isoleucine-mutated LMP1 in mammalian cells, and TRADD constitutively associated with LMP1 in EBV-transformed cells. In transfection assays, TRADD and TES2 synergistically mediated high-level NF-kappaB activation. These results indicate that LMP1 appropriates TRADD to enable efficient long-term lymphoblastoid cell outgrowth. High-level NF-kappaB activation also appears to be a critical component of long-term outgrowth.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The residues between the two transformation effector sites of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 are not critical for B-lymphocyte growth transformation.J Virol. 1999 Dec;73(12):9908-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.12.9908-9916.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10559303 Free PMC article.
-
The Epstein-Barr virus oncoprotein latent membrane protein 1 engages the tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated proteins TRADD and receptor-interacting protein (RIP) but does not induce apoptosis or require RIP for NF-kappaB activation.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Aug;19(8):5759-67. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.8.5759. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10409763 Free PMC article.
-
TRAF1 Coordinates Polyubiquitin Signaling to Enhance Epstein-Barr Virus LMP1-Mediated Growth and Survival Pathway Activation.PLoS Pathog. 2015 May 21;11(5):e1004890. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004890. eCollection 2015 May. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 25996949 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-barr virus transformation: involvement of latent membrane protein 1-mediated activation of NF-kappaB.Oncogene. 1999 Nov 22;18(49):6959-64. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203217. Oncogene. 1999. PMID: 10602470 Review.
-
LMP1 TRAFficking activates growth and survival pathways.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;597:173-87. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-70630-6_14. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17633026 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted Therapies for Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Lymphomas.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Sep 9;12(9):2565. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092565. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32916819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
STAT1 and pathogens, not a friendly relationship.Biochimie. 2010 May;92(5):425-44. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2010.02.009. Epub 2010 Feb 13. Biochimie. 2010. PMID: 20159032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A membrane leucine heptad contributes to trafficking, signaling, and transformation by latent membrane protein 1.J Virol. 2007 Sep;81(17):9121-30. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00136-07. Epub 2007 Jun 20. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17581993 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus infection and human malignancies.Int J Exp Pathol. 2001 Jun;82(3):149-70. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2613.2001.iep0082-0149-x. Int J Exp Pathol. 2001. PMID: 11488990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NF-kappaB inhibits gammaherpesvirus lytic replication.J Virol. 2003 Aug;77(15):8532-40. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.15.8532-8540.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12857922 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

