Tumor necrosis factor alpha and lymphotoxin alpha are not required for induction of acute experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 9182689
- PMCID: PMC2196356
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.185.12.2177
Tumor necrosis factor alpha and lymphotoxin alpha are not required for induction of acute experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
Abstract
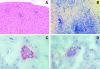
Immunization of mice with myelin components results in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), which is mediated by myelin-specific CD4(+) T cells and anti-myelin antibodies. Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and lymphotoxin alpha (LT-alpha) are thought to be involved in the events leading to inflammatory demyelination in the central nervous system. To ascertain this hypothesis 129 x C57BL/6 mice with an inactivation of the tnf and lta genes (129 x C57BL/6(-/-)) and SJL/J mice derived from backcrosses of the above mentioned mutant mice (SJL-/-) were immunized with mouse spinal cord homogenate (MSCH) or proteolipid protein. Both 129 x C57BL/6(-/-) mice and SJL-/- mice developed EAE. In SJL-/- mice immunized with MSCH, a very severe form of EAE with weight loss, paralysis of all four limbs, and lethal outcome was observed. The histologic hallmark was an intense perivascular and parenchymal infiltration with predominantly CD4(+) T cells and some CD8(+) T cells associated with demyelination in both brain and spinal cord. These results indicate that TNF-alpha and LT-alpha are not essential for the development of EAE.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A critical role for lymphotoxin in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis.J Exp Med. 1997 Oct 20;186(8):1233-40. doi: 10.1084/jem.186.8.1233. J Exp Med. 1997. PMID: 9334362 Free PMC article.
-
An antibody to lymphotoxin and tumor necrosis factor prevents transfer of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis.J Exp Med. 1990 Oct 1;172(4):1193-200. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.4.1193. J Exp Med. 1990. PMID: 2212948 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence that Fas and FasL contribute to the pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2000;48(5):381-8. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2000. PMID: 11140465 Review.
-
Lymphocytes from SJL/J mice immunized with spinal cord respond selectively to a peptide of proteolipid protein and transfer relapsing demyelinating experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):101-7. J Immunol. 1991. PMID: 1701788
-
Tumour necrosis factor-alpha and lymphotoxin-alpha in the pathology of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: is either one responsible or is there another ligand-mediating disease?Res Immunol. 1998 Nov-Dec;149(9):804-10; discussion 849-50, 855-60. doi: 10.1016/s0923-2494(99)80008-x. Res Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9923636 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Effect of targeted disruption of STAT4 and STAT6 on the induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.J Clin Invest. 2001 Sep;108(5):739-47. doi: 10.1172/JCI12563. J Clin Invest. 2001. PMID: 11544280 Free PMC article.
-
A role for surface lymphotoxin in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis independent of LIGHT.J Clin Invest. 2003 Sep;112(5):755-67. doi: 10.1172/JCI18648. J Clin Invest. 2003. PMID: 12952924 Free PMC article.
-
Some misconceptions about understanding autoimmunity through experiments with knockouts.J Exp Med. 1997 Jun 16;185(12):2039-41. doi: 10.1084/jem.185.12.2039. J Exp Med. 1997. PMID: 9221283 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Late-onset chronic inflammatory encephalopathy in immune-competent and severe combined immune-deficient (SCID) mice with astrocyte-targeted expression of tumor necrosis factor.Am J Pathol. 1998 Sep;153(3):767-83. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65620-9. Am J Pathol. 1998. PMID: 9736027 Free PMC article.
-
Challenging cytokine redundancy: inflammatory cell movement and clinical course of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis are normal in lymphotoxin-deficient, but not tumor necrosis factor-deficient, mice.J Exp Med. 1998 May 4;187(9):1517-28. doi: 10.1084/jem.187.9.1517. J Exp Med. 1998. PMID: 9565643 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Issazadeh S, Ljungdahl Å, Höjeberg B, Mustafa M, Olsson T. Cytokine production in the central nervous system of Lewis rats with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: dynamics of mRNA expression for interleukin10, interleukin-12, cytolysin, tumor necrosis factor α and tumor necrosis factor β. J Neuroimmunol. 1995;61:205–212. - PubMed
-
- Renno T, Krakowski M, Piccirillo C, Lin J, Owens T. TNF-a expression by resident microglia and infiltrating leukocytes in the central nervous system of mice with experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 1995;154:944–953. - PubMed
-
- Baker D, O'Neill JK, Turk JL. Cytokines in the central nervous system of mice during chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Cell Immunol. 1991;134:505–510. - PubMed
-
- Held W, Meyermann R, Qin Y, Mueller C. Perforin and tumor necrosis factor α in the pathogenesis of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: comparison of autoantigen induced and transferred disease in Lewis rats. J Autoimmun. 1993;6:311–322. - PubMed
-
- Okuda Y, Nakatsuji Y, Fujimura H, Esumi H, Ogura T, Yanagihara T, Sakoda S. Expression of the inducible isoform of nitric oxide synthase in the central nervous system of mice correlates with the severity of actively induced experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol. 1995;62:103–112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

